Solar
-
Solar
Think Water When Designing CSP Plants
The operation of solar thermal power plants differs substantially from that of fossil-fired plants, as the sun determines the generation rather than market demand. However, design of the power island to minimize water usage is very similar to that of a fossil plant. This renewable technology requires renewed thinking of its water systems’ design.
-
Solar
Large China Energy Storage Project Begins Operation
Chinese state entity State Grid Corp. of China (SGCC) and battery maker BYD in January said they had finished construction on what they call “the world’s largest battery energy storage station”—a project in Zhangbei, Hebei Province that combines 100 MW of wind and 40 MW of solar capacity, a smart power transmission system, and 36 MWh of energy storage in arrays “larger than a football field.”
-
Solar
Spain Inaugurates Two More Parabolic Trough Units
Two identical 50-MW parabolic trough plants with thermal storage in Cadiz, in the south of Spain, began operating this January.
-
Gas
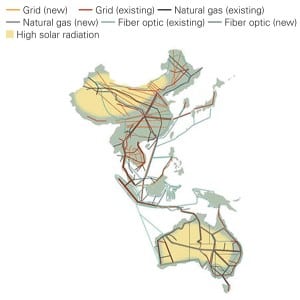
Desertec Ambitions Turn to Asia, Australia
The ambitious Desertec project—a $9 billion initiative to develop, harness, and transmit 2,000 MW of renewable power from North Africa and the Middle East to Europe by 2050—has been trumped by a vaster concept that spans Asia and Australia.
-
Coal
Vietnam Works Hard to Power Economic Growth
For the past 15 years, Vietnam has enjoyed enviable gross domestic product increases, averaging 7% annually. That kind of economic growth increases power demand, but financing new capacity remains a challenge. Reaching its ambitious capacity growth goals will require Vietnam to expand its financing and vendor base, attract foreign investment, and ensure future fuel supplies in a region thick with competition for those resources.
-
Nuclear
The Big Picture: DOE Loan Guarantees
Of the $35.9 billion in loan guarantees awarded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) since 2009, roughly $26.5 billion have financed nuclear and renewable power projects across the nation through the Section 1703 and 1705 loan guarantee programs.
-
Coal
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Solar
The U.S. Military Gets Smart Grid
At home and abroad, U.S. military microgrid and smart grid projects are driven by energy security concerns. The pace of such projects, however, can be slow, and the potential for civilian grids to benefit from lessons learned and technologies developed for these important installations may be limited.
-
Coal
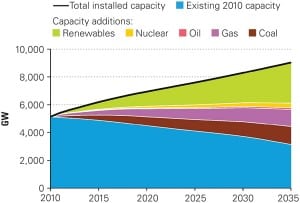
World Energy Outlook Forecasts Great Renewables Growth
Driven by policies to limit carbon emissions, as well as government subsidies, the share of worldwide nonhydro renewable power is set to grow from just 3% in 2009 to 15% in 2035, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its recently released World Energy Outlook 2011. Under the same scenario—which assumes that carbon pricing, explicit […]
-
Coal
U.S. Confronts Pipeline Gaps While Europe Juggles Renewables and Debt
U.S. optimism has been restored by reports of abundant, reasonably priced natural gas to fuel most new generation; however, huge gaps in the fuel delivery system (thousands of miles of pipelines are needed) will soon challenge gas plant development. Meanwhile, the cloud of sovereign debt hangs over all major capital projects in Europe, where the UK moves ahead with new nuclear projects while many of its neighbors shut the door on nuclear and struggle to finance their commitment to renewables.
-
Coal
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan Pushes Power Industry in New Directions
The Five-Year Plan is the expression of the centralized planning goals for China’s economy. The 12th Five-Year Plan, approved by the Chinese Government on March 14, 2011, established many social and economic goals, including significant expansion of the country’s power generation industry in many new directions.
-
Solar
U.S.-China Solar Trade Dispute Gets Thornier
A trade row between the Chinese government and solar panel makers around the world intensified in December. As China’s Ministry of Commerce refuted allegations that the Chinese government uses illegal subsidies, discounts for raw materials, preferential loans, tax incentives, and currency manipulation to drive down prices and amplify exports of Chinese solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) affirmed the U.S. solar industry is “materially injured” by imports, at “less than fair value,” of Chinese crystalline silicon PV cells and modules.
-
Coal
Editors Select Top Five Stories of 2011
The POWER editorial staff’s picks for the most significant stories of 2011.
-
Solar
Top Plant: Copper Mountain Solar 1, Boulder City, Nevada
The current largest photovoltaic plant in the U.S., the 48-MW Copper Mountain Solar 1, utilizes approximately 775,000 solar panels to generate emission-free electricity for about 14,000 homes without the use of water. The facility was constructed in less than a year—an unprecedented achievement for a project of this size.
-
Solar
Top Plant:Â Kimberlina Solar Thermal Energy Plant, Bakersfield, California
The 5-MW Kimberlina Solar Thermal Energy Station is the first to use compact linear Fresnel reflector technology developed to generate continuous superheated steam, a key element for higher-efficiency power generation and integration with new and existing plants. The facility’s innovative technology helps deliver power even during periods of transient cloud cover.
-
Solar
Top Plant: Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center, Indiantown, Martin County, Florida
The 75-MW Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center is the first hybrid solar facility in the world to combine a solar thermal array with a combined cycle natural gas power plant. Because the facility uses a steam turbine, transmission lines, and other infrastructure from an existing combined cycle unit, financial savings of approximately 20% were achieved compared to what a similar stand-alone solar plant would have cost.
-
Solar
Top Plant: Sarnia Solar Project, Sarnia, Ontario, Canada
The 80-MW Sarnia Solar Project is the world’s largest operational photovoltaic plant, with 1.3 million solar modules. The facility utilizes First Solar’s proven thin-film photovoltaic (PV) technology, which has the lowest environmental footprint and the fastest energy payback of current PV technologies.
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.
-
Gas
Nordic Nations Provide Clean Energy Leadership
In the past few years, nuclear concerns, rising oil prices, and a growing understanding of our environmental impact has given energy issues a higher profile worldwide. In this report on the Continental Nordic countries, we look at the efforts being made in much of the Nordic region to secure a sustainable energy supply for the future and at the extent to which the innovative solutions of these countries can be exported around the globe.
-
Solar
Epic Fail
Over the past 18 months, four solar energy equipment companies have closed their doors. Each one blamed poor market conditions for its economic woes, even though each had fundamental weaknesses that went unaddressed. It now appears that the Department of Energy (DOE) did insufficient due diligence before backstopping one of those four companies, Solyndra, with a $535 million loan guarantee.
-
Solar
THE BIG PICTURE: A Solar Switch
The plummeting cost of photovoltaic (PV) panels—resulting from lower costs for high-grade silicon and advancements in thin-film technology, solar storage, and electronic control technologies—has a slew of firms rethinking concentrating solar power (CSP) projects. Although there is a CSP project pipeline (including both CSP and concentrating PV) of more than 9 GW in the U.S., […]
-
Solar
Murkowski: Renewables Future Not "All Sunshine and Roses"
There’s lots of reason for optimism about clean technologies, Sen. Lisa Murkowski (R-Alaska) told a packed crowd on Tuesday afternoon at the RETECH 2011 Keynote Session. New ideas are emerging, costs are coming down and deployment is increasing, she noted—all welcome developments for America’s energy supply and the global environment. The rapid growth of the renewables is partially due to federal policies, but much of the progress has been a "direct result of your creativity and determination."
-
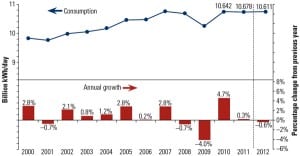
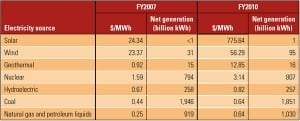
Hydro
Chart a New Course
I examined the magnitude of electricity subsidies for renewables compared with conventional generation technologies in my May 2011 editorial, based on data from a 2008 report prepared by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). An updated EIA report released in July determined that federal government subsidies have risen substantially during the past three years. In fact, overall renewable energy subsidies have almost tripled, increasing from $5.1 billion to $14.7 billion. In my opinion, we aren’t getting value for the money spent.
-
Solar
Spanish Power Tower Supplies 24 Hours of Electricity
In Spain this June, a new 19.9-MW concentrated solar power (CSP) tower in Fuentes de Andalucía, Seville, reached the unprecedented milestone of storing thermal energy to its fullest capacity and supply power for an uninterrupted 24-hour period.
-
Gas
Who Pays for Firming Up Variable Energy Resources?
The major economic hurdle for renewable power generation technologies continues to be substantial installation costs. But another cost is associated with continuous load-balancing, made possible by backstopping that variable generation with dispatchable generators that typically consume expensive fossil fuels. Bottom line: Who pays for the capacity firming or backstopping resources?
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.
-
Solar
Utilities Increase Renewable Energy Capacity
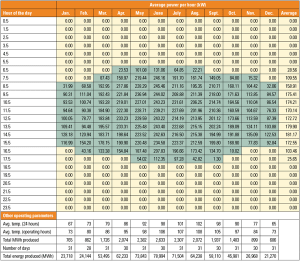
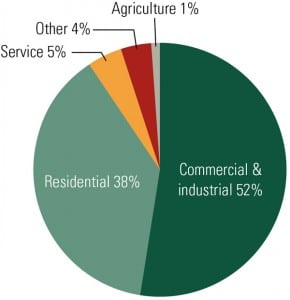
Driven by state RPS requirements and the desire to diversify their energy sources, U.S. utilities continue to add more renewable power to their generation portfolios. As a result, they must deal with a number of important issues, including resource availability that varies geographically.
-
Solar
Sunny Days Ahead for Solar
In the U.S., developers of thermal and photovoltaic solar plants face a number of challenges in their efforts to deploy more utility-scale solar power. Some trends, however, are helping solar proponents move this renewable energy source closer to becoming a mainstream generating option.
-
Coal
Using Fossil-Fueled Generation to Accelerate the Deployment of Renewables
It may seem counterintuitive, but the strategic coupling of simple- and combined- cycle technologies with renewable generation could establish the conditions necessary for adding more renewable megawatts to transmission grids around the world.
-
Solar
Countries Abandon Subsidies for Renewables en Masse
Stricken by the economic crisis and forced to implement austerity measures, several countries around the world have been forced to abandon or slash subsidies for renewable power producers.