Features
-
Coal
Biomass Cofiring: Another Way to Clean Your Coal
Demand for renewable power is burgeoning as state governments (and maybe soon the U.S. federal government) impose increasingly rigorous environmental and procurement standards on the energy industry. Surprisingly, biomass cofiring has yet to attract much attention, even though it could help many utilities meet their renewable portfolio requirements, reduce carbon emissions, and solve other regional environmental problems. U.S. developers, investors, and regulators should consider including cofiring as part of the energy mix going forward.
-
Coal
Designing an Ultrasupercritical Steam Turbine
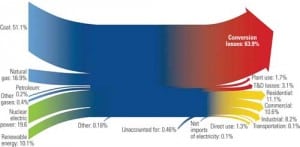
Carbon emissions produced by the combustion of coal may be collected and stored in the future, but a better approach (in the near term at least) is to reduce the carbon produced through efficient combustion technologies. Increasing the efficiency of new plants using ultrasupercritical technology will net less carbon released per megawatt-hour using the world’s abundant coal reserves while producing electricity at the lowest possible cost.
-
Environmental
Power Industry Needs to Do a Better Job of Educating and Messaging
At the opening ELECTRIC POWER 2009 plenary session, both the keynote speaker and the Power Industry Executive Roundtable participants kept circling back to the problems created by a public and lawmakers who seem to be promoting policies without an adequate understanding of energy realities. Most of the speakers acknowledged that the industry itself is partly to blame, but nobody offered a way forward.
-
Waste to Energy
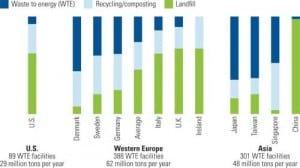
The Growing Role of Waste-to-Energy in the U.S.
Using nonhazardous waste for power generation is a trend that’s gaining steam for several reasons. Though there are several environmental reasons, another is the reliability of the fuel supply.
-
Coal
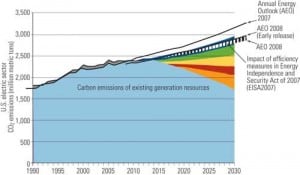
Carbon Control: The Long Road Ahead
The industry is preparing for carbon legislation by exploring options for dealing with CO2. But even if the technical issues are resolved, actually sequestering CO2 poses a number of other daunting challenges.
-
Coal
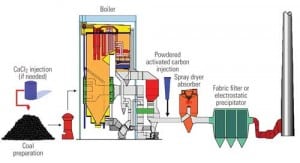
Technology Could Deliver 90% Hg Reduction from Coal
Reducing mercury emissions at coal-fired power plants by 90% has been considered the holy grail of mercury control. A new technique promises to get us there — at a price.
-
Coal
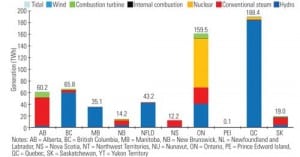
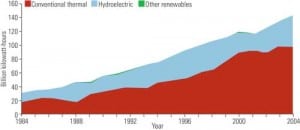
Canada Moves to Rebalance Its Energy Portfolio
Though Canada is rich in fossil fuels, nuclear power may fuel a significant portion of the nation’s future electrical generation needs, especially in provinces that have traditionally relied on hydropower and fossil fuels.
-
O&M
Turkey Opens Electricity Markets as Demand Grows
Turkey’s growing power market has attracted investors and project developers for over a decade, yet their plans have been dashed by unexpected political or financial crises or, worse, obstructed by a lengthy bureaucratic approval process. Now, with a more transparent retail electricity market, government regulators and investors are bullish on Turkey. Is Turkey ready to turn the power on?
-
Coal
CHP: Helping to Promote Sustainable Energy
Because combined heat and power (CHP) plants optimize energy use, they cut fuel costs and pollution. Even though U.S. power plants have been using CHP for decades, today’s energy experts have a newfound appreciation for its ability to promote sustainable energy use.
-
O&M
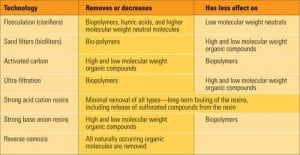
Focus on Organics in Steam
Organic compounds can enter the steam cycle from a number of sources, including water treatment chemicals, or as part of a manufacturing process. Regardless of the source of the organics, their effects range from fouling polisher resins to causing significant steam turbine damage. Conventional water pretreatment systems are available to remove organics from water, but removing organic compounds at their source is the best place to start addressing the problem.