Latest
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Distributed Control Technology: From Progress to Possibilities
The past decade has seen an explosion of technology that has significantly altered the process control industry. The adoption of commercially available technology driven by desktop computing has allowed suppliers to focus on applications to enhance the process and deliver ever-greater value to the user.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Optimize Your Plant Using the Latest Distributed Control System Technology
Distributed control systems are powerful assets for new and modernized power plants. Thanks to three product generations of technology innovations, these systems now provide new benefits — including improved O&M efficiency, greater plant design flexibility, and improved process control and asset reliability — that help competitive plants advance in the game.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Power Plant Automation: Where We Are and Where We’re Headed
Over the past decade, power plant control systems have evolved from DCS-centered platforms with proprietary software, to open systems using industry standard hardware and software, and then to totally integrated plant automation systems with almost unlimited connectivity and the ability to interrogate field instruments from many different manufacturers. What’s next?
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Enhancing Plant Asset Management with Wireless Retrofits
Wireless technology is a mostly untapped resource in the power generation industry that can have a significant impact on the way business is done. It enables a greater degree of connectivity among devices for enhanced monitoring and asset utilization and has led to the development of new applications that improve productivity, uptime, and overall business performance.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Wireless Technology Unlocks Possibilities
Modern wireless systems improve productivity, monitoring activities, and safety at power plants by enabling the right people to be at the right place at the right time. Wireless technology can put hard-to-access process and asset information at your fingertips, wherever you are, to enable more accurate and timely decisions.
-
Coal
New Laser Technology Helps Reduce Coal-Slagging Headaches
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy is starting to light the way for power plant operators who want to reduce coal ash deposition in their boilers.
-
Business
HTS Cables Speed up the Electric Superhighway
High-temperature superconducting cables deliver up to 10 times as much power as conventional electric power transmission cables. They are poised to help to reduce grid congestion as well as installation and operating costs.
-
Business
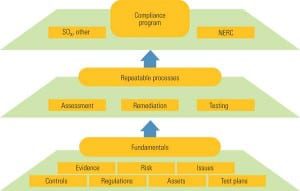
NERC Drives Development of Sustainable Compliance Programs
Compliance with reliability standards has moved beyond the "check the box" phase to one of regulations with real deliverables and fines for noncompliance. Utilities that aren’t vigorously evaluating and refining their compliance procedures today may find NERC’s 2009 audit cycle much more challenging.
-
News
Upward Mobility
The Max Climber 2000P-IPM rack and pinion personnel and material elevator by Beta Max Inc. uses little space while providing a safe and efficient means of access for workers performing maintenance work at high levels. The Max Climber 2000P-IPM easily attaches to scaffolding or a building exterior and is designed with a base system footprint […]
-
Commentary
The Obama Administration’s Energy Challenge
As the Obama administration takes office, energy resource allocation is both the most critical national security issue and the most critical economic issue facing us. It will be difficult to sustain and improve economic growth unless we implement policies that result in the more rational use of energy resources, especially those for which there is a finite supply.