Features
-
Nuclear
Modularizing Containment Vessels in New Nuclear Power Plants
Using modularization in the construction of nuclear containment vessels can be one way to control both cost and schedule when building the next generation of U.S. nuclear power plants. Although the advantages of modularization can be significant, each new reactor design and plant site poses unique construction challenges and must be individually analyzed to determine the benefits of this approach.
-
Environmental
Techniques for Determining Limestone Composition and Reactivity
Limestone composition and reactivity are critical factors that determine the performance of limestone-based wet flue gas desulfurization systems. Limestone quality affects sulfur dioxide (SO2) removal, reaction tank sizing, limestone consumption rate, and composition of the gypsum product and waste streams. Reactivity is a direct measure of how readily a limestone will provide alkalinity to neutralize the acid resulting from SO2 dissolution in water. In this article we review your limestone analytic measurement options and discuss their relative accuracy and limitations.
-
O&M
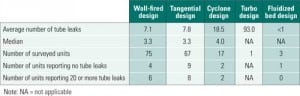
Update: Benchmarking Boiler Tube Failures
Boiler tube failures continue to be the leading cause of downtime for steam power plants. Is your boiler tube failure reduction program showing improvement when compared to programs at peer plants? The EUCG’s recent update of its boiler tube failure study can help you answer that question. The full study is available only to members, but this POWER exclusive presents many of the key results, which could help you improve the operation of your plant.
-
Coal
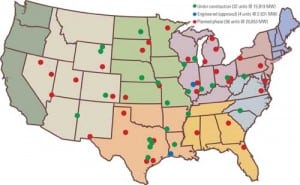
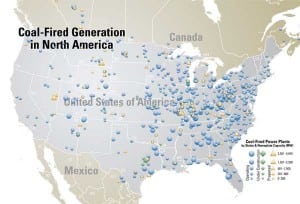
Coal-Fired Generators Worried About Getting Burned
The expected renaissance for U.S. coal-fired generation has been more evolutionary than revolutionary: Less than half of the announced plants will likely progress to construction. However, the percentages for coal-fired plants aren’t significantly different from those for combined-cycle plants a decade ago, when dozens were ultimately canceled, leaving developers with warehouses full of unused gas turbines. The difference this time: The threat of carbon control legislation has moved many projects to the “wait and see” category.
-
O&M
Measuring Coal Pipe Flow
Once pulverized coal flows have been measured, they can be balanced and optimized. Until then, tuning is simply guesswork. The right way to balance furnace fuel flows is to establish solid baseline performance by proper measurement of fuel flow, fineness, and velocity. Only then can all the coal pipes be accurately balanced and followed by a tune-up of the boiler controls.
-
Coal
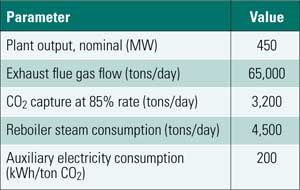
Combined-Cycle Carbon Capture: Options and Costs, Part I
Uncertainty about CO2 emissions legislation is prompting power plant owners to consider the possibility of accommodating "add-on" CO2 capture and sequestration solutions for coal-fired plants in the future. Those same plant owners may be overlooking the possibility that future natural gas – fired combined cycles will also be subject to CO2 capture requirements. This month we examine the capture options. In a future issue, Part II will present the installation and operating costs of different carbon capture technologies.
-
Gas
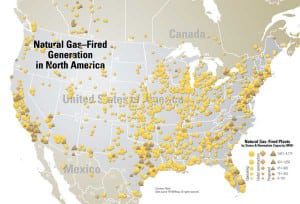
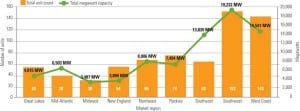
New Natural Gas–Fired Projects on an Upswing
Over the past decade, the development of new natural gas – fired generating assets has been similar to an amusement park roller coaster ride — very high peaks and the lowest of lows, with fast and stomach-churning movement between. Expect the ride to continue into the near future.
-
O&M
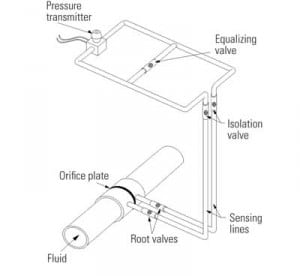
Pressure-Sensing Line Problems and Solutions
Improper pressure-sensing line design or installation is often found to be the cause of poor sensing system accuracy and response time. Here’s how to identify and solve those pesky pressure sensor problems in short order.