Distributed Energy
-
Coal
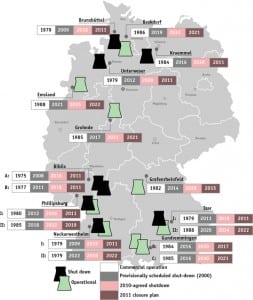
Germany’s Energy Transition Experiment
Germany has chosen to transform its energy system within a few decades—an ambition that has evoked equal admiration and confusion. Has Europe’s largest economy embarked on a rational path to an energy future that will make it the bellwether for global acceptance of renewables, or will the complex array of current challenges encumber its grand transformation?
Tagged in: -
O&M
Emerging Technologies Enable “No Regrets” Energy Strategy
Achieving a balance between affordable and sustainable electricity while improving reliability is a challenge unlike any the electricity sector has faced since its inception. Technology innovations in key areas such as energy efficiency, smart grid, renewable energy resources, hardened transmission systems, and long-term operation of the existing nuclear and fossil fleets are essential to shaping the future of electricity supplies.
-
Solar
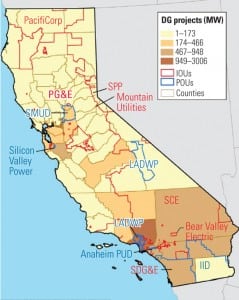
Distributed Generation: California’s Future
Once you synthesize all the elements of the Golden State’s clean energy strategy and extrapolate current trends, it’s easy to see that an impending break with the traditional power generation paradigm is coming, intended or not.
-
Distributed Energy
Is CHP Ready for Prime Time?
Long the redheaded stepchild of North American power generation, combined heat and power (CHP) may finally be poised for a big leap forward.
-
Distributed Energy
UBC Generates Heat, Power, and Buzz with Renewable CHP
Already in the midst of a drive to cut its greenhouse gas emissions, the University of British Columbia didn’t just look to clean energy for its new combined heat and power system. Instead, it decided to combine research with cutting-edge green power.
-
Distributed Energy
Feds and States Join Forces to Push CHP
Though subsidies and incentives for wind and other renewables have grabbed the headlines, federal and state initiatives are quietly building some momentum behind combined heat and power.
-
Distributed Energy
Improving Grid Resiliency After Superstorm Sandy
For the power generation and delivery industry, the lesson of Hurricane Sandy was how fragile much of the grid is. Distributed generation, smart grid technology, and combined heat and power offer cost-effective ways to improve grid resiliency. -
Hydro
Hawaii’s Largest Wind Project Online as State Struggles to Integrate Renewables
On Monday, as First Wind announced its 69-MW Kawailoa Wind Project had gone into commercial operations on Oahu, other news underscored the difficulty the island state faces in trying to substitute renewables for expensive, imported fossil fuels.
-
Wind
Energy Storage Startup Gets $37.3 Million from High-Profile Investors
Berkeley, Calif., startup LightSail Energy, which aims to produce “the world’s cleanest and most economical energy storage systems,” has secured $37.3 million in a Series D round that included three big-name investors: Bill Gates, Vinod Khosla, and Peter Thiel.
-
Distributed Energy
Clear Energy Systems Debuts Smallest-Ever Mobile 1-MW Power System
Bigger isn’t always better, but when you’ve got big power needs in a remote location, your options are often limited. A new mobile gas-fired generator aims to change that, offering both big capacity and a small footprint.