Instrumentation & Controls
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Cation conductivity monitoring: A reality check
The ability to detect contaminated feedwater or steam before it can corrode the internals of a turbine or HRSG and cause a forced outage is worth millions. One knock against cation conductivity monitoring—still the most common technique for the early detection of contamination—is the difficulty of interpreting conductivity readings when the plant’s makeup contains significant levels of organics or CO2. Here are the pros and cons of cation conductivity monitoriting and some alternative monitoring methods.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
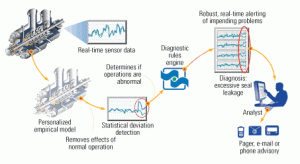
Making PM systems sweat the small stuff
Modern predictive maintenance systems can monitor the health of most plant equipment. By sorting through the wealth of information those systems deliver, operators can discern important trends, including the early signs of a system or component failure.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
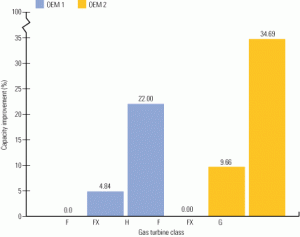
Turbine technology maturity: A shifting paradigm
Selecting the right turbine(s) for a specific power project is a complex process that poses two challenges. One is understanding which field experience cited by suppliers represents proven technology; the other is evaluating whether a turbine upgrade represents an evolutionary change or a revolutionary transformation that warrants further study before deploying it in the field. Here‘s how a leading EPC contractor makes technology-neutral equipment selection decisions on behalf of its customers.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
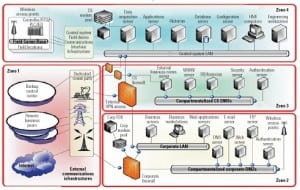
Time to get serious about security
Managing ongoing threats to power plants’ digital, telecommunications, monitoring, control, and automation systems is no longer just a good idea. It’s an essential element of superior plant operations and now a regulatory requirement as well, thanks to new critical infrastructure protection standards recently approved by FERC.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Wireless technologies connect two LCRA plants
Lower Colorado River Authority recently put two separate plants at its Lost Pines Power Park under one functional management system. The project has already deployed a layered wireless infrastructure that allows the two plants to communicate at a fraction of the cost of a wired solution while providing a platform for optimizing work processes and reducing operating costs. What’s not to like?
-
Coal
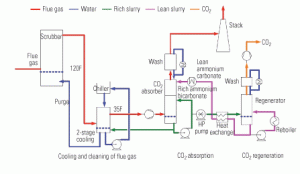
Alstom’s chilled ammonia CO2-capture process advances toward commercialization
Carbon dioxide emissions aren’t yet regulated by the EPA, but it’s likely they will be soon. There are many technically feasible, but as-yet-undemonstrated ways to reduce the considerable carbon footprint of any coal-fired plant, whether it uses conventional or unconventional technology. One promising approach to removing CO2 from a plant’s flue gas uses chilled ammonium bicarbonate to drive the separation process.
-
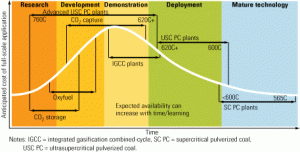
Coal
Accelerating the deployment of cleaner coal plants
The dearth of commercial operating experience for advanced coal-fired facilities is forcing their early adopters and builders to use long development cycles and pay high costs for unique engineering design studies. A broad-based industry collaborative effort fostered by EPRI to address this issue is beginning to show results.
-
O&M
The case for cathodic protection
All fossil fuels carry some risk with their reward of an energy density that’s sufficient for producing electricity economically. For coal and natural gas, that threat is a fire or explosion. However, the risk of an explosion isn’t limited to gas-fired plants. Gas poses a threat to any plant that uses the fuel, even in small quantities for heating. Here’s an overview of what you should be doing to keep gas pipelines from corroding and exploding.
-
Distributed Energy
Aggregated backup generators help support San Diego grid
Last year, San Diego Gas & Electric tapped Boston-based EnerNOC Inc. to aggregate 25 MW of backup generators throughout SDG&E’s service area to relieve the grid when it’s stressed by peak demand for electricity. By combining stringent environmental controls with field-proven expertise managing distributed assets, EnerNOC has helped to improve grid stability in Southern California.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (January 2008)
Single-window control of CHP plant’s energy converters / Safety stuffers entertain as they inform / Doubling up for a heavy load