Hydro
-
History
The Russian Power Revolution
Exports of natural resources have given Russia increased global political and economic clout. But domestically, the world’s fourth-largest generator of electricity has had to embark on the most ambitious reforms ever undertaken to modernize dilapidated Soviet-era power infrastructure and incentivize a massive capacity expansion to support a revived economy.
-
Coal
Report: Fuel for Power Generation to Lead Energy Growth Through 2040
Fuel for power generation will account for about 55% of demand-related energy growth through 2040, ExxonMobil forecasts in its freshly released annual energy forecast. Like several other forecasters, the Irving, Texas–based oil and gas company also predicts that natural gas will emerge as the leading source of electricity generation by 2040. Among key findings in […]
-
Coal
EIA Projects Faster Growth of Natural Gas Production, Gas Generation
Compared to projections from last year, an Early Release Overview of the Energy Information Administration’s (EIA’s) Annual Energy Outlook 2013 (AEO2013) released on Wednesday foresees higher gas production and, with it, a higher share of gas generation by 2040. The outlook also projects a growing share of renewable and nuclear power, but dampened future coal use.
-
History
Modernization of Century-Old Hydro Facility Yields Rich History
When the Boulder Canyon Hydroelectric Facility was built in the steep, forested mountains between Boulder and Nederland, Colo., in 1910, it was the highest head hydroelectric facility in the western U.S.
-
Hydro
TOP PLANT: Three Gorges Dam, Yangtze River, Hubei Province, China
After nine years of construction, installation, and testing, the Three Gorges Dam is now complete. On May 23, 2012, the last main generator finished its final test, increasing the facility’s capacity to 22.5 GW and making it the world’s largest capacity hydroelectric power plant.
-
Hydro
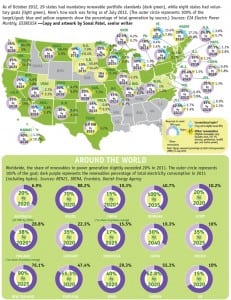
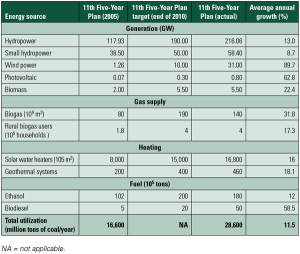
Renewable Energy Development Thrives During China’s 12th Five-Year Plan
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan calls for expanding the use of renewable energy in all forms throughout the country. From solar and wind to biomass gas and briquettes, China has a true “all of the above” renewable energy policy.
-
Hydro
Hawaii’s Largest Wind Project Online as State Struggles to Integrate Renewables
On Monday, as First Wind announced its 69-MW Kawailoa Wind Project had gone into commercial operations on Oahu, other news underscored the difficulty the island state faces in trying to substitute renewables for expensive, imported fossil fuels.
-
Hydro
Trend Shows Growth of Renewables on Contaminated Lands
Renewable energy projects installed on potentially contaminated lands, landfills, and mine sites have increased by 40% since 2008, a new list released last week by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems make up the bulk of about 184.7 MW installed at 60 sites in 25 U.S. states.
-
Hydro
Three Gorges Dam Completed Amid Technical Victories, Controversy
China in early July installed the 32nd and final turbine of its mammoth Three Gorges Dam, virtually completing the controversial 1994-initiated hydropower project on the middle reaches of the Yangtze River.