Features
-
O&M
Achieving Sustainable Performance Improvement
Well-organized operations and maintenance (O&M) and outage efforts enable power plants to reduce overall operating costs, improve equipment reliability, and increase long-term productivity. Experienced contractors can help plant staff maximize the success of their outages and O&M endeavors.
-
O&M
Optimizing Outages with Outage Readiness Analysis
In order to ramp up the success of planned outages at its power plants and lower the risk of unexpected and costly problems, OG&E management has begun using the outage readiness index process. This method identifies and defines the scope of the work needed prior to the commencement of an outage and quantifies the amount of preparedness needed to implement the outage in the most cost-effective manner.
-
O&M
Enhancing Plant Performance Through Formal Outage Planning and Execution
By thoroughly planning their outage strategies well in advance, Southern Company personnel are better able to achieve a number of important objectives, including improving unit economic performance, reducing unplanned maintenance outage hours, completing outages on time and within budget, and ensuring that outage workmanship is of the highest quality.
-
Coal
Vietnam Works Hard to Power Economic Growth
For the past 15 years, Vietnam has enjoyed enviable gross domestic product increases, averaging 7% annually. That kind of economic growth increases power demand, but financing new capacity remains a challenge. Reaching its ambitious capacity growth goals will require Vietnam to expand its financing and vendor base, attract foreign investment, and ensure future fuel supplies in a region thick with competition for those resources.
-
Business
Ensuring Resource Adequacy in Competitive Electricity Markets
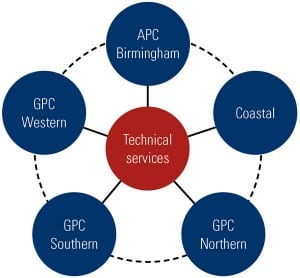
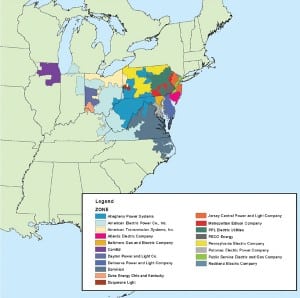
Planning for resource adequacy—something that was relatively simple in the context of vertically integrated utilities—continues to be a difficult issue in competitive electricity markets. Whereas state public utility commissions used to have exclusive authority to determine what generation needed to be built and when it was to be available, this responsibility has been assumed by RTO/ISOs in regions with competitive markets. Each region approaches resource planning differently, and each region faces unique problems.
-
Smart Grid
EEI Proposes Road Map for Electric Vehicle Integration
Several new models of plug-in electric vehicles will enter the market in 2012, joining the Nissan LEAF and Chevrolet Volt. The Edison Electric Institute has prepared four suggestions to help utilities smoothly handle the introduction of these vehicles to roads and grids.
-
Business
Automating Crew Callouts
Progress Energy has adopted an emergency worker callout program that has eliminated manual dialing, improved work acceptance rates, and increased the speed of worker reporting. The standardized process also complies with union work rules that require equality in overtime opportunities, by seniority. The business case for automating the worker callout process is compelling.
-
Coal
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
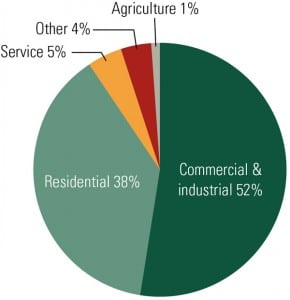
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Coal
Colstrip’s Cure for Mercury
In January 2012 a new mercury control system at the Colstrip power plant in Montana reached its first major milestone: two years of operation with mercury emissions below the state regulatory limit. The plant uses Alstom’s unique Mer-Cure technology to capture up to 90% of the mercury leaving the stack.
-
O&M
Condenser Backpressure High? Check Vacuum System Sizing
In a power plant, the primary use of vacuum systems is to remove air and other noncondensable gases from the shell side of the condenser in order to maintain design heat transfer and thus design vacuum. If holding condenser vacuum is a persistent problem, one often-overlooked cause is an inadequately sized vacuum system.