Latest
-
Commentary
The Supreme Court and Best Environmental Practices
Did a recent Supreme Court decision give a license to firms to use “best practices” concepts to gut effective environmental standards?
-
Commentary
Go Ahead, Close Oyster Creek
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) in early April granted Entergy Nuclear an extended license for the Oyster Creek nuclear plant in New Jersey, the oldest operating nuke in the U.S. The plant will now be able to operate until 2029, unless the NRC at some point in the future grants a further license extension. Nuclear power advocate William Tucker, with tongue in cheek, advocated closing the plant and other elderly units in the Northeast, in a commentary in the National Review. Tucker’s comments are reprinted with permission.
-
Legal & Regulatory
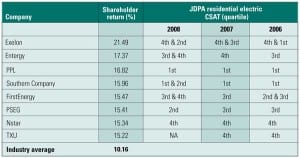
Utility Customer Satisfaction: A Faith-Based Initiative?
Does customer satisfaction play a meaningful role in guiding utility operations? Many utilities think it does, as do many regulators. The market apparently doesn’t. Data suggest that the jury is out on the question, and the intuitive answer may not match the empirical evidence.
-
Legal & Regulatory
TREND: Coal Industry’s Future Faces Challenges
What role will coal play as the nation moves toward trying to reduce greenhouse gases? The picture is mixed, as these news stories from around the country demonstrate.
-
News
Cap-and-Trade Bill Clears House Committee
After a week of long and heated arguments, the House Energy and Commerce Committee on Friday passed by a vote of 33 to 25 the American Clean Energy and Security Act of 2009, a massive 946-page bill that would set up a cap-and-trade program and a federal renewable energy standard.
H.R. 2454 now heads to the House Ways and Means Committee, which will review the tax and trade implications of the bill. That committee could make more revisions to the bill. -
News
U.S. Power Sales Plunge on Weak Economy
U.S. power sales have plunged in the past six months on the back of an unprecedented demand decline that was caused by sharp contractions in the economy, and recovery is not anticipated until the 2010 to 2015 period, an analysis from Edinburgh-based Wood Mackenzie shows.
-
News
Russia Clinches $1 Billion Uranium Supply Deal with U.S. Companies
Russia’s federal atomic energy agency, Rosatom, reportedly said Tuesday that it had reached a landmark deal to supply enriched uranium fuel rods to nuclear power plants in the U.S.
-
News
Duke Energy Vindicated on Majority of EPA Pollution Control Charges
A jury in U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Indiana last week ruled in favor of Duke Energy and against the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on four of six projects involved in a decade-long pollution controls lawsuit affecting the company’s Midwest power plants. The jury ruled against the company on two Indiana projects.
-
News
Planned U.S. CCS Demonstration Will Be Largest Test of MHI’s Amine Technology
A public-private partnership that includes the Energy Department, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI), the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), and Southern Co. is planning the largest start-to-end coal-fired demonstration of MHI’s amine solvent carbon capture technology at an existing Alabama coal-fired unit by 2011.
-
News
U.S. Power Sector Carbon Emissions Fell 2.1% in 2008
Carbon dioxide emissions from the power sector decreased by about 2.1% as power generation declined by 1% last year, according to preliminary estimates released last week by the Energy Information Administration (EIA). The decrease reflected, among other factors, falling emissions from fossil fuel generation and an increase in wind-powered generation, the agency said.