Environmental
-
Coal
EPA, DOJ Settle with Dominion Energy on CAA Violations
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced on Monday that Dominion Energy has agreed to pay a $3.4 million civil penalty and spend approximately $9.8 million on environmental mitigation projects to resolve Clean Air Act (CAA) violations.
-
Coal
EPA Updates MATS for Power Plants
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on March 28 finalized updates to emission limits for new power plants under the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). The rule includes emission limits for mercury, particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), acid gases, and certain individual metals.
-
Environmental
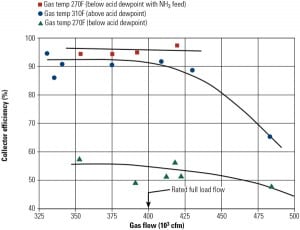
Electrostatic Precipitator Upgrade Opportunities
The results of stack emissions testing conducted at several coal-fired power plants during the past three years have provided useful guidance for plant operators who are required to meet new federal guidelines regarding the release of particulate matter. The data and guidelines presented here will assist those who operate plants with electrostatic precipitators to develop a strategy for filterable particulate emissions control.
-
Environmental
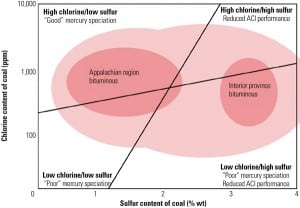
Enhancing Mercury Capture: An Asset-Based Approach
The Mercury and Air Toxics Standards will soon force many coal-fired plants to install mercury-specific emission control equipment. Planners can use particular characteristics of a plant to quickly screen for the best mercury removal technology.
-
Coal
EPA Directs 36 States to Revise SIPs for Emissions During Plant Startup, Shutdown, Malfunction
A rule proposed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) directs 36 states to revise their Clean Air Act State Implementation Plans (SIPs) to eliminate exemptions for excess emissions of air pollutants at power plants during startup, shutdown, or when the plant malfunctions.
-
Environmental
When Dinosaurs Roamed California: The Coming Extinction of Fossil Fuel Use
California’s push to boost its renewable capacity may be doing more than spurring the development of wind and solar. A review of recent data suggests the state’s regulatory schemes have the potential to spell the end of fossil-fuel generation altogether.
-
Coal
EIA: U.S. Power Sector SO2, NOx Emissions Lowest Since 1990
Power plant emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the U.S. declined to their lowest level since 1990, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) said in early March.
-
Environmental
Carbon Capture for Gas Power Appears on the Horizon
You may think of carbon capture and sequestration as a coal industry issue, but two forward-thinking companies are joining forces to make it work for gas.
-
Coal
Four Major EPA Air and Water Rules Forthcoming Through May, Agency Schedule Shows
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates final regulations curbing greenhouse gas (GHG), mercury, and air toxics emissions from new sources could appear in the Federal Register by the end of April. Also forthcoming are final cooling water intake rules and proposed effluent guidelines. The coal ash rule, which has no target date for a final rule, may not be issued this year, the agency said.
-
Coal
Kemper County IGCC Project Update
The integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) plant located in Kemper County, Mississippi, is a 2 x 1 plant that will produce 582 MW at peak and 524 MW fired on syngas, with ammonia, sulfuric acid, and carbon dioxide as by-products. The carbon dioxide will be used for enhanced oil recovery (EOR). Engineering was completed in Q3 2012, and the facility’s commercial operation date is planned for May 2014.