Solar
-
Coal
World Energy Outlook Foresees Distinct Generation Shift
Global generating capacity is poised to soar by more than 72%, to 9,340 GW, by 2035 from 5,429 GW in 2011, despite retirement of about 1,980 GW, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its World Energy Outlook 2012, released in November.
-
Solar
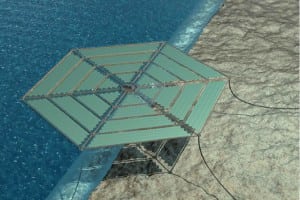
Floating Solar—on Water
The recent explosive growth of massive solar plants in some of the world’s most remote deserts has stolen some of the spotlight from smaller solar installations that float on water. But in November, a concept proposed by researchers at Norwegian foundation DNV (Det Norske Veritas) for a dynamic floating offshore solar field concept stirred up myriad possibilities, particularly for congested urban regions such as coastal megacities.
-
Coal
Slow Growth Ahead—with Unexpected Flares of Activity
North American shale gas was supposed to realign the generation fleet here and abroad (thanks to anticipated exports) far into the future. Turns out, that’s not exactly how the near term is shaping up. Despite stagnant (and even putrid) economies and legislative bodies in the U.S. and EU, there promises to be sufficient market volatility to keep everyone alert.
-
Solar
DOE Announces $29M to Bring Down Costs for Solar Installation
The Department of Energy (DOE) on Friday announced a $29 million investment in four solar projects aimed at improving grid connection and reducing installation costs through plug-and-play technologies and reliable solar power forecasts. The awards are part of the agency’s SunShot Initiative, which is working to make solar energy competitive with other forms of energy without subsidy by the end of the decade.
-
Solar
New Batteries and Energy Storage Hub Aims to Improve Grid and EV Performance
U.S. Secretary of Energy Steven Chu announced on Oct. 30 that a multi-partner team led by Argonne National Laboratory in Illinois has been selected for an award of up to $120 million over five years to establish a new Batteries and Energy Storage Hub.
-
Coal
EIA Projects Faster Growth of Natural Gas Production, Gas Generation
Compared to projections from last year, an Early Release Overview of the Energy Information Administration’s (EIA’s) Annual Energy Outlook 2013 (AEO2013) released on Wednesday foresees higher gas production and, with it, a higher share of gas generation by 2040. The outlook also projects a growing share of renewable and nuclear power, but dampened future coal use.
-
Solar
14-MW Solar PV Plant Completed at Naval Station
The U.S. Navy in late October saw the completion of its largest solar generation system, a 13.78-MW (DC) solar photovoltaic (PV) power system at Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake (NAWS China Lake) in California.
-
Solar
TOP PLANT: Alamosa Solar Project, San Luis Valley, Colorado
As the largest solar plant of its type in the world, the 30-MW Alamosa Solar Project is currently enjoying its place in the sun. The innovative project consists of 504 concentrating photovoltaic (CPV) solar trackers, each featuring a CPV solar cell panel assembly mounted on a support column. The modular design of the assembly allows the project to easily accommodate future improvements in cell technology.
-
Solar
TOP PLANT: Gujarat Solar Park, State of Gujarat, India
Set up by the Gujarat government, the Gujarat Solar Park is actually a group of solar parks that provide dedicated common infrastructure for photovoltaic-powered projects owned and operated by numerous individual companies. When construction at all the parks is completed by the end of 2013, the Gujarat Solar Park is projected to reach a combined capacity of almost 1,000 MW, which will make it the world’s largest solar energy generation installation.
-
Solar
TOP PLANT: Stillwater Solar-Geothermal Hybrid Plant, Churchill County, Nevada
The Stillwater hybrid facility is the world’s first renewable energy project that pairs geothermal power’s baseload generation capacity with solar power’s peak capacity. Inaugurated in May, the 26-MW solar plant is integrated with the adjacent 33-MW geothermal plant, which began operations in 2009, and provides energy to run the geothermal plant’s auxiliary loads.
-
Solar
Distributed Solar Challenges Utilities, Markets, and Regulation
Electricity produced from solar energy is being added to the grid—before and after the meter—in greater amounts each year. The uniqueness of this resource is pushing utilities, developers, users, and regulators to develop new and innovative interconnection rules and to rewrite some old rules that balance the costs and rewards among stakeholders.
-
Hydro
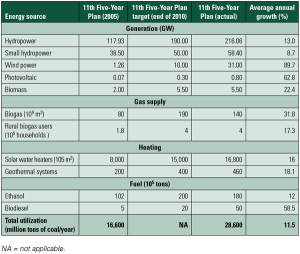
Renewable Energy Development Thrives During China’s 12th Five-Year Plan
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan calls for expanding the use of renewable energy in all forms throughout the country. From solar and wind to biomass gas and briquettes, China has a true “all of the above” renewable energy policy.
-
Hydro
Hawaii’s Largest Wind Project Online as State Struggles to Integrate Renewables
On Monday, as First Wind announced its 69-MW Kawailoa Wind Project had gone into commercial operations on Oahu, other news underscored the difficulty the island state faces in trying to substitute renewables for expensive, imported fossil fuels.
-
Solar
European Solar Initiative to Source Power from North Africa Hits Blocks
The Desertec Industrial Initiative (Dii) oversees a $508 billion initiative to establish 6,500 square miles of concentrated solar power plants in the vast African and Middle Eastern deserts. Those plants are expected to furnish a fifth of Europe’s power needs by 2050, but in recent weeks the Dii has seen the exit of two of its 57 partners from 16 countries and a project held up by the Spanish government.
-
Hydro
Trend Shows Growth of Renewables on Contaminated Lands
Renewable energy projects installed on potentially contaminated lands, landfills, and mine sites have increased by 40% since 2008, a new list released last week by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems make up the bulk of about 184.7 MW installed at 60 sites in 25 U.S. states.
-
Gas
Blowing Sunshine
The influx of cheap Chinese-manufactured solar panels has upended the solar industry in more ways than one. The saga offers some lessons on what to do about LNG exports.
-
Solar
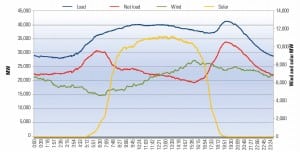
Maintaining Grid Reliability with a High Renewables Portfolio
The first problem with high renewable penetration is that wind and solar are not dispatchable.
-
Solar
California’s Streamlined DG Interconnection Process Bodes Well for Solar
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) last week approved a deal involving the state’s major utilities and renewable energy advocates that is aimed at streamlining the process for connecting distributed generation (DG) resources to the grid. The CPUC’s action will make it easier for small amounts of distributed resources—such as rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) systems—to connect to the grid. The agreement also revises upward the amount of DG that can be connected to a specific power line segment without the need for supplemental studies.
-
Solar
Ariz. Now Home to World’s Largest Solar PV Plant
The title of world’s largest operating solar photovoltaic (PV) power plant goes to Arizona. On Monday, First Solar Inc. announced that the Agua Caliente solar project has achieved a peak generating capacity of 250 MW connected to the electrical grid. The project, under construction in Yuma County, will have a total capacity of 290 MW when completed.
-
Solar
DOE Offers $10M to Bring Down Rooftop PV "Soft Costs"
The Department of Energy (DOE) on Wednesday announced its SunShot Prize, a new competition to make it faster, easier, and cheaper to install rooftop solar energy systems. A total of $10 million in cash awards are available to the first three teams that repeatedly demonstrate the non-hardware costs, or price to plug in, can be as low as $1 per watt for small-scale photovoltaic (PV) systems on American homes and businesses.
-
Coal
Congressional Briefs: Back from Recess
Congress has returned from its summer break. As the House prepares to vote on its Upton-Stearns "No More Solyndras Act," lawmakers also expect to focus on a bill that could prohibit finalization of any Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) power plant rules that curb greenhouse gas emissions while carbon capture and storage technology is commercially unavailable. House Democrats, meanwhile, called for hearings to examine the impacts of climate change on the nation’s generators.
-
Coal
Chile’s Power Challenge: Reliable Energy Supplies
Droughts, unreliable gas imports, and protests against proposed projects have hampered the Chilean power sector and its largest economic driver, the copper-mining industry. Recent policies designed to foster more reliable supplies are a move in the right direction, but remaining obstacles are formidable.
-
Solar
Trade Representatives Request Investigation on U.S. Renewables in Global Context
The U.S. Trade Representative on Monday asked the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) to investigate how U.S.-provided renewable energy services affect development of renewable energy projects worldwide. The ITC’s report, expected by June 28, 2013, will focus on the development, generation, and distribution of renewable energy—specifically onshore and offshore wind and solar energy.
-
Solar
Solyndra Story Doesn’t Get Stearns Reelected
Washington, 17 August 2012 — Poor Cliff Stearns. The soon-to-be-former Republican congressman from Florida found out Tuesday that voters in his district didn’t much care about the ruckus he’s been raising about the Obama administration and its funding of the failed Solyndra solar photovoltaic maker.
-
Hydro
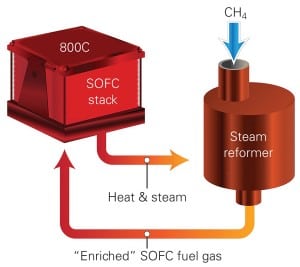
Major Developments for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which oxidize a fuel to produce electricity, have received much attention of late for the technology’s myriad benefits, including high efficiency, long-term stability, fuel flexibility, and low carbon emissions—all at a relatively low cost.
-
Solar
Smart Grid Award: Customers Motivate San Diego Gas & Electric’s All-Inclusive Smart Grid Vision
“If you build it, they will come” has proven a risky strategy for some smart grid projects. One of California’s largest investor-owned utilities faced the opposite challenge—customers whose behaviors necessitated a smarter grid. Customer involvement in and support for smart grid plans is a major reason SDG&E’s smart grid efforts continue to garner accolades, including the 2012 POWER Smart Grid Award.
-
Solar
Solar Trade Tensions Intensify as China Launches Polysilicon Dumping Probe
Global solar trade tensions escalated on Friday as the Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China announced it would launch both anti-dumping and countervailing investigations on imports of solar-grade polysilicon from the U.S. and an anti-dumping probe on South Korean polysilicon imports. Germany on Friday, meanwhile, said it would support its solar industry in anti-dumping action against China.
-
Solar
Large Thin-Film CIS Plant Goes Online in Germany
In May—as a trade war raged between Chinese solar panel manufacturers and exporters and their counterparts in the U.S. and the European Union concerning the world’s plummeting crystalline silicone photovoltaic module prices—a 28.8-MW thin-film copper indium gallium (di)selenide (CIGS or CIS) solar power plant came online. Developers Solar Frontier, the world’s largest manufacturer of CIS […]
-
Coal
Power in India: Opportunities and Challenges in a Fast-Growing Market
India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth. India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth.