Nuclear
-
Coal
Best Practices for Natural Gas Line Cleaning
As barriers to new coal-fired generation expand and enthusiasm for nuclear plants wanes, the commissioning of natural gas–fired plants promises to increase. However, gas plants pose hazards, too. An explosion last year that was caused by unsafe use of natural gas to blow residue from a gas pipeline during commissioning of a gas-fired power plant has focused regulator and industry attention on finding safer alternatives for this task. Fluor shares its gas pipeline cleaning best practices.
-
Commentary
Advancing America’s Nuclear Infrastructure
It is fair to say that 2011 is bringing some uncertainty into the nuclear energy industry. The tsunami and subsequent events at Fukushima present Japan and our industry with new challenges but also serve as a catalyst for continuous improvement. In the U.S., we are learning from these events and improving our operations, designs, and emergency response approaches to make our plants safer, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly.
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Nuclear
The Fukushima Fallout: Six Months After the Nuclear Crisis
(WEB EXCLUSIVE) Much has transpired during the nearly six months following the Great East Japan Earthquake—a 3-minute, magnitude 9.0 temblor that generated a series of tsunami waves as tall as 38.9 meters (130 feet), killed more than 25,000 people, and set off the worst nuclear disaster in 25 years.
-
Nuclear
THE BIG PICTURE: Underground Nuclear Waste Disposal
According to the International Atomic Energy Commission, deep disposal in stable geological formations is the only sustainable way to safely manage spent fuel and high-level waste (HLW) from nuclear power reactors. No permanent geological repository has yet been built, but some countries have found a location for a future repository. Others are researching the option…
-
Nuclear
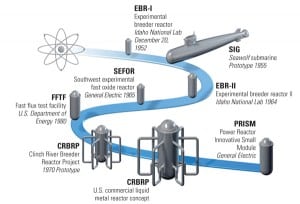
PRISM: A Promising Near-Term Reactor Option
PRISM is an advanced sodium-cooled reactor that simultaneously reduces proliferation concerns by consuming transuranics and weapons-grade plutonium and closes the nuclear fuel cycle. PRISM’s passive safety systems, successfully demonstrated in earlier liquid metal reactor programs, combined with modern design requirements, make PRISM invulnerable to most serious accidents that can affect light water reactors.
-
Nuclear
Nuclear Power in the Shadow of Fukushima
Risk, risk management, and the specter of Fukushima ran through the nuclear track at May’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference in Chicago. The reality of risk, driven home by the horrendous events in Japan, was a recurring theme in many presentations, in questions to speakers, and in the conversations among delegates during informal moments.
-
Nuclear
Germany to Shut Down All Nuclear Reactors
Germany’s Chancellor Angela Merkel at the end of May officially endorsed a plan to shut down all 17 of the nation’s nuclear power plants by 2022. The decision, which gives the power-intensive nation just over a decade to find new sources of power for 23% of its energy needs, has had reverberations all over the world, though the future of nuclear—through growth in developing nations—continues to look sturdy.
-
Nuclear
TEPCO: Most Fuel at Daiichi 1 Melted
Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO) in May discovered—after calibrating water gauges—that the water level in the reactor pressure vessel of Unit 1 at the quake- and tsunami-ravaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant may have dropped to such low levels that the fuel was completely uncovered. This caused almost all the fuel pellets to melt and fall to the bottom of the vessel at a relatively early stage in the accident—roughly 15 hours after the March 11 earthquake that killed an estimated 28,000.
-
Nuclear
Holtec, Westinghouse Roll Out Small Modular Reactor Designs
As the Daiichi nuclear crisis has governments around the world reconsidering their nuclear-heavy energy plans and scrutinizing the safety of existing reactors and third-generation designs, several developers are touting the merits of small modular reactors (SMRs).