Coal
-
Coal
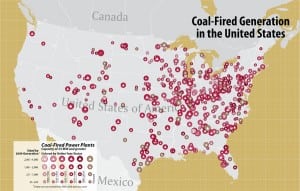
Map of Coal-Fired Generation in the United States
Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed.
-
Coal
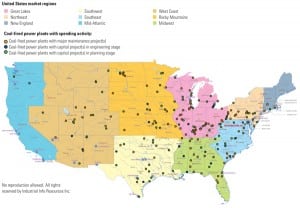
U.S. Coal-Fired Power Development: Down but Not Out
Environmentalists renewed their attacks on coal-fired power development in 2010. At the same time, Congress dithered on cap-and-trade legislation while the Environmental Protection Agency marched forward rules to reduce carbon emissions from coal-fired power plants. Couple the regulatory uncertainty with lean economic times that have flatlined electricity demand growth plus low natural gas prices, and the result is predictable: New coal-fired plant construction is in the doldrums.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Coal Ash Regulation: Playing the Name Game
What’s in a name? Would coal ash labeled as “special” hazardous waste be as easily recycled as that labeled nonhazardous waste?
-
Coal
Xcel Energy Fires Up Solar/Coal Hybrid Demonstration
At the end of June, Xcel Energy fired up a demonstration project that integrates a 4-MW parabolic trough solar technology with an existing 44-MW coal-fired power plant.
-
Coal
Fourth Circuit Scuttles NC Air “Nuisance” Suit
Scuttling a high-profile “public nuisance” lawsuit, a federal appeals court has reversed a lower court ruling that required the Tennessee Valley Authority to accelerate plans to install pollution controls at four TVA coal-fired power plants to reduce the amount of pollution blowing into western North Carolina, saying the lower court decision could lead to other public nuisance suits that would wreak havoc on federal and state regulatory regimes for combating air pollution.
-
Coal
House Members Warn EPA on Coal Ash
Saying they have “grave concerns” about the agency’s two-option proposal to regulate coal combustion ash, 31 members of the House Energy and Commerce Committee have urged the Environmental Protection Agency to continue to regulate coal ash as a non-hazardous waste, saying an EPA proposal to designate it as a “special” hazardous waste eligible for reuse would lead to costly and unnecessary management and disposal requirements.
-
Coal
AEP Blasts EPA Transport Rule; PSEG Supports It
An Environmental Protection Agency proposal to tighten sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides limits in 31 states and the District of Columbia to address transported air pollution fails to give utilities and state air regulators sufficient time to develop rules and install controls, according to American Electric Power Co. Officials from the EPA and New Jersey-based Public Service Enterprise Group said utilities already had begun making investments to cut emissions and they believed the agency’s compliance schedule could be met.
-
O&M
Wind Integration: Does It Reduce Pollution and Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
Many claim that wind generation is beneficial because it reduces pollution emissions and does not emit carbon dioxide. This isn’t necessarily the case. When wind is introduced into a generation system that uses carbon technologies to back up the wind, it actually reduces the energy efficiency of the carbon technologies.
-
O&M
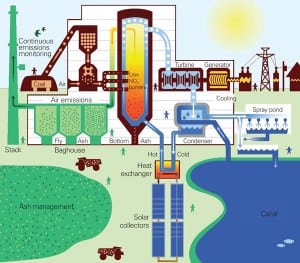
Power 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power Plants, Part III
Every power engineer must have a firm grasp of the rudiments of how fuel is processed to produce electricity in a power generation facility. With this article, we conclude our three-part series on the essentials of recovering heat from flue gas to dry and process coal, with the goal of improving overall plant operating efficiency.
-
O&M
Improve Furnace Reducing Atmosphere Using Fuel/Air Ratio Control
Progress Energy has incorporated online combustion optimization/tuning to eliminate furnace reducing atmospheres at its Asheville Plant. The optimization project utilized individual burner airflow measurement and continuous burner coal flow measurement to adjust burner air/fuel ratios. The result: significantly improved boiler combustion.