Hydro
-
Hydro
New York City Backs Tidal Power
The Roosevelt Island Tidal Energy (RITE) pilot project used six full-scale hydrokinetic turbines to capture the power of river tides and currents and convert it into electricity. Located in New York City’s East River, it is the first and only grid-connected tidal array project in the world. RITE project developers are seeking approval to install up to 30 additional turbines in the near future.
-
O&M
Fire Protection Options for Air-Cooled Hydroelectric Generators
Fire protection systems for air-cooled hydroelectric generators have several special requirements due to these generators’ unique geometries. This survey of options will help plant owners and operators make the best equipment selections for their plants and thereby avoid unexpected surprises.
-
Hydro
Brazil Greenlights 11-GW Belo Monte Project
Brazil’s environment agency, IBAMA, in January issued a partial installation license that allows for construction of the controversial Belo Monte dam complex, an 11,233-MW project estimated to cost some 19.6 billion reals (US$11.7 billion), to begin on the margins of the Amazon’s Xingu River. Saying the project is needed to meet soaring electricity demand when completed, as planned in 2015, the government gave license to dam-building consortium Norte Energia to begin clearing 238.1 hectares (588 acres) of forestland.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Hydro
Transmission and Distribution in Canada
Like its neighbor to the south, Canada faces enormous costs to upgrade and expand its transmission and distribution system. The desire to integrate more renewable power into the grid, build a smarter grid, and export more power are providing the rationale for action, but capital and political will lag behind.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Hydro
Laos Inaugurates Major Revenue-Generating Hydropower Plant
Lao People’s Democratic Republic (PDR), the tiny landlocked country in Southeast Asia of just 6.3 million people, in December inaugurated the 1,070-MW Nam Theun 2 Power Station, a hydropower project in Khammouane Province.
-
Hydro
Marine Power Developments Move Forward in North America
In early January, Verdant Power—a decade-old company based in New York—made headlines for filing an application with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) for a project that could allow it to install up to 30 new tidal power turbines in the East Channel of the East River in New York City.
-
Hydro
German Researchers Develop Cost-Efficient Small Hydro Plant
Researchers at Germany’s Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) claim to have developed a small-scale hydroelectric power plant that is capable of operating profitably even at modest dam heights while minimizing impact on waterways.
-
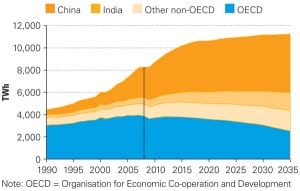
Coal
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.