Waste to Energy
-
Commentary
WTE: Next-Generation Sustainable Energy
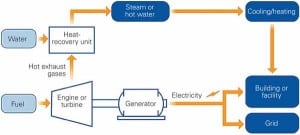
It is clear that energy use will expand in the future as our population and society’s standard of living increase. Meanwhile, the push toward a sustainable lifestyle requires that all resources be utilized efficiently and sparingly. The National Academy of Sciences has identified paradigm shifts from current processes to an ideal vision centered on renewable energy and an atom economy—defined as maximum incorporation of starting materials into final products. These seemingly disparate paths converge if one considers energy production from municipal solid waste (MSW).
-
Coal
OPG Charts Move from Coal to Biomass
In response to Ontario’s provincial regulatory mandates to phase out the use of coal by the end of 2014, Ontario Power Generation (OPG) is exploring its capability to employ biomass feedstocks to displace coal in some units within the OPG thermal fleet. The primary fuels employed during the respective trials at its Nanticoke and Atikokan Generating Stations have been agricultural by-products and commercial grade wood pellets. The Canadian utility has learned valuable lessons about fuel supply and logistics, and the technical challenges of safely handling and firing high levels of biomass.
-
Coal
Plant Efficiency: Begin with the Right Definitions
The race is on to claim the title of "most efficient coal-fired power plant" on the planet. However, it’s tricky identifying finalists because of the widespread misuse of the term "efficiency" and all those nagging assumptions. Let’s first establish clear definitions and then identify the title contenders.
-
O&M
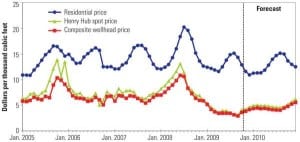
The U.S. Gas Rebound
"It’s déjà vu all over again," said Yogi Berra. The Hall of Fame catcher could easily have been predicting the coming resurgence of natural gas – fired generation. Yes, a few more coal plants will be completed this year, but don’t expect any new plant announcements. A couple of nuclear plants may actually break ground, but don’t hold your breath. Many more wind turbines will dot the landscape as renewable portfolio standards dictate resource planning, but their peak generation contribution will be small. The dash for gas in the U.S. has begun, again.
-
Waste to Energy
Top Plants: Harrisburg Resource Recovery Facility, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania
After decades of struggling with serious air contamination issues and large financial losses, this Pennsylvania waste-to-energy facility, which was built in 1972, was in need of an extreme makeover. In the wake of an unsuccessful $84 million retrofit attempt in 2005, the faltering facility’s last hope lay with a Covanta project team that took over its operation in 2007. After almost two years of hard work, the facility is now producing up to 17 MW while achieving its environmental compliance goals and earning substantial revenues.
-
Waste to Energy
Top Plants: Rio Bravo Rocklin Power Station, Lincoln, California
By 2008, the 19-year-old wood-fired Rio Bravo Rocklin Power Station’s operating performance had been significantly degraded by boiler erosion and corrosion caused by (among many other problems) poor fuel. After much consideration, the plant owners elected to invest in a comprehensive upgrade to restore the plant to its as-built performance. Today, the plant operates very reliably. A newly implemented predictive maintenance program should continue to drive down operating costs and further reduce the number of forced outages.
-
-
Waste to Energy
Biomass Electricity More Efficient than Ethanol, Researchers Say
Biomass — plant matter that’s grown to generate energy — converted into electricity could result in 81% more transportation miles and 108% more emissions offsets than ethanol, according to U.S. researchers. In addition, the electricity option would be twice as effective at reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The study, published in the May 22 issue […]
-
Waste to Energy
Turning Sewage into Renewable Energy
News has been emerging from around the world about several projects that seek to turn human sewage — arguably the dirtiest of manmade wastes — into clean energy.
-
Waste to Energy
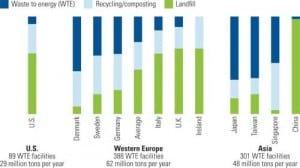
The Growing Role of Waste-to-Energy in the U.S.
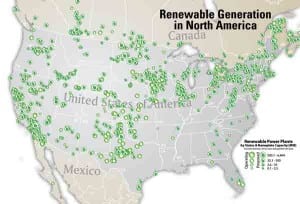
Using nonhazardous waste for power generation is a trend that’s gaining steam for several reasons. Though there are several environmental reasons, another is the reliability of the fuel supply.