-
Commentary
Stream Conductivity: It’s Not Just a Mining Issue
Coal mining, and related industries that consume coal, have attracted quite a bit of attention from the federal government as of late. Most of that attention has focused on how to further, or "better," regulate the industry. The EPA is now moving to regulate downstream conductivity of surface mining runoff.
-
O&M
Designing Large Package Boilers
Designing large package boilers rated at over 400,000 lb/h steam production is a challenge because of shipping limitations within the U.S. and Canada.
-
Legal & Regulatory
What Legal & Regulatory Issues Are at the Top of Your Mind?
All of our legal column writers have this issue off (they’ll be back in the March issue), so we are using this opportunity to invite readers to share their legal and regulatory (L&R) concerns.
-
Commentary
EPA Expands Climate Agenda to the Current Fleet of Power Plants and Refineries
On December 23, 2010, one day before the Yuletide season, when members of Congress, the media, and Tea Party activists are least likely to watchdog the federal bureaucracy, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced rulemakings to establish New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) for greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from power plants and refineries. Or maybe "whispered" would be more accurate.
-
Business
The Great Solar Storm of 2012?
The 2009 blockbuster movie 2012 about a global cataclysm combined Hollywood special effects with supposed predictions by Nostradamus; a Mayan calendar that ends on December 21, 2012; and a very rare planetary alignment that supposedly occurs on the same day. Hollywood producers seldom let technical accuracy get in the way of a good story, but suppose, this one time, the story has an element of truth.
-
Water
Readers Write
In the September and October 2010 issues, POWER Contributing Editor David Daniels explored the causes and damage mechanisms of condenser tube leaks (“Taming Condenser Tube Leaks,” Part I and Part II). Dennis J. Schumerth, Valtimet’s director of business development, took issue with several of Daniels’ statements regarding the proper use of titanium condenser tubes. We have given Schumerth the opportunity to express his concerns and for Daniels to reply.
-
O&M
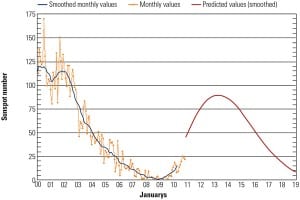
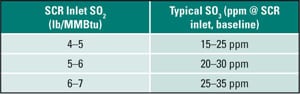
Continuous SO3 Monitoring Can Reduce Sorbent Consumption
An unintended consequence of employing selective catalytic reduction and wet flue gas desulfurization to reduce nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide levels at coal-fired power plants has been unwanted sulfur trioxide (SO3) emissions. Picking the right sorbent in the right amount can eliminate that problem.
-
O&M
Increasing Generation Ramp Rate at Morgantown Generating Station’s Coal-Fired Units
At Morgantown Generating Station, plant personnel used innovative methods to combine model predictive control with distributed control system–based process control algorithms to improve waterwall temperature control and main steam temperature control and to enhance unit ramp rate capability. The previous heat rate and NOx optimization performance gains were retained. Focusing beyond basic loops of feedwater, air, and O2, the project considered issues such as PID controller override configuration and limitations. The techniques used to overcome these challenges improved unit ramp rate capability beyond any previous unit performance.
-
Business
POWER Digest (Feb. 2011)
MHI to Continue Pre-Construction Work for North Anna Unit. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (MHI), through Mitsubishi Nuclear Energy Systems Inc., and Dominion subsidiary Virginia Electric and Power Co. on Dec. 27 said they had reached an agreement to continue pre-construction, engineering, and planning work in preparation for a third unit at Dominion’s North Anna Nuclear […]
-
Nuclear
I&C Update on Plant Vogtle Units 3 and 4
Development of Vogtle Electric Generating Station Units 3 and 4—the first new nuclear power plant units in the U.S. in decades—has generated considerable excitement. The next generation of nuclear plants, represented by these units, includes at least two major improvements: the use of passive safety systems and a reliance on digital control systems. The latter represents a gigantic leap in modernization and a fundamental change in control of the plant.
-
O&M
New Tools for Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Power Plant Equipment Faults
The Electric Power Research Institute has developed a pair of diagnostic tools that combine and integrate features from multiple sources of plant information. The Diagnostic Advisor and the Asset Fault Signature Database will improve diagnostics for and troubleshooting of equipment faults by providing a holistic view of the condition of plant equipment.
-
General
Not Your Father’s Energy Committee
By Kennedy Maize Washington, D.C., January 28, 2011 – The Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee in the 112th Congress won’t be your father’s Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee (and certainly not Lisa Murkowski’s father’s committee). With a slew of newcomers – mostly Republican – and none of them particularly attuned to the way […]
-
News
New Mexico Supreme Court to Governor: Publish State Cap-and-Trade Rules
The New Mexico Supreme Court today ruled unanimously that freshly elected Republican Gov. Susana Martinez violated the state constitution when she halted publication of cap-and-trade rules that were adopted by the state’s Environmental Improvement Board (EIB) last year.
-
News
Allowance Theft Freezes EU Carbon Spot Market
The European Union (EU) on Tuesday said it was waiting for member countries to confirm that minimum-security requirements had been installed in their emissions registries before reactivating its emissions trading scheme (ETS). The European Commission halted spot carbon trading last week for at least seven days after hackers stole emission permits from accounts in the Czech Republic and Austria.
-
News
Beacon Starts Commercial Operation of Flywheel Frequency Regulation Plant
Massachusetts–based Beacon Power Corp. on Monday said it had energized and grid-interconnected the first 8 MW of flywheel energy storage at its 20-MW frequency regulation plant in Stephentown, N.Y., bringing in the first commercial revenue for the company.
-
News
DOE Grants $967M Loan Guarantee to Ariz. Thin-Film PV Project
NRG Energy last week received a $967 million federal loan guarantee for its 290-MW Agua Caliente thin-film photovoltaic (PV) solar project. When the Yuma County, Ariz., project, which began construction in 2010, is complete in 2014, NRG says it will be the largest PV generation facility in the world.
-
News
India Starts Up New Kaiga Nuclear Reactor
The fourth unit of India’s Kaiga Generating Station, a 220-MW indigenous reactor that achieved first criticality on Nov. 27, 2010, was synchronized to the grid last week. The unit now brings India’s nuclear power capacity to 4,780 MW with 20 reactors in operation, state-owned Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) said.
-
News
DOE, NOAA to Collaborate on Renewable Energy Modeling and Forecasting
The U.S. Departments of Energy and Commerce on Thursday signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to collaborate further on renewable energy modeling and weather forecasting to help the renewable sector more effectively use the nation’s resources.
-
News
Report: Amid U.S. Climate Policy Uncertainty, Canada Should Consider Cap-and-Trade
Uncertainty about U.S. climate policy direction means that Canada may need proceed with its own measures to mitigate climate change—including a carbon cap-and-trade system—a government-appointed advisory panel has recommended.
-
News
Obama: Ramp Up Clean Energy—Including Clean Coal and Natural Gas Power
In his State of the Union address on Tuesday evening, President Barack Obama set a new goal for the nation: To obtain 80% of its electricity from “clean energy” by 2035. But his definition of “clean energy” included “nuclear, clean coal, and natural gas” as well as “wind and solar.”
-
News
Court Denies EPA Extension for MACT Boiler Rules
A federal district court judge on Thursday sided with environmental groups in a suit against the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and gave the Obama administration only 30 extra days to issue Maximum Achievable Control Technology (MACT) rules for large and small boilers, and solid waste and sewage sludge incinerators—not a year, as the agency had sought.
-
General
EV’s? Here Come the Hydraulic Hybrids
By Kennedy Maize Washington, D.C., January 24, 2011 — While many of us have fixated on electric approaches to vehicle propulsion, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has been working on another technology that may turn out to be a killer ap for conventional gasoline cars. Earlier this month, with little fanfare or hoopla, Chrysler announced […]
-
News
Federal Settlement Forces NIPSCO Coal Plant Closure, $600 M in Pollution Controls
A settlement over alleged Clean Air violations reached by the Environmental Protection Agency and the Justice Department with Northern Indiana Public Service Co. (NIPSCO) requires the Merrillville, Ind.–based company to shut down a coal plant while investing about $600 million in pollution control technology at the other three plants in its 3,300-MW coal-fired fleet. In related news, Ameren Missouri strongly disputed similar allegations made in a lawsuit over modifications at a 1,200-MW Missouri coal plant.
-
News
Court Allows EPA to Proceed with GHG Regulation in Texas
A federal court last week lifted an emergency stay that had prevented the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from proceeding with a Federal Implementation Plan (FIP) for Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) permitting of greenhouse gas sources in Texas while it considered legal challenges against the agency’s authority. The court’s decision means that EPA-issued regulations can curb greenhouse gas emissions from power plants and other large stationary sources in that state.
-
News
Supercritical Coal Unit Starts Commercial Operation in Wisconsin
The second 615-MW supercritical pulverized coal unit of We Energies’ Oak Creek Power Plant went commercial last week. The first unit—a POWER Top Plant—went into service on Feb. 2, 2010, and Elm Road Unit 2’s turnover to the Wisconsin Electric Power Co. by general contractor Bechtel Power Corp. last Wednesday completed the controversial expansion of the 1,135-MW power plant.
-
News
NRC to Address Containment Sump Issue at U.S. Nuclear Plants
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) last week instructed staff to address a potential problem at nuclear power plants around the U.S. where the containment sump—an emergency long-term cooling water source—could be clogged by debris accumulating after a high-pressure coolant break.
-
News
GAO: Smart Grid Standards Are Incomplete and Unenforceable
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed smart grid cybersecurity guidelines as tasked by Congress, but major gaps still need to be addressed; furthermore, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has failed to develop a coordinated approach for monitoring if and how the standards are being followed by industry, a new report from the Government Accountability Office (GAO) says.
-
News
State Supreme Court to Hear Arguments in N.M. Cap-and-Trade Plan Dispute
In New Mexico, where freshly elected Governor Susana Martinez (R) passed—as one of her first acts upon taking office—an executive order placing a hold on cap-and-trade rules adopted last year by a state agency, the state’s Supreme Court agreed to hear arguments later this month on whether Martinez’s actions were legal.
-
General
China Nuke Dreams: Paper Dragon?
By Kennedy Maize Washington, D.C., January 17, 2011 – With Hu Jintao, China’s president, in Washington this week, it is worth taking a look at that mammoth country’s energy future. More specifically, it is valuable to look at China’s announced ambitious nuclear power agenda and ask whether it can be realized. China at the end […]
-
News
EPA Defers GHG Permitting for Carbon-Emitting Biomass Sources by Three Years
Greenhouse gas (GHG) permitting requirements for carbon dioxide as they apply to biomass-fired and other biogenic sources of power will be deferred three years so that the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) could have enough time to better weigh the issue, the federal agency announced today.
Search