Environmental
-
Coal
Combined-Cycle Carbon Capture: Options and Costs, Part I
Uncertainty about CO2 emissions legislation is prompting power plant owners to consider the possibility of accommodating "add-on" CO2 capture and sequestration solutions for coal-fired plants in the future. Those same plant owners may be overlooking the possibility that future natural gas – fired combined cycles will also be subject to CO2 capture requirements. This month we examine the capture options. In a future issue, Part II will present the installation and operating costs of different carbon capture technologies.
-
Coal
Report: Costs for First-Generation Carbon Capture Plants Will Soar
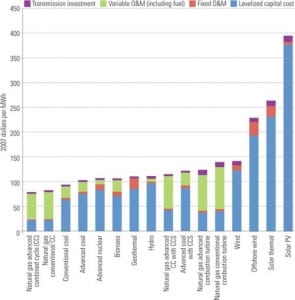
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) has of late gained steam as the best way to mitigate emissions of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) from fossil fuel power plants, despite evidence that the approach would require much energy and increase the fuel needs of a coal-fired plant by more than 25%. A new study from […]
-
Environmental
Dead Man’s Hand
The stage is being set for negotiating a successor agreement to the Kyoto Protocol. The U.S. is trying to exert some leadership in the international climate change debate by attempting to build consensus for binding carbon emission reductions prior to the upcoming Copenhagen meeting. Meanwhile, carbon legislation is, thankfully, stalled in the Senate, and developing countries are rejecting our entreaties. You can’t win if other countries don’t want to play.
-
Gas
Top Plants: Edward W. Clark Generating Station, Clark County, Nevada
The Edward W. Clark Generating Station, which has supplied electricity to the Las Vegas Strip for more than half a century, has learned the secret of life in the desert: adaptability. The plant’s early years featured conventional steam plants operated around the clock. By mid-life, Clark had been upgraded with two combustion turbine combined-cycle power blocks operated as intermediate-load resource. Today, the old steam plants have been replaced with fast-start peaking gas turbines.
-
O&M
What if New Source Review Were Repealed?
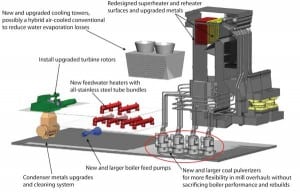
The New Source Review (NSR) permitting program was originally created as part of the 1977 Clean Air Act Amendments to ensure that new power generation facilities were properly outfitted with all the necessary air quality control systems when constructed. Plants in operation were exempt until they made plant modifications viewed as beyond “routine maintenance,” a term whose definition has been a moving target. Is it time for the NSR to take a back seat to improved plant efficiency and reduced carbon emissions?
-
O&M
High-Hazard Coal Ash Sites, and the TVA Spill Revisited
The EPA has identified 44 "high hazard" coal ash ponds around the U.S., and a recent Tennessee Valley Authority report indicates that the agency should have known its Kingston Plant pond would have been one of them.
-
Coal
Utility Business Customers to Feast on Free Allowances
An analysis by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities concluded that two-thirds of the value of carbon emission allowances described by the recent H.R. 2545 will benefit utility business customers and households in the top quartile of personal income. The middle quintile will see increased cost for electricity.
-
Coal
MIT Report Urges Faster Action on Carbon-Capture Retrofits
MIT researchers push for faster commercialization of carbon capture technologies for coal-fired power plants by reducing system costs.
-
Coal
Commercially Available CO2 Capture Technology
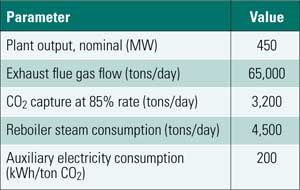
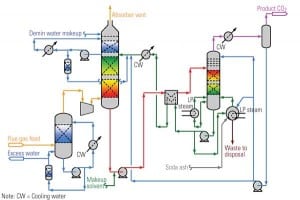
While many CO2 removal technologies are being researched through laboratory and pilot-scale testing, an existing technology has a significant operating history at commercial-scale facilities, where it is collecting CO2 from multiple sources, including low-CO2 concentration flue gas (<3.1% by volume) with high oxygen concentrations (>13% by volume).
-
Environmental
Help Build the Global Energy Observatory
How would you like to be able to access data on all the power plants in the world and all of their performance metrics, analyze that data, and map it? Those abilities are part of the vision behind the Global Energy Observatory (GEO), an OpenModel website that serves as a wiki for global energy data.