-
News
A breakthrough in hydroturbine design
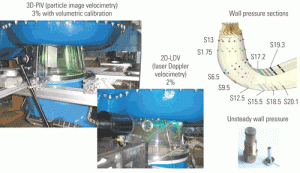
One of the distinguishing characteristics of deregulated power markets is variable demand. The ability to operate efficiently at partial loads can determine whether a plant is profitable or not. This need creates special challenges for hydroelectric turbines, because at partial loads they often exhibit strong swirl in the draft tube at the outlet of the […]
-
-
Legal & Regulatory
Get involved!
The Combined Cycle Users’ Group (CCUG) was formed to address issues of importance to users, particularly the interactions among the major systems of combined-cycle power plants: the steam turbine, combustion turbine(s), and heat-recovery steam generator. The added value of becoming a CCUG member is the opportunity to interact with other operators, as well as designers, […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Hybrid generation markets endanger competition and innovation
Competition in power generation fosters technical innovation, cleaner power plants, and downward pressure on prices. Before the 1980s, such competition was almost nonexistent: vertically integrated utilities built and operated the vast majority of U.S. plants with oversight by state regulators. The Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 and the Energy Policy Act of 1992 […]
-
Gas
Designing HRSGs for cycling
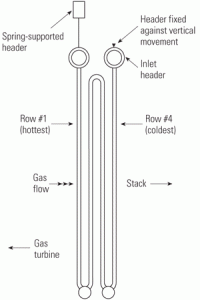
With U.S. combined-cycle plants increasingly being cycled—rather than being run continuously, as they were designed to do—owner/operators worry that units expected to last two or three decades may survive only a few years without an expensive overhaul. Cycling takes as much of a toll on heat-recovery steam generators as it does on gas turbines. Whether you’re procuring a new HRSG or adapting an existing one for cycling service, robust design features should be what you’re looking for.
-
Coal
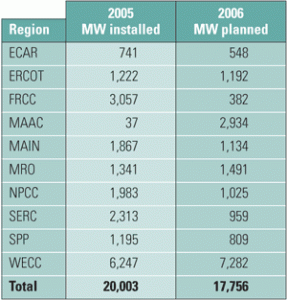
Stressed merchant industry hopes for better days
The U.S. power generation industry is changing at warp speed, via regulatory changes, consolidation, mergers, and sales of assets at yard-sale prices. New players have entered the market and become major players overnight, while several mainstays have gone bankrupt. Though many of the latter blamed high gas prices for their woes, well-diversified merchants enjoyed a record year. Whatever changes are in store for the business of combined-cycle generation, you can be sure that innovations in plant design and O&M such as those described in this special section will keep pace with them.
-
Gas
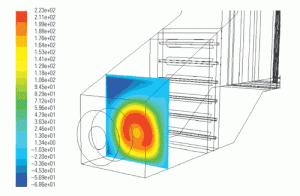
Fluid dynamics of the HRSG gas side
Designers of heat-recovery steam generators are using computational fluid dynamics software as one tool to reveal the invisible forces affecting the flow over, under, around, and through structures such as inlet ducts, distribution grids, and guide vanes.
-
Coal
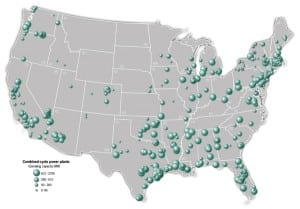
Map: Combined-cycle plants constitute about 20% of U.S. generating capacity
Copyright 2006 Platts, a Division of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. 800-PLATTS-8. Data Source: Platts Energy Advantage www.maps.platts.com
-
Coal
Designing wet duct/stack systems for coal-fired plants
A multitude of variables must be accounted for during the design and development of a wet-stack flue gas desulfurization system. The five-phase process detailed below has proven effective on more than 60 wet-stack system design studies. A basic understanding of these concepts will help inform early design decisions and produce a system amenable to wet operation.
-
Coal
Designing HRSG desuperheaters for performance and reliability
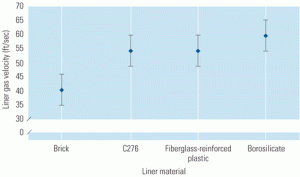
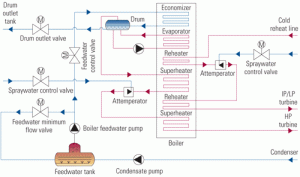
Increased cycling of combined-cycle plants has made precise control of attemperator spray water within heat-recovery steam generators more important if damage to their hardware and piping is to be avoided. Complicating the issue is the industry’s still-limited experience with cycling and the fact that demands on the attemperator and turbine bypass of cycled plants are more stringent than those on baseloaded units.
Search