Geothermal
-
Legal & Regulatory
Regulators should stop playing the greed card
In early February, Western GeoPower (WGP) announced its termination of a 20-year geothermal power purchase agreement (PPA) with Pacific Gas and Electric Co. (PG&E). A WGP press release explains that the company terminated the agreement because a regulatory approval condition had not been obtained within a 180-day time period stipulated in the PPA. WGP’s CEO, […]
-
Geothermal
Raft River Geothermal Project, Malta, Idaho
Geothermal power is a unique renewable energy because it has the best potential capacity factor and is perhaps the only option for baseload power generation. U.S. Geothermal has constructed the first geothermal plant in Idaho in a generation by restoring an abandoned DOE demonstration project site that may possess a development potential of over 100 MW using proven power generation technology. The success of Raft River may well determine the future of geothermal energy production in Idaho.
-
Nuclear
Global Monitor (July 2007)
Pistachio plant gives new meaning to green/Slightly sun-powered grill/Will lithium revolutionize hydrogen storage?/Calpine’s major Geysers geothermal upgrade/Rhone-Alps is French PV hot spot/Fuel cell–powered ice-resurfacing machine/Westinghouse proposes revised AP100 design/Sandia perfects solar alignment/SCE wants comprehensive coal study/POWER digest
-
Coal
Investment in generation is heavy, but important needs remain
Forecasting the direction of the U.S. electric power industry for 2007, much less the distant future, is like defining a velocity vector; doing so requires a direction and speed to delineate progress. In this special report, POWER’s first stab at prognostication, the editors look at current industry indicators and draw conclusions based on their more than 100 years of experience. To borrow verbatim the title of basketball legend Charles Barkley’s book: I May Be Wrong but I Doubt It.
-
Coal
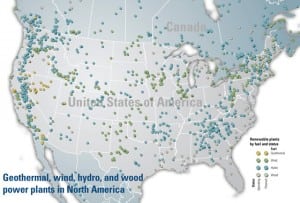
Near-term capital spending in the North American power industry
Following the money invested in projects is a viable way to compare growth trends for power projects using the four major generation types: coal, natural gas, nuclear, and renewable.
-
Commentary
Turning the corner on global warming
In his keynote speech this May to the Global Roundtable on Climate Change, held in Iceland and hosted by the Earth Institute of Columbia University, Ólafur Ragnar Grimsson—the president of Iceland—challenged government and business leaders to take measurable steps now to build a prosperous and sustainable future through smart science and public policy. Grimsson’s call […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Renewable contracts merit longer terms
The length of term allowed for power sales contracts is a critical determinant of the ability of states to meet their increasingly ambitious renewable power targets. Many utilities advocate limiting terms to 10 or perhaps 15 years for renewable energy contracts, emphasizing the "flexibility" that shorter terms offer. In contrast, contract terms of 20 or […]
-
Hydro
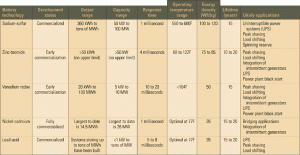
Big batteries blooming
Several advanced battery technologies tailored for utility applications have doffed their white coats and donned hard hats. These new bulk energy storage devices, which can almost instantly shave peaks and shift loads, are the answer to the dreams of T&D system designers and operators. Finally, years of R&D in electrochemistry are beginning to pay dividends in the field.
-
Geothermal
Geothermal: Hotter than ever
Balmy days are on the horizon for geothermal energy. The renewal of the Production Tax Credit in the U.S. and improved drilling and electricity production techniques are the two main reasons geothermal energy advocates are bullish about the industry. POWER looks at some interesting installations and explains why the optimism is well-founded.