This article explores the role video borescopes play in nuclear plant inspections, emphasizing the value they bring in terms of safety, efficiency, and long-term plant integrity.
Nuclear power plants operate under strict safety protocols to ensure that their critical systems function reliably. A significant part of this reliability is the routine inspections and maintenance of nuclear reactors and associated systems.
Video borescopes have become essential tools in these efforts. They not only streamline the inspection process but also minimize radiation exposure, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Importance of Routine Inspections in Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power generation requires a high level of vigilance to maintain safety. Several key components are visually inspected during routine maintenance. Items regularly examined include:
- Reactor Pressure Vessels (RPVs). The RPVs hold the nuclear fuel and coolant under extreme pressure, making any failure a severe safety risk. Inspections are crucial for identifying corrosion, cracking, or wear in a vessel’s materials or welds.
- Fuel Assemblies. Deformation or cracking of fuel rods can affect reactor power output and cooling efficiency, leading to hazardous conditions.
- Steam Generators. These systems transfer heat from the reactor coolant to produce steam for turbines. Wear, corrosion, or blockages can hinder heat exchange and potentially lead to radioactive contamination in secondary systems.
- Control Rods and Drive Mechanisms. Inspections ensure that the rods, which regulate fission by absorbing neutrons, are free from wear or deformation that could lead to uncontrolled reactions.
- Primary and Secondary Coolant Systems. Leaks or cracks in piping or valves in these systems can lead to overheating and potential core damage.
- Containment Structures. The concrete walls and steel liners that surround reactors prevent radioactive material from escaping. Inspections are critical for maintaining the structural integrity of these barriers.
These inspections are essential for early detection of potential problems, helping prevent catastrophic failures. However, conducting them comes with challenges related to radiation exposure, access to confined spaces, and time constraints. This is where video borescopes are crucial, offering solutions to many of these issues.
Radiation Exposure and Safety Standards
Radiation exposure poses a significant health risk to personnel working in nuclear facilities, which is why regulatory bodies such as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) impose strict limits on acceptable doses. The NRC sets the annual effective dose limit for nuclear plant workers at 5 rem (0.05 sieverts), which is significantly higher than the exposure a person typically receives from natural background radiation but is carefully monitored to ensure worker safety.
The ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) Principle is the guiding framework for radiation safety. This principle mandates that exposure should be reduced to the lowest possible level, regardless of whether the expected exposure is within given limits. In practice, this means using advanced technology, such as remote video borescopes, to conduct inspections from safe distances, reducing direct exposure to hazardous areas.
The Role of Video Borescopes in Overcoming Inspection Challenges
Video borescopes provide a safe and efficient solution for inspecting components in high-radiation environments. These advanced tools are capable of capturing high-resolution images and videos from confined spaces, allowing inspectors to monitor and assess reactor components remotely. The following are some of the benefits of utilizing video borescopes.
Minimizes Radiation Exposure. One of the most significant advantages of video borescopes is their ability to perform remote visual inspections (RVIs). This technology allows personnel to inspect critical reactor components, such as the RPV or steam generators, without having to enter high-radiation zones. Video borescopes with long insertion tubes can navigate reactor internals, minimizing the need for human entry and reducing radiation doses in compliance with NRC guidelines.
For instance, video borescopes like the IPLEX GAir video borescope feature insertion tubes up to 30 meters long, allowing workers to conduct inspections from a safe distance. Additionally, with wireless capabilities, these devices can be operated remotely, enabling real-time visual monitoring without bringing personnel into close contact with radiation sources.
Allows Easier Admission to Confined Spaces. Nuclear reactors are complex environments with many areas that are difficult to reach manually. Components such as fuel assemblies, coolant system pipes, and control rod housings are often located in confined spaces. Video borescopes with flexible insertion tubes can easily navigate these areas, providing a thorough visual assessment without the need for disassembling large structures.
For example, the IPLEX GAir’s flexible tube can maneuver through tight openings and deliver detailed visual data on hard-to-reach reactor components, reducing the need for invasive inspection methods. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of human error and equipment damage during disassembly.
Permits Access to High-Temperature and High-Pressure Areas. Even during shutdowns, some reactor systems retain high temperatures and pressures, making direct inspection dangerous. Borescopes are designed to withstand these extreme conditions, allowing inspections to proceed with less waiting for cooldown periods. This accelerates maintenance processes, ensuring that reactors can return to operation quickly.
Accommodates Time Constraints. Reactor shutdowns for maintenance are tightly scheduled to minimize operational downtime. Video borescopes help streamline inspections, allowing technicians to quickly assess critical components. High-resolution imaging and the ability to record video for post-inspection review make borescopes an invaluable tool for ensuring thorough yet efficient inspections.
Advanced Features of the IPLEX GAir Video Borescope
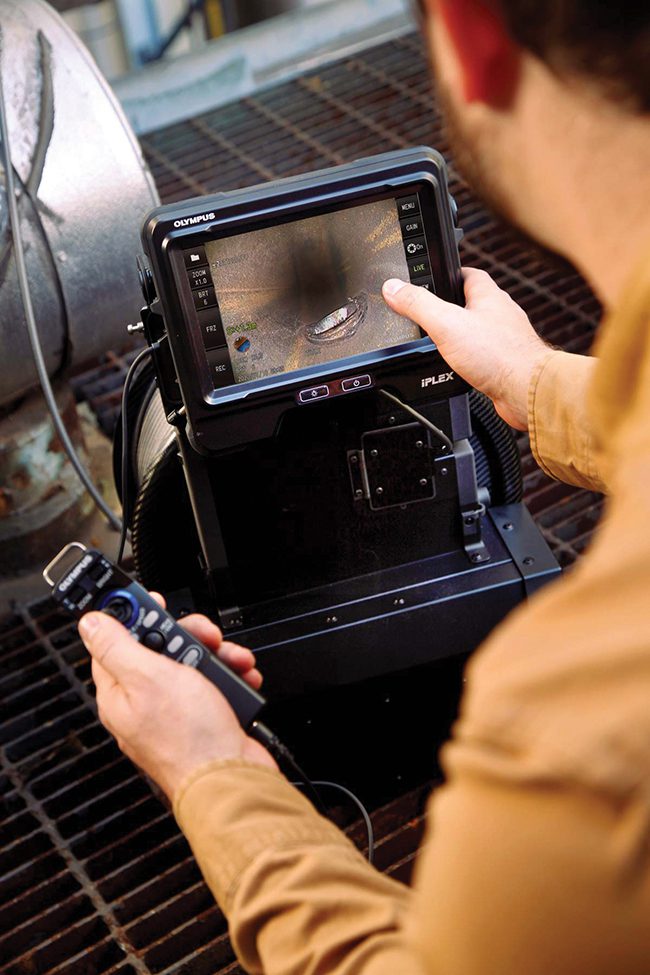 |
|
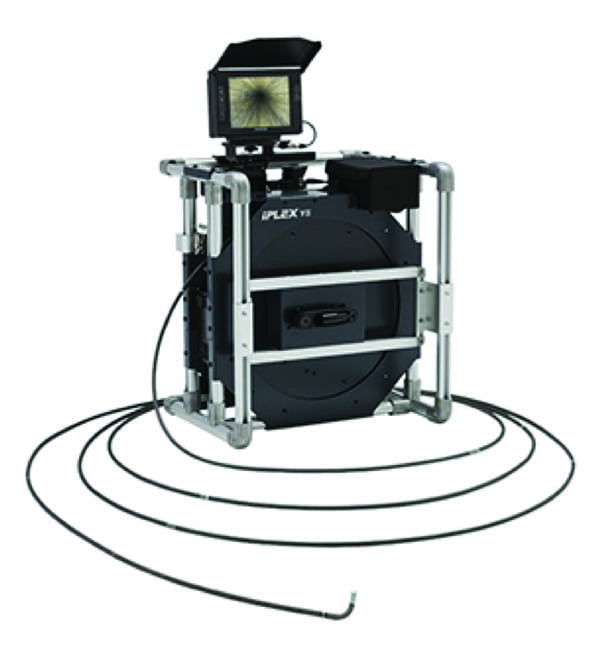
1. The IPLEX GAir video borescope system offers inspectors the ability to quickly identify issues, facilitating faster decision-making and targeted maintenance. Courtesy: Evident |
The IPLEX GAir video borescope (Figure 1), designed for nuclear plant applications, provides several key advantages that make it particularly suited for use in high-radiation environments. These include:
- Radiation Resistance. The IPLEX GAir’s insertion tube is designed to withstand high levels of radiation, continuing to function effectively even after exposure to up to 1,400 gray (Gy) of radiation (equal to about 1 sievert). This durability helps ensure that the borescope remains operational for extended periods, even in highly radioactive environments. For example, insertion tubes that use optical fibers in the tip illumination can yellow with exposure to radiation, which causes it to absorb light, thereby reducing the light intensity. The LED illumination of the GAir’s optical tip adapter eliminates this problem as it does not contain fiberoptics.
- Long-Distance Inspection. With a 30-meter (100-foot) insertion tube, the IPLEX GAir enables inspections from a safe distance, minimizing radiation exposure for personnel. Its wireless capabilities further enhance safety, allowing the device to be operated from up to 100 meters away using commercially available repeater systems.
- Replaceable Insertion Tubes. In high-radiation environments, such as dirty water-filled pipes, the insertion tube may become contaminated or degraded. In some cases, decontaminating the equipment may be considered too risky for the health of the workers, or too costly, so the plant may opt to sacrifice the insertion tube, leaving it permanently in the radiation area. Regardless, the IPLEX GAir’s replaceable insertion tube can be swapped out quickly onsite, reducing inspection downtime and limiting the costs associated with radiation-exposed equipment.
- Optimal Illumination and Imaging. The IPLEX GAir features an advanced LED optical tip adapter that provides bright, uniform lighting, essential for inspecting dark, confined reactor spaces. Its WiDER image processing system delivers clear, high-contrast images, making it easier to detect defects such as cracks, corrosion, or wear. Additionally, the tip adapters can be swapped easily to accommodate specific inspection needs. Adapters with different optical characteristics, including a wide field of view, are available. Although these tip adapters are designed for drop resistance, protecting the lens within a robust metal frame, if a lens is damaged onsite, the optical tip can be replaced so inspection can continue.
- Efficient Handling. The IPLEX GAir’s pneumatic articulation system, combined with an integrated air compressor, makes the equipment easy to carry and use in the field. Its gravity-sensing technology automatically orients images on the display, reducing confusion during inspections and speeding up the process.
Supporting Preventive Maintenance and Regulatory Compliance
Video borescopes also play a crucial role in preventive maintenance programs. By identifying early signs of wear, corrosion, or other issues, they allow nuclear plant operators to address problems before they lead to more serious failures. This proactive approach not only enhances plant safety but also reduces long-term maintenance costs.
Furthermore, borescope inspections support regulatory compliance. The NRC requires detailed documentation of inspections, including visual records. Video borescopes enable inspectors to capture high-quality images and videos, which can be stored, analyzed, and referenced in future maintenance activities. This documentation is essential for meeting the stringent safety standards imposed on nuclear plants.
Inspections Made Easy with Video Borescopes
Video borescopes, such as the IPLEX GAir, have revolutionized inspections in nuclear power plants by enhancing safety, improving efficiency, and ensuring compliance with radiation safety standards. By allowing remote visual inspections from safe distances, reducing the need for human entry into high-radiation zones, and offering detailed visual data on complex reactor components, these tools play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and reliability of nuclear power plants.
As nuclear power plants age and global energy demands continue to rise, the importance of advanced inspection tools like video borescopes will only grow. Moreover, as new nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs) gain traction, the need for compact, flexible inspection tools like the IPLEX GAir will become critical for ensuring these advanced systems meet the same rigorous safety standards as their larger counterparts. Since nuclear energy continues to be a key player in global power generation, advanced borescope technology will remain vital in optimizing plant operations and helping ensure the safety of both personnel and the environment.
—Ryan Sterling is product manager of Evident’s industrial remote visual inspection equipment.