O&M
-
O&M
Top Plants: Royal Pride Holland Commercial Greenhouse Cogeneration Plant, Middenmeer, North Holland Province, Netherlands
At Royal Pride Holland’s commercial tomato greenhouse, green thumbs and green energy go hand in hand. With a total energy utilization of 95% in this application, GE’s new Jenbacher J624 natural gas – fired engines offer the innovative greenhouse an economical supply of on-site electrical and thermal power, as well as CO2 fertilization, to support its operations.
-
O&M
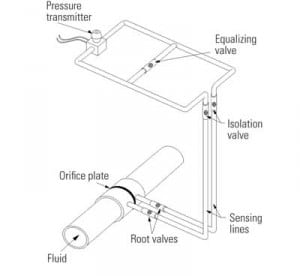
Pressure-Sensing Line Problems and Solutions
Improper pressure-sensing line design or installation is often found to be the cause of poor sensing system accuracy and response time. Here’s how to identify and solve those pesky pressure sensor problems in short order.
-
O&M
Accurate Online Silica Analyzers Ensure Boiler Performance, Add Boiler Life
One key area at the 800-MW Michoud power station where O&M excellence is evident is in maintaining plant water quality.
-
O&M
What if New Source Review Were Repealed?
The New Source Review (NSR) permitting program was originally created as part of the 1977 Clean Air Act Amendments to ensure that new power generation facilities were properly outfitted with all the necessary air quality control systems when constructed. Plants in operation were exempt until they made plant modifications viewed as beyond “routine maintenance,” a term whose definition has been a moving target. Is it time for the NSR to take a back seat to improved plant efficiency and reduced carbon emissions?
-
O&M
Leading-Edge Conveyor Technologies Reduce Dust Emissions
Reducing dust from coal conveyors has moved from a housekeeping chore to a safety challenge, especially with Powder River Basin coals. Here’s what you need to know about the latest coal-handling system design.
-
O&M
High-Hazard Coal Ash Sites, and the TVA Spill Revisited
The EPA has identified 44 "high hazard" coal ash ponds around the U.S., and a recent Tennessee Valley Authority report indicates that the agency should have known its Kingston Plant pond would have been one of them.
-
O&M
PRB Coal Users’ Group Educates Industry on the Dangers of Combustible Dust
The annual meeting of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group was held in association with the ELECTRIC POWER conference in early May in Chicago. Get a taste of the festivities, technical meetings, and the announcement of the group’s 2009 Large and Small Plant of the Year winners in this conference report.
-
O&M
The 7,000-Foot Challenge
The Springerville Generating Station in Springerville, Ariz. (Unit 3 was POWER’s 2006 Plant of the Year), uses two lined ponds to hold water collected from its cooling towers. With the construction of Unit 4, the plant’s owner, Salt River Project (SRP), one of Arizona’s largest utilities, wanted to increase the capacity of pumps used to move effluent from one pond to another to avoid the possibility of overflow. SRP engineers wondered if using a vertical turbine pump on a floating barge would improve managing the water levels in the two ponds.
-
O&M
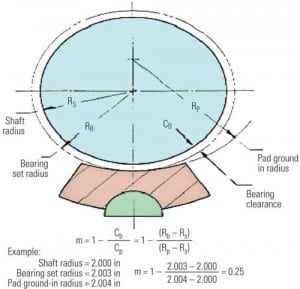
Preventing Turbine Water Damage: TDP-1 Updated
ASME’s latest revision of its Recommended Practices for the Prevention of Water Damage to Steam Turbines Used for Electric Power Generation: Fossil-Fuel Plants, ASME TDP-1-2006, contains much important design and operating advice that is proven to protect steam turbines. However, many in the industry are not as familiar with the update as they should be. This article provides a concise overview of this critical design standard.
-
O&M
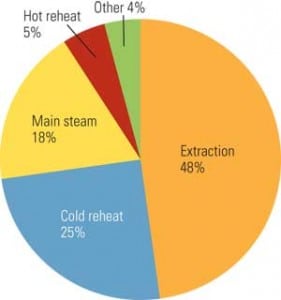
Managing Minimum Load
Reducing the minimum load at which a steam turbine can reliably operate is one way to increase revenue for marginal base-loaded units during periods of low electrical demand. For this reason, it is not unusual to see merchant plants operating at "super minimum" load levels that are well below the typical 25% rated full-load limits. However, such units are operating well outside the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) design basis, and owners may experience undesirable damage to their turbines for a number of reasons. That’s why it is important for owners to understand the trade-offs and risks that come with such operation.