Gas
-
Coal
Woods and power company CEOs agree: “The state of the industry is cautious”
It is rare indeed to witness, at an otherwise staid industry forum, the public rebuke of the country’s most prominent supplier to the electric power industry. But at the Keynote session and Power Industry CEO Roundtable of the 2008 ELECTRIC POWER Conference & Exhibition in Baltimore this May, Milton Lee, general manager and CEO of […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (June 2008)
Artificial photosynthesis for solar power? / Poultry litter to fuel 55-MW N.C. plan / First fuel cell-powered plane takes flight / First HTS transmission cable energized / PTC powers wind power industry / Renewing Greensburg / GAO deems coal-to-gas switch impractical / Assessing the Congo River’s power potential / POWER digest / Corrections
-
Coal
Global Monitor (April 2008)
Tenaska proposes first new coal-fired plant with carbon capture/ Concerns raised over growth of China’s CO2 emissions/ Sandia, Stirling Energy Systems set new world record/ Indonesia orders first Wärtsilä Gas Cubes/ First wind turbines on Galapagos Islands cut oil imports/ Harnessing waste heat for electricity/ POWER digest/ Correction
-
Gas
Castejon 2: Ready to reign in Spain
The new, 424-MW Castejon 2 combined-cycle plant designed and built by Alstom was recently given its provisional acceptance certificate. Alstom used its “Plant Integrator” approach to fast-track delivery of a plant just like Castejon 1, which averaged 98% availability during its first three years of operation. That kind of performance is crucial to generators operating in the Spanish merchant power market—or any market.
-
O&M
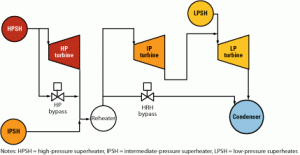
Desuperheating valves take the heat
Hot reheat steam bypass actuators are some of the most critical, yet least understood components in a typical combined-cycle plant. If you’re using pneumatic actuators to stroke your main steam or hot reheat bypass valves in a cascading bypass system, you’re behind the times. Here’s a way to get better control of the bypass process, shorten unit start-up and train blending times, and decrease your plant’s heat rate—all at the same time.
-
O&M
Extend EOH tracking to the entire plant
Predicting combined-cycle system longevity and determining optimal maintenance intervals at the same time is difficult: It requires balancing repair costs against the risk of trying to squeeze that last bit of life out of some component before it fails. One solution to the problem is to extend coverage of an equivalent operating hours (EOH) preventive management program for turbines to the entire plant.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (March 2008)
DOE scraps FutureGen / U.S. nuclear plants have record year / Westinghouse wins TVA contract / UniStar Nuclear to file for COL / AEP ranks second in U.S. construction / China moving to the driver’s seat / New solar cycle poses risks / Dutch favor power from natural gas / POWER digest / Corrections
-
Gas
How to make a power plant a welcome neighbor
Developing power projects has become less a technical challenge and more an exercise in developing good relationships among all the stakeholders. If a community understands the need for a new plant and is involved in its development process, the odds of a successful project increase.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (February 2008)
FutureGen picks Mattoon, Ill./Duke applies for first greenfield COL/PPL to work with UniStar on another COL
/Areva seeks NRC certification of its reactor/Mitsubishi also in line at the NRC/PV project shines in Nevada/SunEdison commissions Colorado PV plant/Big concentrating solar plant proposed/Super Boiler celebrates first anniversary/Small fuel cell uses JP-8 jet fuel/POWER digest -
O&M
The case for cathodic protection
All fossil fuels carry some risk with their reward of an energy density that’s sufficient for producing electricity economically. For coal and natural gas, that threat is a fire or explosion. However, the risk of an explosion isn’t limited to gas-fired plants. Gas poses a threat to any plant that uses the fuel, even in small quantities for heating. Here’s an overview of what you should be doing to keep gas pipelines from corroding and exploding.