POWER
-
Coal
Europe: More Coal, Then Less
Europe’s continuing drive toward sustainable energy does not rule out a new generation of coal power plants to replace those scheduled to close by 2015.
-
News
Abundance of Minerals
What do iPads, flat screen TVs, Chevrolet’s plug-in Volt, and Raytheon’s Tomahawk cruise missiles have in common? Each uses one or more of the 17 rare earth elements in their manufacture, and over 95% of those elements come from China.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Upgraded Controls Position McIntosh Plant for Efficient Operations
Lakeland Electric’s C.D. McIntosh, Jr. Power Plant is a microcosm of the entire power generation industry. On a single site is a once-baseload coal-fired plant that is now operating fewer hours plus a peaking gas-fired combined cycle plant that has swung to baseload operation. A complete controls upgrade of the gas-fired plant last year prepared the plant for its expanded role in producing electricity for this 108-year-old public power provider.
-
Legal & Regulatory
States Promote Clean Energy Programs
While the proposed federal renewable portfolio standards (RPS) continue to be caught in Washington gridlock, a number of states are aggressively enacting programs that promote renewable energy, such as wind and solar power.
-
O&M
Managing the Catalysts of a Combustion Turbine Fleet
Natural gas–fired fleets comprising diverse turbine unit types are operating their units more these days because of the historic low price of natural gas. With increased operating hours, fleet owners are challenged to find the best ways to manage their SCR catalyst systems.
-
Business
POWER Digest (April 2012)
CSP Giants Form Alliance. Concentrating solar power companies Abengoa, BrightSource Energy, and Torresol Energy in early March formed the Concentrating Solar Power Alliance, an organization dedicated to educating U.S. regulators, utilities, and grid operators about the unique benefits of concentrating solar power (CSP) and of thermal energy storage. The U.S. has more than 500 MW […]
-
O&M
Safe Work Practices in Confined Spaces at Power Plants
Confined space work is often considered to be one of the most dangerous types of work performed in power generation settings. Confined spaces may contain hazardous atmospheres, they can trap entrants, and they generally can increase the hazards associated with otherwise common tasks. When the risks are not recognized, workers all too often regard incidents as surprises, but the hazards of working in confined space can be predicted, monitored, and mitigated. These “accidents” are caused by unsafe conditions, unsafe acts, or both; all accidents are preventable.
-
O&M
Preventing Downtime by Picking the Best Switch Technology
Common fuel-handling problems in the power industry often result in production downtime, costing the owner perhaps up to $200,000 per hour. There are many areas within a coal-fired power plant where mishaps can cause stoppage of material flow. Here we discuss how to select the best switch technology to reduce the possibility of coal flow stoppages.
-
Waste to Energy
Waste-to-Energy Technology Options Increase but Remain Underutilized
WTE technologies offer cost-effective, near-term solutions for producing baseload electric power, meeting renewable energy targets, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S. and other countries. They also present opportunities for improving resource management practices, increasing energy security, enhancing environmental quality, and supporting climate policy goals around the world.
-
Waste to Energy
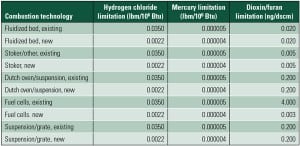
Has Boiler MACT Improved the Future for Biomass Power?
The impact of recently released air emissions regulations has stirred heated debate about forced coal plant closures and the possibility of reduced grid reliability in some regions. Biomass power may be an unexpected beneficiary of the new rules.