Environmental
-
Coal
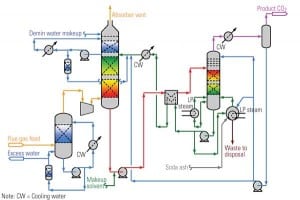
Commercially Available CO2 Capture Technology
While many CO2 removal technologies are being researched through laboratory and pilot-scale testing, an existing technology has a significant operating history at commercial-scale facilities, where it is collecting CO2 from multiple sources, including low-CO2 concentration flue gas (<3.1% by volume) with high oxygen concentrations (>13% by volume).
-
Environmental
Help Build the Global Energy Observatory
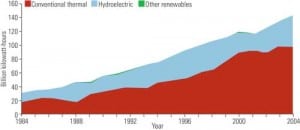
How would you like to be able to access data on all the power plants in the world and all of their performance metrics, analyze that data, and map it? Those abilities are part of the vision behind the Global Energy Observatory (GEO), an OpenModel website that serves as a wiki for global energy data.
-
Environmental
Power Industry Needs to Do a Better Job of Educating and Messaging
At the opening ELECTRIC POWER 2009 plenary session, both the keynote speaker and the Power Industry Executive Roundtable participants kept circling back to the problems created by a public and lawmakers who seem to be promoting policies without an adequate understanding of energy realities. Most of the speakers acknowledged that the industry itself is partly to blame, but nobody offered a way forward.
-
Coal
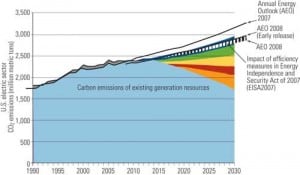
Carbon Control: The Long Road Ahead
The industry is preparing for carbon legislation by exploring options for dealing with CO2. But even if the technical issues are resolved, actually sequestering CO2 poses a number of other daunting challenges.
-
Coal
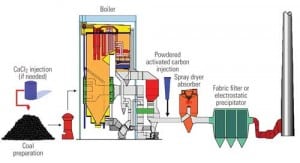
Technology Could Deliver 90% Hg Reduction from Coal
Reducing mercury emissions at coal-fired power plants by 90% has been considered the holy grail of mercury control. A new technique promises to get us there — at a price.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Looking Downstream After the Cooling Water Case
In the wake of the recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling related to cooling water intake practices at large power plants, many utilities are relieved to be off the hook as far as implementing expensive control upgrades to protect fish and other aquatic organisms.
-
Coal
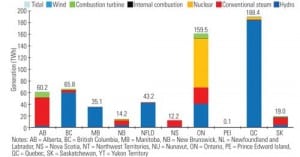
Canada Moves to Rebalance Its Energy Portfolio
Though Canada is rich in fossil fuels, nuclear power may fuel a significant portion of the nation’s future electrical generation needs, especially in provinces that have traditionally relied on hydropower and fossil fuels.
-
O&M
Turkey Opens Electricity Markets as Demand Grows
Turkey’s growing power market has attracted investors and project developers for over a decade, yet their plans have been dashed by unexpected political or financial crises or, worse, obstructed by a lengthy bureaucratic approval process. Now, with a more transparent retail electricity market, government regulators and investors are bullish on Turkey. Is Turkey ready to turn the power on?
-
Coal
CHP: Helping to Promote Sustainable Energy
Because combined heat and power (CHP) plants optimize energy use, they cut fuel costs and pollution. Even though U.S. power plants have been using CHP for decades, today’s energy experts have a newfound appreciation for its ability to promote sustainable energy use.
-
Coal
Capturing CO2: Gas Compression vs. Liquefaction
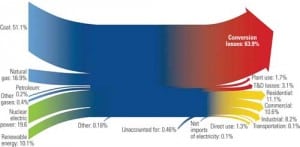
Carbon capture and sequestration is very likely to be a key element of any future greenhouse gas legislation. Integrated gasification combined-cycle plants now under design have provisions to separate the CO2 at elevated pressures. Coal-fired plants have a far more difficult and expensive task — separating and compressing CO2 from pressures just above atmospheric conditions.