Features
-
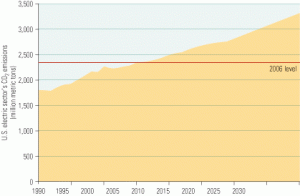
Coal
At CERA Week 2007, most life was carbon-based
For the past 25 years, Cambridge Energy Research Associates has hosted an annual conference that has drawn the captains of the worldwide oil and gas and electricity industries. The 120 distinguished speakers at this year’s summit attracted more than 2,000 delegates from 55 countries, making it the largest and most diverse ever. Naturally, one of POWER’s contributing editors was there, too; here’s his take on what transpired.
-
Business
ELECTRIC POWER Conference set for record year
ELECTRIC POWER 2007, sponsored by POWER magazine, will be presented at the Donald E. Stephens Convention Center in Rosemont, Ill., May 1 through May 3, 2007. A full agenda of preconference workshops and tutorials is scheduled for Monday, April 30.
-
News
This month in POWER …
March 1886 POWER reported on the latest development of a new and improved engine: "The chief feature of the Corliss engine [from Kendall & Roberts, Cambridgeport, Mass.] is the valve gear, which consists of four cylindrical valves, two each for admission and exhaust, operated from a central swing or stud plate; the steam valves being […]
-
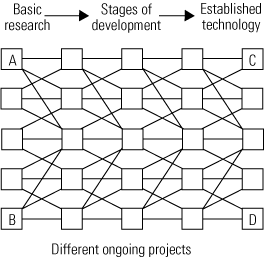
Business
Mapping technology chaos
Power engineers are in a predicament: Technology is advancing at a dizzying pace, but we are unsure how to mine information from disparate sources or predict the next big thing. Becoming expert at finding technology hones your competitive edge in both the workplace and the marketplace. Bring your pick and shovel, and we’ll show you where to start digging.
-
Business
U.S. Commercial Service helps suppliers go global
Successful exporting of goods and services is essential for U.S. companies seeking to exploit the increasingly open world economy. In the export business, the challenge is learning the ropes without getting hung out to dry when entering a potentially lucrative but unfamiliar market. Take advantage of the significant experience of the U.S. Commercial Service—its people really are here to help.
-
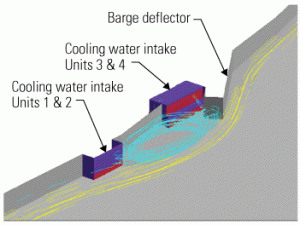
Water
Fish and cooling water intakes: Debunking the myths
Thermal power plants are required to use fish protection technologies or make changes in plant operation to protect aquatic organisms. We intuitively understand that some organisms in the water drawn in to cool a power plant can be injured or killed when they hit a screen or enter the circulating water system. You have options for compliance with EPA rules; some are extremely expensive and burdensome, whereas others are brilliant in their simplicity. This article debunks several fish impingement myths and gives practical advice for successful compliance.
-
O&M
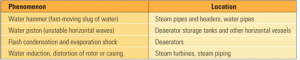
Water hammer and other hydraulic phenomena
The term "water hammer" encompasses a handful of hydraulic and thermohydraulic mechanisms. They include water hammer in steam and water piping, water piston, water induction, flash condensation and evaporation, and shock waves generated by transonic flow. All can lead to failures of steam and water cycle components and put plant operators and workers at risk. Proper design and O&M practices can keep water hammer and similar phenomena under control.
-
Gas
Will turbines require expensive retrofits to handle imported LNG?
With domestic reserves of natural gas declining and demand for gas rising, imported liquefied natural gas will increasingly fill the shortfall in U.S. pipeline supply. More than 40 LNG receiving/regasification terminals on three coasts are in various stages of development. Yet many questions about the operational and emissions impacts of the "hotter" LNG imports on today’s cleaner-burning gas turbines remain unanswered.
-
O&M
Practical guidelines for determining electrical area classification
A century ago, boiler explosions were an all-too-familiar event. But with the universal adoption of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Codes in 1914, explosions caused by poor design or manufacturing became relics of history. Electrical classification codes had the same effect on safety. This article explains how designers and operators practically apply those standards. Code details and samples of area classification drawings for a gas turbine plant are included in an online supplement (see end of story).
-
Gas
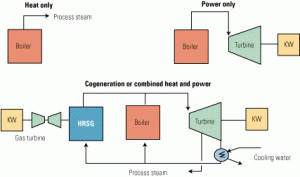
Balancing power and steam demand in combined-cycle cogeneration plants
The 2005 amendment to the 1978 Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act created some unique challenges for the design of cogeneration plants in general and combined-cycle cogeneration plants in particular. Because utilities are no longer obligated to buy electricity at "avoided cost" from qualifying facilities, plant owners must simultaneously balance power and thermal demand efficiently and economically. Here’s a prescription for your next plant design.