Gas
-
Gas
Gas Turbine Makers Gear to Flexibility Needs with New Models
Competition among gas turbine makers heated up this September as Alstom unveiled its upgraded GT24 gas turbine and corresponding 60 Hz KA24 combined cycle power plant, while Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) introduced the M701F5 gas turbine—a 50 Hz F-class gas turbine upgrade. An Upgraded GT24 Alstom’s upgraded product launches came on the heels of its […]
-
Gas
NorthWestern Energy Builds a Regulating Reserve Plant
Stable grid operation is challenging, especially when intermittent and unpredictable renewable generation is added to the generation mix. For NorthWestern Energy, the best solution was adding fast-acting gas-fired generation to its Montana electricity grid to meet required reliability standards while replacing expensive third-party contracts for ancillary services.
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.
-
Gas
Siemens Releases “Shaping Power” Option for Renewables Integration
The need for flexible power generation has increased drastically over the past few years, particularly when integrating renewables. Another driver is seasonal peaks in demand that have become more severe as global drought conditions have reduced hydropower production. One option for addressing this need is the Siemens Energy SGT6-5000F with Shaping Power. It offers the familiar gas turbine reoptimized for increased output and higher efficiency during hot weather and for improved operating flexibility at part-load conditions.
-
Gas
GE Develops FlexEfficiency 50 for Increased Operational Flexibility
The newest member of the 60% thermal efficiency combined cycle club is GE Energy’s FlexEfficiency 50. In an era when flexible grid operation is growing in importance, this 50 Hz, single-shaft combined cycle also holds its design point efficiency down to 87% load and features turndown to 40% of rated load.
-
Gas
Blackout Leaves Southwest in the Dark
A large swath of Southern California, parts of Arizona, and Northern Baja Mexico was blacked out on Sept. 8—leaving seven million people in the dark—after an Arizona utility worker fixing faulty equipment near Yuma reportedly tripped the 500-kV North Gila–Imperial Valley transmission line, causing the outage. The blackout prompted two units at the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station to go offline, stranded many people in elevators and trains, shut down airports, cut air conditioning on a day well above 90F, and caused damages of $97 million to $118 million, according to early estimates from the National University System’s Institute for Policy Research.
-
Gas
Nordic Nations Provide Clean Energy Leadership
In the past few years, nuclear concerns, rising oil prices, and a growing understanding of our environmental impact has given energy issues a higher profile worldwide. In this report on the Continental Nordic countries, we look at the efforts being made in much of the Nordic region to secure a sustainable energy supply for the future and at the extent to which the innovative solutions of these countries can be exported around the globe.
-
Gas
Global Gas Glut: An Update
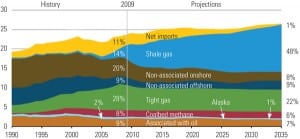
In our September article about the global profusion of natural gas, we based a portion of our discussion on the latest, vastly increased natural gas reserve estimates reported by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Since our article was published, the EIA has adjusted its estimates downward. We want you to be aware of those lower recoverable reserve estimates. We also want you to know that the conclusions reached in that article do not change with the new estimates of natural gas reserves.
-
Gas
New Peaking Plant to Balance California’s Renewables
As utilities in California are scrambling to meet the state’s 33% renewable mandate by 2020, a 49.6-MW peaking plant in Modesto, Calif., built by Finnish firm Wärtsilä for the Modesto Irrigation District, has been commissioned to provide flexible, fast-start peaking generation to balance the state’s increase in intermittent renewable generation (Figure 4). 4. Flexible peaking. […]
-
Gas
Kuwait Starts First Turbines of 2,000-MW Gas Plant
Kuwait put online the first 1,400 MW of its massive 2,000-MW combined cycle gas turbine Sabiya facility in June to mitigate looming power shortages it faces each summer. The plant—Kuwait’s largest power plant and one of the largest in the Gulf region—is now operating six GE 9FA gas turbines; the remaining 600 MW are expected […]
-
Gas
Global Gas Glut
Marcellus Shale gas has increased recoverable natural gas reserves in the U.S. by about a third over estimates prepared a few years ago. Europe is also exploring shale gas as an alternative to problematic Russian gas supplies and low proven natural gas reserves. POWER contributors in the U.S. and UK examine the comparative economic value, public acceptance, and political implications of these massive shale gas reserves.
-
Coal
Best Practices for Natural Gas Line Cleaning
As barriers to new coal-fired generation expand and enthusiasm for nuclear plants wanes, the commissioning of natural gas–fired plants promises to increase. However, gas plants pose hazards, too. An explosion last year that was caused by unsafe use of natural gas to blow residue from a gas pipeline during commissioning of a gas-fired power plant has focused regulator and industry attention on finding safer alternatives for this task. Fluor shares its gas pipeline cleaning best practices.
-
Gas
Who Pays for Firming Up Variable Energy Resources?
The major economic hurdle for renewable power generation technologies continues to be substantial installation costs. But another cost is associated with continuous load-balancing, made possible by backstopping that variable generation with dispatchable generators that typically consume expensive fossil fuels. Bottom line: Who pays for the capacity firming or backstopping resources?
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: Lights Out
Heat waves, droughts, and other weather and climate phenomena; economic woes; aging or inadequate infrastructure; fuel shortages. These are some of the most obvious causes that have led to record peaks in power demand or sudden drops in available capacity. The results have been sometimes debilitating load-shedding, brownouts, and blackouts around the globe this summer (and, in some cases, for much longer). Here’s an overview of which countries are affected by which difficulties. For a more detailed look at the extent of shortages and what’s causing them, visit Web Exclusives at https://www.powermag.com
-
Coal
Explosion Devastates Major Cypriot Power Plant
A brush fire that spread and detonated explosives stored at the Evangelos Florakis naval base in Mari on the southern coast of Cyprus on July 11 killed 13 people, injured 62 others, and severely damaged the Vassilikos Power Station—an oil- and gas-fired plant that supplied almost 60% of the island nation’s power. Cyprus, which was once considered an “economic miracle,” has been battling crippling power shortages that have beleaguered its financial and tourism sectors since the blast and left it on the verge of economic collapse.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Adapazari Power Plant, Adapazari, Sakarya Province, Turkey
In 2010, the 2,310-MW Adapazari Power Plant achieved 99.8% availability, which is nearly 7% higher than the industry average and a global record in F-class gas turbine technology. The new turbine upgrade is helping ENKA Power bolster Turkey’s evolving economy by improving its energy sector’s efficiency and productivity.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Arvah B. Hopkins Generating Station, Unit 2, Tallahassee, Florida
Known for its progressive, pro-sustainability policies, the City of Tallahassee recently repowered a 30-year-old conventional steam plant unit, turning it into a new 300-MW facility. The utility redesigned the Arvah B. Hopkins Generating Station, Unit 2 as a 1 × 1 combined cycle plant in order to improve efficiency, switched the primary fuel from oil to natural gas, and thereby reduced fuel costs and emissions. The plant’s flexible design even will enable expansion to a 2 × 1 configuration when additional capacity is needed in the future.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Astoria II Combined Cycle Plant, Queens, New York
Managing construction of the 550-MW Astoria II Combined Cycle Plant in the midst of Queens, a densely packed New York City borough, required extensive off-site modular construction and a high level of logistical organization. Now the new Astoria II plant is operating successfully in conjunction with the Astoria Energy I plant as the largest natural gas–fired power plant in the Big Apple.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Emirates Aluminum Smelter Complex (EMAL), Al-Taweelah, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
The new 2,100-MW Phase 1 EMAL combined cycle power plant provides dedicated power with a high level of reliability to the Emirates Aluminum Smelter Complex, which is designed to be the world’s largest aluminum smelter upon completion. Located on the Persian Gulf, the gas-fired combined cycle plant uses seawater cooling towers to eliminate thermal stress on local marine life.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Irsching 4 Combined Cycle Power Plant, Irsching, Bavaria, Germany
The Irsching 4 Combined Cycle Power Plant has set a new world record in power plant efficiency with its new SGT5-8000H gas turbine. With an output of more than 578 MW and efficiency of 60.75% (net) achieved at a world record test run in May 2011, the plant demonstrates that climate protection, low-cost power generation, and flexible operation using fossil fuels can be attained simultaneously through technical advances. Due to its high efficiency, the gas-fired plant uses significantly less fuel and produces lower carbon dioxide emissions than traditional combined cycle plants.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Montoir-de-Bretagne Combined Cycle Plant, Montoir-de-Bretagne, France
The 435-MW Montoir-de-Bretagne gas-fired power plant is ramping up Gallic generation in the Loire-Atlantique region of western France. The plant’s innovative natural gas combined cycle technology offers high efficiency and low emissions.
-
Gas
Alstom Launches Upgraded GT26
Just as GE Energy, Siemens, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) in May announced gas combustion technology developments—each seeking to push the 60% barrier with new gas turbine designs—Alstom has quietly been upgrading its KA26 combined cycle power plant. (See the July 2011 “Global Monitor” for more information on the GE, Siemens, and MHI turbines.) The firm says that the next generation of the 500-MW power plant, based on the advanced class GT26 gas turbine, features “achievable” efficiencies of over 61%, increased flexibility, and more than 350 MW, which can be delivered in less than 15 minutes to help integrate renewable energy sources (Figure 3).
-
Gas
E.ON Commissions 433-MW Hungary CCGT
Two years after it laid the foundation stone, Germany’s E.ON on June 27 opened Hungary’s most efficient combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) power plant (Figure 7). The €400 million ($573 million) plant in Gönyü has a capacity of 433 MW and an efficiency of over 59%, E.ON claims. Siemens supplied the main components: an SGT5-4000F gas turbine, an SST5-5000 steam turbine, an SGEN 5-3000W generator, and the entire electrical and instrument and control equipment. The natural gas–fired power plant is of single-shaft design with the main components arranged in a single driveline.
-
O&M
Marmaduke Award: CFE Extends CTG Universidad Unit 2’s Life with Conversion to Synchronous Condenser
CTG Universidad is a two-unit combustion turbine plant commissioned in late 1970 by the Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) on the north side of Monterrey, Mexico’s third-largest city and an important industrial center. By the 1990s, the two 14-MW turbines were obsolete, used sparingly, and slated for demolition in 2010. However, by 2002, portions of Monterrey began experiencing power restrictions caused by a lack of sufficient reactive power production, and that situation presented an opportunity for the plant. By repurposing an old combustion turbine for use as a synchronous condenser to provide local reactive power, CFE significantly reduced local power supply limitations. For that savvy plant repurposing, CFE’s CTG Universidad Unit 2 is the winner of POWER’s 2011 Marmaduke Award for excellence in power plant problem-solving. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence.
-
O&M
Make Your Plant Ready for Cycling Operations
Cycling your steam power plant is inevitable, so now is the time to learn how to minimize equipment damage and assess the true costs of cycling. Whether cycling is required by the grid operator because of renewable integration or other factors, you must be proactive about updating operating processes and upgrade equipment so the transition to cycling operation goes smoothly.
-
O&M
Mitigating the Effects of Flexible Operation on Coal-Fired Power Plants
As coal-fired power plants increasingly operate in cycling modes, many plants are confronting the potential for higher levels of component damage and degraded performance of environmental control equipment. Generators and EPRI are working together to find ways to mitigate the effects of cycling operation and to manage the transition of formerly baseload plants to flexible operation.
-
Gas
Pushing the 60% Efficiency Gas Turbine Barrier
Gas turbine makers GE, Siemens, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) in the last week of May separately profiled unprecedented results from development or testing of three innovative combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) technologies.
-
Coal
Using Fossil-Fueled Generation to Accelerate the Deployment of Renewables
It may seem counterintuitive, but the strategic coupling of simple- and combined- cycle technologies with renewable generation could establish the conditions necessary for adding more renewable megawatts to transmission grids around the world.
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.