Latest
-
Smart Grid
Microgrids promise improved power quality and reliability
Last month, POWER explored the growing importance of the smart grid, which is envisioned as using digital technologies to enable integrated, real-time control of all the system’s elements, from generation to end use. This month we focus on the emerging technology of microgrids: controlled groupings of dispersed generation sources that are connected to the main electrical grid but that can function independent of it. We examine their benefits and their potential impact on 21st-century utilities and their customers.
-
Coal
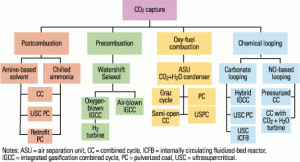
Options for reducing a coal-fired plant’s carbon footprint: Part I
Caps on greenhouse gas emissions are imminent in the U.S., and they will change how we design tomorrow’s coal-fired power plants. Efforts are already under way to develop alternative capture and sequestration technologies, mainly for CO2. Unfortunately, the proposed processes all consume lots of energy, reducing plants’ net output and efficiency. In Part I of our look at these technologies, we list and quantify the negative impacts of postcombustion removal of CO2 from a coal plant’s flue gas. Next month, in Part II, we’ll do the same for four other CO2 reduction techniques: oxyfuel combustion, using higher-temperature and higher-pressure boilers, cofiring biomass, and replacing some coal-fired capacity with renewable capacity.
-
O&M
Digital radiographic systems detect boiler tube cracks
Boiler water wall leaks have been a major cause of steam plant forced outages. But conventional nondestructive evaluation techniques have a poor track record of detecting corrosion fatigue cracking on the inside surface of the cold side of waterwall tubing. EPRI is performing field trials of a prototype direct-digital radiographic system that promises to be a game changer.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Assessing and addressing cyber threats to control systems
Control systems used by utilities and other operators of America’s industrial infrastructure increasingly rely on an Internet connection that makes them as vulnerable to hackers as any computer or network. One reason many utility control systems are vulnerable is that, unlike your ISP’s systems, they don’t record an audit trail that reveals the source of the attack.
-
Synfuel
Biofuels help green up gas turbines
Ethanol and biodiesel have become mainstream fuels that are increasingly used in combination with gasoline or petroleum diesel in automobiles. Now these same versatile fuels are starting to be used to power gas turbines. LPP Combustion LLC has developed a fuel preparation and delivery system that converts liquid fuels such as No. 2 fuel oil, biodiesel, ethanol, and coal liquids into substitute natural gas, which existing natural gas hardware can burn while enjoying reduced emission rates similar to those of natural gas.
-
O&M
Boiler optimization increases fuel flexibility
Burning spot market fuels can reduce plant fuel costs, but it can also introduce unexpected operational problems throughout the boiler island. Orlando Utilities Commission’s Stanton Energy Center optimized its Unit 2 combustion system and improved O&M practices as part of a project to increase the unit’s fuel flexibility without degrading reliability or heat rate. OUC’s attitude: If you can measure it, you can manage it.
-
Commentary
Growing a green economy
I believe there are three basic objectives for the energy industry in the modern era. First, to provide a reliable and ample supply. Second, to ensure that the supply is provided at the least cost to consumers. And third, to accomplish the first and second objectives with the least possible adverse effects on the environment. […]
-
News
Guns and Moses
Charlton Heston’s legacy will surely rest on his iconic performance as Moses in The Ten Commandments and his unwavering support of the Second Amendment. I had the privilege of watching a classic Heston performance at the 2000 National Rifle Association convention in Charlotte, N.C., when he raised a handmade Brooks flintlock above his head and […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (May 2008)
National Grid divested of Ravenswood/ GE to sell Baglan Bay plant; From prairie grass to power/Renewables experience 40% growth/ The sustainable city/Solar recharger for developing countries/ Seeking CCS solutions/ Hoover Dam could stop generating/ Japan turns to fossil fuels/U.S. reactors produce record power/ POWER digest
-