Nuclear
-
Nuclear
NRC to Start EIS, Revise Waste Confidence Rule for Spent Nuclear Fuel
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) on Thursday directed its staff to develop an environmental impact statement (EIS) and a revised waste confidence decision and rule on the temporary storage of spent nuclear fuel (SNF). Last week’s decision was in response to a June 8 federal court ruling, which said the NRC had erred in deciding that SNF from the nation’s power plants could be stored as long as 60 years after a plant’s operating license expires.
-
Coal
Congressional Briefs: Back from Recess
Congress has returned from its summer break. As the House prepares to vote on its Upton-Stearns "No More Solyndras Act," lawmakers also expect to focus on a bill that could prohibit finalization of any Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) power plant rules that curb greenhouse gas emissions while carbon capture and storage technology is commercially unavailable. House Democrats, meanwhile, called for hearings to examine the impacts of climate change on the nation’s generators.
-
Nuclear
Too Dumb to Meter, Part 4
As the book title Too Dumb to Meter: Follies, Fiascoes, Dead Ends, and Duds on the U.S. Road to Atomic Energy implies, nuclear power has traveled a rough road from its origin as a tightly controlled military program to civilian applications meant to benefit society as a whole. In this POWER exclusive, we present the fourth and fifth chapters, “What Friendly Atom?” and “The Atomic Chimera.”
-
Nuclear
Troubled Fort Calhoun Reactor Restart Delayed Again
Omaha Public Power District (OPPD) has postponed restart of its troubled 478-MW Fort Calhoun nuclear plant for the third time since it was shut down 16 months ago. Restart of the reactor, located 19 miles north of Omaha, Neb., requires regulatory approval, and that is now tentatively anticipated early next year.
-
Nuclear
Exelon Withdraws Early Site Permit Application for Victoria County Reactor
Exelon on Tuesday said it plans to withdraw its Early Site Permit (ESP) application for construction of a new reactor at an 11,500-acre tract of land southeast of Victoria, Texas, saying “low natural gas prices and economic and market conditions . . . have made construction of new merchant nuclear power plants in competitive markets uneconomical now and for the foreseeable future.”
-
Nuclear
On Katrina’s Anniversary, Generators and Regulators Respond to Hurricane Isaac
Hurricane Isaac soaked the Gulf Coast of Louisiana and Mississippi after making landfall Tuesday night with sustained winds of up to 80 mph, leaving thousands without power in five states. On Tuesday, Entergy took its Waterford 3 nuclear plant offline as a precautionary measure.
-
Nuclear
Report: Implementing Federal Dry Storage Program by 2020 Is Nation’s Best Waste Storage Option
Implementation of a new federal nuclear spent fuel–handling program starting in 2020 to remove 6,000 metric tons of uranium (MTU) per year for 10 years and 3,000 MTU per year thereafter could allow for full decommissioning of U.S. sites awaiting fuel removal. It would also enable retirement of all private Independent Spent Fuel Storage Installations by 2030, and achieve approximately a 10% reduction in average wet pool density, a new study from consulting firm The Brattle Group suggests.
-
Nuclear
Warm Water, Repairs, and a “Dropped” Control Rod Separately Prompt Reactor Shutdowns
As warmer-than-average waters in Connecticut’s Long Island Sound last week prompted Dominion to shut down one unit at its Millstone Nuclear Plant, an ammonia release caused an evacuation of part of Tennessee Valley Authority’s Watts Bar Unit 1, and Constellation Energy shut down of its Calvert Cliffs Unit 1 reactor after a control rod unexpectedly dropped into the reactor’s core. Then, on Tuesday, Xcel Energy shut down its Monticello Nuclear Generating Plant and Unit 1 of its Prairie Island Nuclear Generating Plant for repairs.
-
Nuclear
UPDATED: NRC Freezes Final License Decisions, Court Prolongs Yucca Mountain Saga
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) on Tuesday put a hold on all final licensing decisions—include those for 19 construction and operating licenses (COLs), 12 license renewals, and one operating license—until the federal body can hash out how it will deal with spent nuclear fuel. The order comes on the heels of an Aug. 3 federal court ruling that puts off a decision on whether to force the NRC to act on the Yucca Mountain permanent nuclear waste repository’s long-pending license application.
-
Nuclear
A Bumpy Road for Nukes
Washington, D.C., 6 August 2012 — It’s been a rough road for nuclear advocates in the U.S. of late, although nothing seems to dent the Pollyanna armor of the nuclear crowd, always appearing to believe a revival is just over the horizon and headed into view. Here are a few fraught developments for the nuclear […]
-
Nuclear
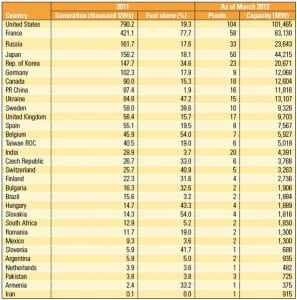
2011 Nuclear Industry Scorecard
The world nuclear industry experienced few substantial changes in performance metrics for 2011—beyond Japan, that is. In the aftermath of Fukushima, the once–world leading Japanese nuclear industry fell to the bottom of the rankings, perhaps for good.
-
Nuclear
Too Dumb to Meter, Part 3
As the book title Too Dumb to Meter: Follies, Fiascoes, Dead Ends, and Duds on the U.S. Road to Atomic Energy implies, nuclear power has traveled a rough road. In this POWER exclusive, we present the third chapter, “Micro-Mismanagement by Committee.” During the frenzy to manage atomic power after World War II, Congress created an executive branch agency that threatened to be too independent, too powerful, and too isolated from the rest of government. Compounding their errors, perhaps in recognition of what they had created, the solons also developed a way to insert their own power into the action. This proved to be a major mistake—blurring the lines between executive and legislative authority—causing no end of problems for the nation’s nascent atomic energy venture.
-
Nuclear
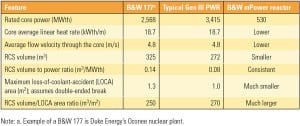
Small Is the New Big: The B&W Small Modular Reactor
Small reactors are big news, particularly the 180-MWe Generation III++ Babcock & Wilcox mPower small modular reactor (SMR). This SMR has all the features of its larger cousins, but the entire reactor and nuclear steam supply system are incorporated into one reactor vessel, all about the size of single full-size pressurized water reactor steam generator. Expect the first mPower—and probably the first SMR—to enter service before 2022.
-
Nuclear
EIA: U.S. Nuclear Uprates Since 1977 Equal Construction of Six New Nuclear Plants
Since 1977, more than 6,500-MW of nuclear uprates and been approved and many implemented in the U.S.—equivalent to the construction of six new nuclear power plants, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) said in an update on Wednesday.
-
Nuclear
SCE: Most Tube Wear at San Onofre “Not Unusual”
Most steam generator tube wear or tube wall thinning at Southern California Edison’s (SCE’s) two-reactor San Onofre Generating Station (SONGS) was less than 20%—far below the 35% wall-thinning limit that would require the tubes to be plugged, data released last week by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission shows. Much of the wear was not "unusual," SCE said in a statement.
-
Nuclear
DOE Announces $13 M in Nuclear Innovation Awards
The Department of Energy (DOE) on Tuesday announced nearly $13 million in nuclear energy innovation awards. The awards include $10.9 million to 13 projects to solve common challenges, including improving reactor safety, performance and cost competitiveness and $1.6 million in three university-led education projects.
-
Nuclear
Court Increases Spent Nuclear Fuel Storage Award to Kansas Plant Owners
Owners of the Wolf Creek Nuclear Power Plant in Kansas are entitled to $12.6 million in damages stemming from the federal government’s partial breach of a contract for disposal of spent nuclear fuel, $2 million more than previously awarded, a federal court ruled last week.
-
Nuclear
Small Modular Reactors Vie for DOE Funding
Within the two months since the Department of Energy (DOE) flourished $452 million in cost-shared federal funding to support engineering, design certification, and licensing from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) for up to two small modular reactor (SMR) designs over five years, four developers of reactors under 300 MW have submitted applications: Westinghouse, Babcock & […]
-
Coal
Power in India: Opportunities and Challenges in a Fast-Growing Market
India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth. India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth.
-
Coal
Clean Air, Dirty Water
Efforts by power producers to meet clean air rules mean that wastewater effluent streams now face revised EPA regulations. A skirmish involving a New Hampshire power plant could set the tone for the next battle over regulations.
-
Nuclear
Fukushima Disaster Continues to Cloud Nuclear Outlook
With new reactors finally under construction, this should be an optimistic time for nuclear power in the U.S. But cheap natural gas, rising construction costs, and the Fukushima accident’s lingering pall have darkened the mood.
-
Gas
Switzerland Contemplates Filling Future Nuclear Energy Gap
A model of Switzerland’s energy future to 2050 that abides with the country’s post-Fukushima decision not to build any new nuclear power plants suggests the phase-out could cost nearly $33 billion.
-
History
Japan Scrambles to Revamp Its Electricity Sector
The March 2011 Japanese earthquake and tsunami that destroyed a number of Japanese power plants—most notably, four nuclear units—hit quickly. Almost as speedy were calls to take all other nuclear units out of service for safety reviews. What will take much longer is developing a new, sustainable energy plan to fill the generation gap left by a potential total lack of nuclear power.
-
Nuclear
Too Dumb to Meter, Part 2
As the book title Too Dumb to Meter: Follies, Fiascoes, Dead Ends, and Duds on the U.S. Road to Atomic Energy implies, nuclear power has traveled a rough road. In this POWER exclusive, we present the second chapter, “Manhattan Transfer,” which covers the open fight for control of the development of nuclear power between the newly created Atomic Energy Commission and the military services, with the politicians playing both sides against each other.
-
Nuclear
Japan’s Nuclear Infrastructure
This overview of Japan’s nuclear fleet is a web supplement to the June 2012 feature “Japan Scrambles to Revamp Its Electricity Sector.” For a list of major Japanese generating companies, see Figure 1 in that article.
-
Nuclear
Vogtle Gets Green Light
In February 2012, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission approved two combined construction and operating licenses for Southern Nuclear’s Plant Vogtle Units 3 and 4 in Georgia. They were the first licenses ever approved for a U.S. nuclear plant using the one-step licensing process and the first allowing construction in more than three decades. Now the real work begins.
-
Coal
Europe: More Coal, Then Less
Europe’s continuing drive toward sustainable energy does not rule out a new generation of coal power plants to replace those scheduled to close by 2015.
-
Nuclear
Too Dumb to Meter: Follies, Fiascoes, Dead Ends, and Duds on the U.S. Road to Atomic Energy
The commercial development of nuclear power began immediately after the Second World War ended and the Manhattan Project secrets were released to the public. As the headline—also the title of a new book—implies, the development path was not always straight or even clearly marked. In this POWER exclusive, the first chapter of Too Dumb to Meter begins a serial presentation of the book.
-
Nuclear
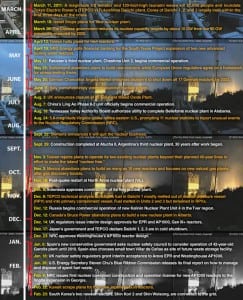
THE BIG PICTURE: Nuclear Aftershocks
In the year following the Fukushima accident in Japan, the nuclear sector has seen several setbacks (text in orange) as well as major milestones (white).
-
Nuclear
Less-Familiar Generation III+ Reactors Make Inroads
Following key regulatory approvals in the UK and U.S. of Westinghouse’s AP1000 and AREVA’s EPR Generation III+ reactor designs, France’s nuclear safety authority in February determined that the little-known ATMEA 1 reactor design met international safety criteria for Generation III+ reactors. The reactor is a 1,100-MW pressurized water reactor (PWR) developed and marketed by ATMEA, a 2007-created joint venture between France’s AREVA and Japan’s Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI).