Wind
-
Solar
Trade Representatives Request Investigation on U.S. Renewables in Global Context
The U.S. Trade Representative on Monday asked the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) to investigate how U.S.-provided renewable energy services affect development of renewable energy projects worldwide. The ITC’s report, expected by June 28, 2013, will focus on the development, generation, and distribution of renewable energy—specifically onshore and offshore wind and solar energy.
-
Wind
FAA Issues No-Hazard Determination for Cape Wind Project as Congressional Probe Continues
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) issued a determination on Wednesday that finds construction of Cape Wind’s 130 wind turbines in Nantucket Sound, Mass., would pose no hazard to air navigation. The decision was issued as a congressional House committee probes whether the FAA disregarded safety concerns when it issued a prior approval of the nation’s first offshore wind project.
-
Wind
DOE Report: Wind Industry Could See Dramatically Slowed Growth in 2013 and Beyond
A new report from the Department of Energy (DOE) highlights sizeable increases in U.S. wind power capacity and recent improvements in the cost and performance of wind power technology, but it says the U.S. continues to trail several countries in wind energy penetration and warns that the industry is facing "serious federal policy uncertainty" looking into 2013 and beyond.
-
Hydro
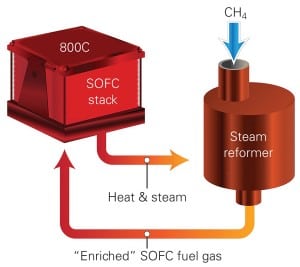
Major Developments for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which oxidize a fuel to produce electricity, have received much attention of late for the technology’s myriad benefits, including high efficiency, long-term stability, fuel flexibility, and low carbon emissions—all at a relatively low cost.
-
Wind
The Age of the Mammoth Wind Turbine Blade
Siemens Energy in June announced it had produced the first batch of its new B75 Quantum wind turbine rotor blades, fiberglass components 75 meters (m) in length that were cast in one piece (Figure 3). The blades were manufactured to be installed this fall on Siemens’ second prototype of the German firm’s SWT-6.0 6-MW offshore […]
-
Commentary
Wind Energy Blown Away by Natural Gas
The environmental push for renewables and mandates to force them into existence are rightly facing some serious headwinds. The American Renewable Energy Production Tax Credit Extension Act of 2011 foundered in Congress, and more states are experiencing significant power rate increases to cover renewable energy production costs. While renewables are generally not ready for prime time in large quantity on today’s power grid, that doesn’t mean environment concerns ought to be trashed, especially when a more effective off-the-shelf solution is available.
-
Wind
House Republicans to Scrutinize Political Sway in FAA’s Cape Wind Decision
Two Republican lawmakers are probing whether the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) disregarded safety concerns and approved the Cape Wind project—the nation’s first offshore wind project—for political reasons.
-
Wind
DOI Releases Environmental Statements for Massive Wyo. Wind Project, Offshore Wind Leases
The Department of the Interior (DOI) on Monday announced the release of final environmental impact statements for a proposed wind power complex in Wyoming with a nameplate capacity of 3,000 MW and publication of an environmental assessment for commercial wind leases and site assessment activities on the Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) offshore Rhode Island and Massachusetts.
-
Hydro
FERC Rule 1000: What Does It Mean?
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has the responsibility for ensuring just and reasonable rates and preventing undue discrimination by public utility transmission providers. Last year FERC defined a new framework for public utilities and regional transmission organizations planning new transmission networks. The framework is provided in Order No. 1000—Transmission Planning and Allocation by Transmission Owning and Operating Public Utilities. The Final Rule was issued on July 21, 2011, and reaffirmed by Order No. 1000-A on May 17, 2012.
-
Coal
Power in India: Opportunities and Challenges in a Fast-Growing Market
India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth. India’s long-term annual economic growth rate is projected at over 7%, and the country is investing in its hydroelectric, nuclear, and renewable resources. However, the primary fuel used to produce electricity remains coal, and the government has ambitious plans to significantly increase coal-fired capacity. Those plans have been challenged by a number of unexpected factors that threaten to stifle India’s economic growth.