O&M
-
O&M
A Game Plan for Improving Boiler Operations
Operating a boiler is not difficult, but operating a boiler safely and efficiently requires skill and proper training. Following boiler operation best practices will keep your equipment in like-new condition for years to come. This game plan includes a compendium of best practices, with web links to a number of additional key resources you should be famililar with.
-
O&M
Fuels Used for Power Generation Expected to Rebound in 2010
The Energy Information Administraion has predicted that, as the economy gathers steam this year, rising demand for gasoline, crude oil, coal, and natural gas is expected to push up energy prices, aided by a projected boost in crude oil production.
-
O&M
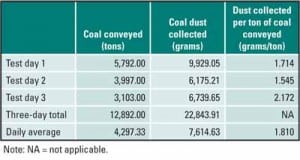
Conveyor Upgrades Increase Plant Availability, Reduce Airborne Dust
The loading and discharge of conveyor belts is the area where many, if not most, of the problems in solids conveying occur. Fortunately, a new technology provides chutes to accomplish conveyor loading and discharge without blockages while minimizing the dust generated: engineered-flow transfer chutes.
-
O&M
Can Your Boiler Feed Pump Handle a Deaerator Pressure Transient?
In a typical steam power plant, the boiler feedwater (BFW) pump takes suction from the deaerator (DA) and discharges high-pressure water to the boiler through the feedwater heaters. During normal operation, the DA is supplied with steam turbine extraction steam to mix with and heat the feedwater.
-
O&M
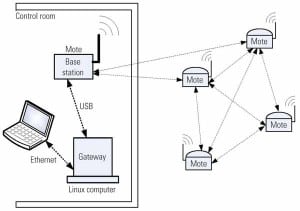
Low-Cost Wireless Sensors Can Improve Monitoring in Fossil-Fueled Power Plants
As equipment ages in fossil-fueled power plants, component wear leading to machinery failure increases as a result. Extending equipment life requires increased attention to maintenance, and one way to improve maintenance planning is to detect faults prior to failure so maintenance can be scheduled at the most cost-effective, opportune time. This type of strategy benefits from the use of additional sensors, and wireless ones can often be installed with the least time and cost.
-
O&M
How to Avoid Alarm Overload with Centralized Alarm Management
In 1999, the Engineering Equipment and Materials Users’ Association (EEMUA) released its general guide to the design, management, and procurement of alarm systems for industrial plants. The guidance document (EEMUA 191), however, is vague about applications to specific facilities, such as electric power plants. This article specifies EEMUA 191 standards and practices applicable to the electric power industry and spells out specific variations in alarming practices that are tailored for today’s power plants.
-
O&M
Widespread Voltage Collapse Demonstrates the Importance of Generator Acceptance Testing
A September 2005 power outage that affected two million people in the California Southland was initiated when workers cut live electrical wires after consulting erroneous design drawings, but it was exacerbated by a number of extant problems with local generation and protection configurations.
-
O&M
Replacing an HP/IP Rotor
Today’s power plant owners face many challenges, including the aging and degradation of equipment. Steam turbines at times may be condemned due to operating inefficiency or rising vibration levels. In such cases the options may be few because the turbine may require a full or partial rotor section replacement. The good news is that a rotor section replacement can be performed in a relatively short time, depending upon the original rotor configuration. Here’s one example.
-
O&M
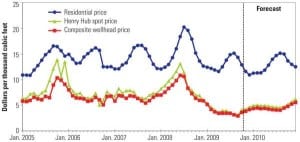
The U.S. Gas Rebound
"It’s déjà vu all over again," said Yogi Berra. The Hall of Fame catcher could easily have been predicting the coming resurgence of natural gas – fired generation. Yes, a few more coal plants will be completed this year, but don’t expect any new plant announcements. A couple of nuclear plants may actually break ground, but don’t hold your breath. Many more wind turbines will dot the landscape as renewable portfolio standards dictate resource planning, but their peak generation contribution will be small. The dash for gas in the U.S. has begun, again.
-
O&M
Sealing Transformer Oil and SF6 Leaks Quickly and Effectively
Transformers, which are prone to leaking, are an excellent example of where using the right materials and techniques can quickly reduce cleanup costs and potential environmental damage from a fluid leak. Transformer leaks are most commonly caused by degrading cork gaskets or holes in the radiator fins or the steel tank. Often these leaks are slow drips, but occasionally a catastrophic leak will occur, spilling hundreds of gallons of mineral oil into the environment and causing the transformer to short-circuit, causing further health and safety concerns. These dangers, coupled with transformers’ isolated locations, make inspection, repair, and maintenance a major challenge.