The surge in adoption of renewable energy driven by carbon neutrality policies has created operational challenges for large thermal power plants. These plants must now accommodate rapid load fluctuations and offer flexible operation, which involves adjusting their outputs rapidly as the renewable generators’ outputs fluctuate. However, operating beyond original design specifications places additional stress on power plants, reduces efficiency, and increases the risk of failure.
Challenges of Flexible Operation in Thermal Power Plants
Thermal power plants designed for baseload operation face critical challenges with flexible operation, including:
- Stress and Wear. Frequent startups and load changes lead to boiler instability, thermal fatigue, corrosion, and turbine degradation.
- Maintenance Risks. Extended startup/shutdown cycles increase erosion, water hammer effect, and valve damage.
- Greater Need for Preservation. Prolonged downtime raises the risk of turbine corrosion and requires better preservation techniques for condensate, feedwater, and cooling systems.
These challenges call for innovative solutions to keep the power generators reliable and efficient under dynamic grid conditions.
Digital Transformation: A Necessity for Power Plants
Today’s industry trends are dominated by digitization, big data, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, mobility, and platform technologies. Traditional methods for managing power assets have reached their limits in addressing the challenges raised by carbon neutrality. Digital transformation for power plants requires processing the vast time-series data from tens of thousands of on-site sensors into big data. Real-time analysis is critical for detecting anomalies early, preventing equipment failures, and enabling smart, data-driven decision-making.
Introduction of the IDPP Platform. The Intelligent Digital Power Plant Platform (referred to as IDPP, IDPP Platform, or the Platform) is an AI-driven system that collects, standardizes, stores, and utilizes massive time-series sensor data from critical equipment such as boilers, turbines, and generators. It makes this data readily available to meet the various needs of plant operators.
Developed over five years by Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) at its Research Institute (KEPRI), IDPP addresses the pressing challenges of efficiency maximization, reliability enhancement, cost reduction, and fault prevention in large power plants intensified by an increased need for flexible operation. The IDPP integrates Internet of Things (IoT) sensor data and applies AI algorithms, and the operators can create their own applications (Apps) that access the Platform’s data to carry out tasks such as condition monitoring, fault prediction, and performance evaluation.
Key Functions and Roles of the IDPP. Unlike traditional systems that relied on rather outdated, developer-centric data collection and analysis methods, the IDPP (Figure 1) is user-oriented and engages up-to-date technologies. The IDPP Platform collects large-scale operational data in real-time, and uses AI and algorithm-based analysis to detect early signs of abnormalities, enabling predictive maintenance. Sensor data from plant equipment is first gathered through the distributed control system (DCS), transmitted to a real-time database (RTDB) server, and stored in parallel using open-source technologies such as Kafka, Druid, and Hadoop.

Key Features
|
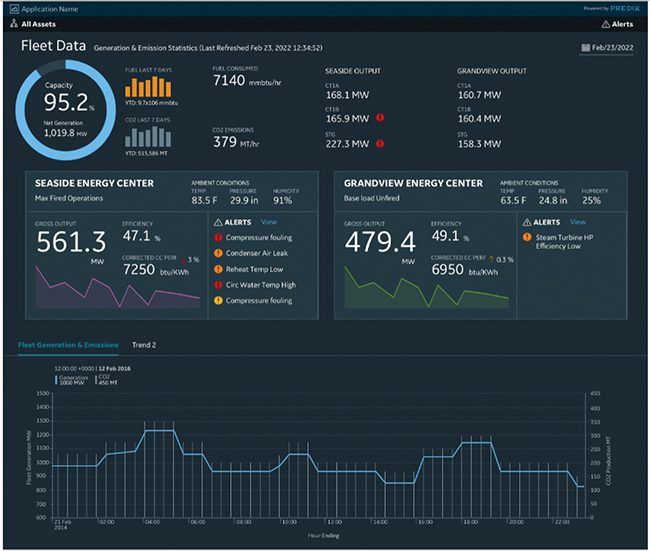
The IDPP Platform significantly enhances operational stability and productivity while lowering maintenance costs. By optimizing energy consumption through advanced analytics and AI-driven processes, it minimizes unnecessary energy loss, directly contributing to a reduction in carbon emissions. This integrated approach supports sustainable operations and reinforces the Platform’s role as a critical tool for modern power plant management. (Figure 2)

Empowering Efficiency: Streamlining App Development with the IDPP Platform
The IDPP Platform also features diverse interfaces, enabling even non-expert users to effectively utilize the data to develop tailored applications. For example, one of KEPCO’s generation subsidiaries trained its employees on Python programming to create in-house Apps. This initiative led to the development of 12 proprietary Apps, directly addressing operational needs. Impressively, these efforts contributed to a 29% year-on-year improvement in the forced outage rate, showcasing the practical and impactful benefits of empowering on-site teams with innovative digital tools. With incentives and a sense of ownership, these employees successfully applied their apps to field operations, boosting pride and satisfaction.
| IDPP Apps
To date, more than 30 Apps have been developed using the IDPP Platform, with more under continuous development. Existing Apps include:
These Apps highlight the IDPP’s advanced capabilities in improving operational reliability and efficiency in power plant management. |
Proven Track Records
By 2023, IDPP had been implemented across 19 thermal power plants operated by KEPCO’s five generation subsidiaries (GENCOs), covering a combined capacity of 7.5 GW. The Platform collects an impressive 7.3 trillion data points annually at sub-second intervals from approximately 230,000 on-site sensor tags. Recently, IDPP expanded its coverage to an additional nine units in Korea, bringing the total capacity to about 17 GW.
The GENCOs are enjoying a significant benefit by implementing the IDPP, including optimization of energy production and substantial cost reduction, reinforcing KEPCO’s commitment to innovation and operational excellence.
International Recognition
KEPCO’s IDPP Platform was featured in a white paper titled “Virtualizing Power Systems: How Digital Twins Will Revolutionize the Energy Sector” that was published in October 2024 by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), a global standards organization that develops and promotes international standards for electrical, electronic, and related technologies. The IEC introduced the following key features of IDPP, emphasizing KEPCO’s success in improving the accuracy of sensor data and enhancing operational efficiency in power plants:
- AI-friendly, real-time sensor data management platforms.
- Siren-X, an early warning system.
- AI-based status diagnosis.
- IoT-based diagnosis.
- Asset performance management.
These advancements demonstrate KEPCO’s leadership in integrating cutting-edge technologies to optimize power generation operations.
Expanding Horizons
KEPCO aims to expand IDPP’s application across all power assets in Korea to optimize power plant operations and achieve carbon neutrality. While currently focused on thermal power plants, the Platform’s capabilities hold potential for other power supply equipment generating large operational datasets. For instance, data centers where power outages can lead to substantial losses require real-time, accurate monitoring and prevention of power supply equipment failures.
On the global stage, KEPCO is actively pursuing opportunities in overseas markets. Discussions are ongoing with utilities that seek smarter asset management solutions to enhance equipment reliability and reduce costs. These efforts are setting the stage for the IDPP to gain traction worldwide, reinforcing KEPCO’s position as a leader in innovative energy solutions.
—This article was contributed to POWER by KEPCO’s Research Institute (KEPRI) and Overseas Business Development Department. KEPCO is a state-owned electric utility company in the Republic of Korea. As a company listed on both the Korea Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange, KEPCO serves as an integrated electric utility company with six generation subsidiaries that produce the majority of electricity in Korea. KEPCO also takes pride in its excellent transmission and distribution (T&D) performances, including 9.05 minutes of System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI) and 3.53% T&D loss rate as of 2022.
As the national T&D systems operator, KEPCO has consistently benchmarked global best industrial practices and cutting-edge solutions to enhance its T&D operations, as well as those of its subsidiaries’ power generation activities. Leveraging a century of operational experiences and rich research and development infrastructure, KEPCO has developed advanced solutions that reflect its commitment to innovation. For more information, contact: biz-globalmarketing@kepco.co.kr.