Gas
-
Gas
An “Exploding Lake” Becomes a Power Source
Rwanda’s Lake Kivu has a nickname: “Killer Lake.” The shimmering 1,040–square mile body of freshwater on the western branch of the Great East African Rift that straddles the Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda has had a bloody history. Not only was it the site of atrocity during the 1994 Rwandan genocide, but scientists say that it is also one of three known “exploding lakes.”
-
Gas
Meeting LNG Demand with Floating Liquefaction Facilities
The past two years have seen a dramatic escalation of global natural gas liquefaction capacity.
-
Gas
MHI Ships First Commercial J-Series Turbine
The first unit of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries’ (MHI’s) much-watched J-Series gas turbine, a technology MHI has been testing for a year, was shipped this December from its Takasago Machinery Works in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan, for commercial use at Himeji Unit 2, also in Hyogo, owned by Kansai Electric Power Co.
-
Gas
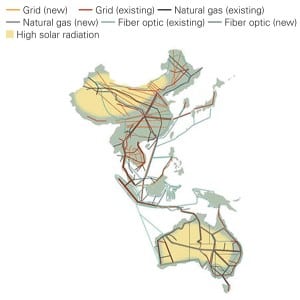
Desertec Ambitions Turn to Asia, Australia
The ambitious Desertec project—a $9 billion initiative to develop, harness, and transmit 2,000 MW of renewable power from North Africa and the Middle East to Europe by 2050—has been trumped by a vaster concept that spans Asia and Australia.
-
O&M
7EA Conversion Saves Time and Money
ProEnergy Services (PES) was recently contracted to install six Frame 7 DLN1.0 dual-fuel assemblies in Venezuela. The problem: The lead time to purchase the conversion hardware from the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) would not meet the customer’s schedule. The only option was for PES to convert the fuel nozzles removed from a gas-only unit to a dual-fuel configuration, a process that had never before been attempted.
-
Coal
Vietnam Works Hard to Power Economic Growth
For the past 15 years, Vietnam has enjoyed enviable gross domestic product increases, averaging 7% annually. That kind of economic growth increases power demand, but financing new capacity remains a challenge. Reaching its ambitious capacity growth goals will require Vietnam to expand its financing and vendor base, attract foreign investment, and ensure future fuel supplies in a region thick with competition for those resources.
-
Gas
Turbine Suppliers Pursue a Different Niche: Steel Mills
Steel mills have long recaptured flue gas from the blast furnace to generate local power and steam. But advances in gas turbine technology have taken what was a low-tech means of increasing plant efficiency and given mill owners ways to increase profits through selling electricity and greatly reducing emissions through more efficient combustion.
-
Gas
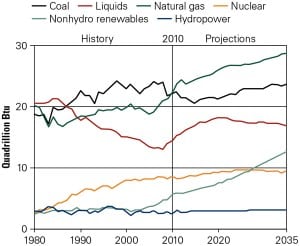
Gas Glut Remains, Prices Keep Falling
Surging supply and plummeting prices during 2011 have worked a sea change in America’s energy policies and use of natural gas. How long can it go on?
-
Gas
American Electric Power Finally Flips the Switch on Beleaguered Ohio Plant
Timing is (almost) everything when it comes to building new power plants. Nobody knows that better than AEP, which finally got a happy ending to a story that took over a decade to complete.
-
Gas
Gas Power Leads Both New Capacity and Retirements
The 2000s saw dramatic growth in gas-fired power generation capacity. But, surprise–this growth was also accompanied by the retirements of numerous older gas-fired plants.