Waste to Energy
-
Hydro
Hawaii’s Largest Wind Project Online as State Struggles to Integrate Renewables
On Monday, as First Wind announced its 69-MW Kawailoa Wind Project had gone into commercial operations on Oahu, other news underscored the difficulty the island state faces in trying to substitute renewables for expensive, imported fossil fuels.
-
History
FuelCell Energy Claims Largest Order in Industry’s History
FuelCell Energy Inc. on Monday announced an order from its South Korean partner, POSCO Energy, for 121.8 MW of fuel cell kits and services to be manufactured at the FuelCell Energy production facility in Torrington, Conn. The company said this represents the largest order for both its company and the fuel cell industry.
-
Hydro
Trend Shows Growth of Renewables on Contaminated Lands
Renewable energy projects installed on potentially contaminated lands, landfills, and mine sites have increased by 40% since 2008, a new list released last week by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems make up the bulk of about 184.7 MW installed at 60 sites in 25 U.S. states.
-
Hydro
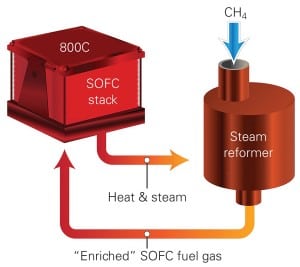
Major Developments for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which oxidize a fuel to produce electricity, have received much attention of late for the technology’s myriad benefits, including high efficiency, long-term stability, fuel flexibility, and low carbon emissions—all at a relatively low cost.
-
Waste to Energy
Marmaduke Award: Combined Solar Technologies’ Hybrid Plant: Using Wastewater and Olive Pits to Produce Clean Water and Clean Energy
Combined Solar Technologies (CST) has designed, built, owns, and operates a water purification system located at the Musco Family Olive Co. facility in Tracy, Calif., that burns olive pits to purify highly saline wastewater through a distillation process while also producing electric power. For its pioneering approach, CST is the winner of POWER’s 2012 Marmaduke Award for excellence in plant problem-solving. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence, whose exploits were chronicled in POWER beginning in 1948.
-
Coal
Safety Implications of Coal and Biomass Fuel Mixes
Practically everyone would agree that the energy policy of the U.S. is in a great state of flux. Not since the introduction of commercial nuclear power some five decades ago has our country come to such an energy crossroads. No matter what your political ideology, no one can refute that conventional coal-fired power plants are being paralyzed by recent and potential U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations designed to cut the nation’s reliance on coal.
-
Hydro
Utility Perspectives on Ramping Up Renewable Power
Panelists at ELECTRIC POWER discussed how U.S. utilities choose renewable power generation technologies based on their geographic locations, state requirements, economics, and other criteria—including reliability and federal regulations.
-
Coal
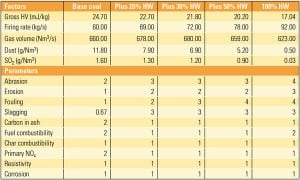
New Technologies Advance Biomass for Power Generation
As U.S. utilities seek to increase the percentage of carbon-neutral biomass used in their generation portfolios, they must deal with a number of complex challenges unique to this fuel source. Several breakthrough technologies are poised to help promote greater use of biomaterials.
-
Waste to Energy
Trash to Gas = Cash
Municipal landfills across the country have been quietly harnessing their methane emissions for years. But as the appetite for natural gas grows and the price of oil skyrockets, some creative sanitation departments are starting to make some real noise.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Can California’s Cap-and-Trade Program Turn Manure into Gold?
California’s Cap-and-Trade Program is the only cross-industry, market-based climate change regulatory program in the United States. This program may provide a good investment opportunity for dairy farmers, livestock owners, and others if the program’s Livestock Project protocol for offsets can get off the ground and maintain a viable price for greenhouse gas (GHG) allowances.