POWER
-
News
Correction (November 2010)
Correction In the September issue’s “Taming Condenser Tube Leaks, Part I,” the first full paragraph in the main text on page 57 should say, “If chloride and sulfate in the steam cannot be maintained below 8 ppb….” POWER regrets the error.
-
O&M
Air Casters Speed Equipment Moves
When it comes to moving megaton items like feedwater heaters or recirculating pumps, conventional moving tools such as wheel rollers, cranes, hoists, and come-alongs may be virtually useless. In some cases, moving large components is dangerous in a space-constrained location surrounded by delicate process control equipment. Feedwater heater and recirculating pump removal and replacement are […]
-
Solar
The Global Smart Grid Scene
Presenters at the inaugural GridWise Global Forum in Washington, D.C., September 21 to 23 had a lot to say about the prospects for smarter grids. This synopsis of facts and opinions shared at the event, which attracted several smart grid A-listers, looks at the major challenges ahead, especially for the U.S.
-
Legal & Regulatory
EPA’s Mercury Rule: Another Incarnation Coming
Much like the shape-shifting substance it regulates, the mercurial enforcement rule that governs mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants has changed unpredictably several times in recent years.
-
Distributed Energy
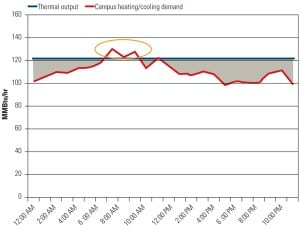
Matching Load and Generation at UCSD
“Smart Power Generation at UCSD” explains how the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) is maximizing the value of combined heat and power. However, like any other grid-controlling entity large or small, the campus has to match generation and load. Its two Solar Turbines gas turbines operate in baseload mode 24/7 while the cogeneration side of the plant maximizes the value of “waste” heat and electricity that isn’t needed to serve immediate load by generating steam and chilled water for campus heating and cooling.
-
Nuclear
Collaborative Team Investigates Long-Term Nuclear Operations
The Atomic Energy Act originally established the length of a U.S. commercial nuclear reactor license as 40 years and made it renewable for another 20 years. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has stated that it bases the length of these licenses (and the 50+ renewed licenses granted to date) not on any particular technical limitation but on whether the plant meets current safety requirements. Does this mean there could be reactor life after 60?
-
Smart Grid
Combined Heat and Power Across the U.S.
The University of California, San Diego (see “Smart Power Generation at UCSD”) is just one of many combined heat and power (CHP), or cogeneration, systems in the U.S. A 2008 report by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), “Combined Heat and Power: Effective Energy Solutions for a Sustainable Future,” notes that Texas has the most CHP capacity—much of it used by the petrochemical and petroleum refining industries. California ranks second, largely a result of “industrial demands, stringent air quality requirements, and effective policies that encourage adoption of CHP.”
-
News
Follow the Leader
Another year has passed and the promised U.S. nuclear renaissance is still in the Dark Ages. Blame for slow progress is usually cast on the pedestrian pace of finalizing loan guarantees, the economy and slow load growth, or the rising cost of construction. The excuses end when competition increases. Two years have elapsed since the […]
-
Nuclear
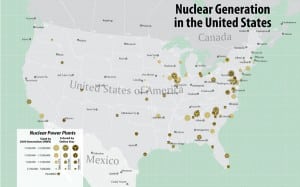
Map of Nuclear Generation in the United States
Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed. For full-sized maps, contact Platts.
-
Nuclear
Russia Powers On, Boosting Nuclear Reactor Sales
Atomstroyexport, the Russian Federation’s nuclear power equipment and services export monopoly, in September signed a US$1.8 billion contract with the Chinese government for development of the second stage of the Tianwan nuclear power plant in Lianyungang City. Under the agreement, Units 3 and 4 are to be built in a way similar to construction of the first stage of Tianwan—two Russian-designed VVER-1000 reactors that came online in 2007, each with a rated capacity of 1,060 MW.