Environmental
-
Environmental
The Effect of Shale Gas on Power Generation in New England
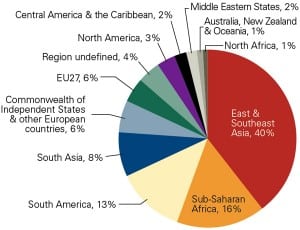
Generators in New England were burned in the 2000s when a fleet of new gas turbine plants couldn’t compete because of high fuel prices. But what goes around comes around, and these same plants are now pushing out oil and coal thanks to cheap shale gas and favorable regulations. -
Legal & Regulatory
With the Gas, the Flow of Fracking Litigation Continues
Few industrial innovations are free of litigation, and fracking is no exception. In this update from last year’s review of litigation trends, favorable early results for explorers and developers suggest cautious optimism may be in order for the natural gas industry. -
Environmental
Air Quality Impacts from Natural Gas Extraction and Combustion
EPRI performed a review of air quality issues related to natural gas extraction and combustion in 2011–2012. This review focused on both traditional pollutants (such as particulate matter and volatile organic compounds) and emerging air pollutants (such as ultrafine particle number) that are being considered in air quality management processes. This article summarizes the major topics and conclusions from this review. -
Coal
Nations Agree to Legally Binding Instrument to Curb World’s Mercury Emissions
Mercury emissions from power plants in 137 United Nations member countries could be subject to strict controls and reductions if an international treaty is signed by participating nations this October.
-
Coal
Despite Pollution-Curbing Efforts, Dense Smog Covers Wide Swath of China
Four bouts of dense smog described as the worst air pollution in recent memory enveloped more than half of China in January, from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei triangle in the north of the country to Nanjing in the south, via the central city of Wuhan.
-
Coal
Techno-Economic Considerations When Using Low-Grade Coal for Power Generation
The use of low-grade coal is becoming synonymous with circulating fluidized bed (CFB) power plants. Although CFB technology may often be a better choice than pulverized coal technology, that is not always the case. Owners and developers need to consider several technical and economic factors before making this decision.
-
Waste to Energy
Expanded Honolulu WTE Plant Delivers Triple Benefits for Oahu
Covanta Energy and the City and County of Honolulu recently completed a $300 million expansion of a 20-year-old waste-to-energy (WTE) facility. The plant is now capable of processing up to 3,000 tons of municipal refuse daily, recycling all the metals, and generating up to 90 MW—enough to supply nearly 10% of Oahu’s electricity.
-
Waste to Energy
Why Aren’t Construction and Demolition Wastes Considered Biomass Fuel?
You may be surprised to learn that even with the increased demand for biomass fuels for power generation, construction and demolition fuel is classified as solid waste, not biomass. Reconsidering this designation is critical as U.S. environmental regulations tighten emission profiles for solid waste combustion units and renewable portfolio standards expand.
-
Gas
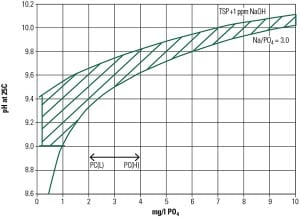
Selecting a Combined Cycle Water Chemistry Program
The lifeblood of the combined cycle plant is its water chemistry program. This is particularly true for plants designed for high pressures and temperatures as well as fast starts and cycling. Even though such plants are increasingly common, no universal chemistry program can be used for all of them.
-
Waste to Energy
Waste Tire Power Generating Facility to Be Shuttered on CAA Violations
A 20-MW facility in Ford Heights, Ill., that burns waste tires to produce power is to be shut down to resolve allegations by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of Clean Air Act violations.