POWER
-
O&M
Fire Protection Options for Air-Cooled Hydroelectric Generators
Fire protection systems for air-cooled hydroelectric generators have several special requirements due to these generators’ unique geometries. This survey of options will help plant owners and operators make the best equipment selections for their plants and thereby avoid unexpected surprises.
-
News
Spanish Wind, Revisited
Two years ago, Spain’s fixation on renewables and “green jobs” was praised by President Obama as a success story worthy of our emulation. How is Spain doing today?
-
Nuclear
Nuclear Fever Breaks
Excitement over an expected nuclear renaissance reached fever pitch over the past decade. Today, the original volume of announced projects has been sifted, leaving just a few serious ones that may match well with the level of loan guarantees recently announced as part of the president’s budget proposal. The pace of progress is slow, yet progress is almost certainly unavoidable.
-
Nuclear
The Battle to Control Quake-Stricken Japanese Reactors
As POWER closes this issue (March 15), 6,000 people have been confirmed dead and 10,000 others are still missing as a result of the magnitude 9.0 earthquake and ensuing tsunami that destroyed Japan’s eastern shore on March 11. At this writing, the country is battling a third cataclysm—the potential meltdown of several reactors at Tokyo Electric Power Co. (TEPCO’s) Daiichi nuclear power plant in Fukushima Prefecture.
-
Coal
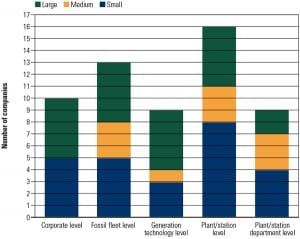
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part II: Fleet-Level Metrics
Part II of this three-part series moves up the typical utility organization to consider important fleet-level fossil plant operating metrics. This portion of the EUCG-sponsored benchmarking survey found that utilities favor fleet-level metrics that are similar to plant-level metrics but assign them different priority. Utilities generally agreed on what were important metrics in the eight categories examined, although none were favored by a majority of the surveyed utilities.
-
Nuclear
Nuclear Monitor: News from France, Japan, U.S., Belgium, Germany
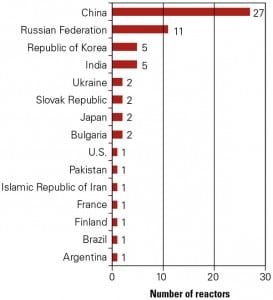
Five new nuclear reactors were connected to the grid while construction of 14 others began in 2010, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) reported in early March. Around the world, a total 65 reactors with a net power capacity of 62.9 GW were in various stages of construction—almost half of them in China.
-
News
Linear Heat-Detection System
Tendeka’s advanced monitoring solutions arm, Sensornet, introduced its FireLaser linear heat-detection system, which has been specifically designed for fire hazard detection applications. The FireLaser connects to a fiber-optic cable and determines temperature and distance data at thousands of points along its length. The fiber-optic cable is installed within the asset to be protected, acting as the […]
-
Coal
U.S. and China Push Forward with Cleaner Coal Projects, Amid Setbacks
In his January State of the Union speech, President Barack Obama called on Congress to pass legislation that would allow the U.S. to source 80% of its electricity from “clean energy” sources by 2035—including traditional renewable sources like wind and solar as well as nuclear and “clean coal.” That broadened definition of “clean energy” was designed to inspire bipartisan interest, as was widely reported. But, as was also widely pointed out, the speech followed a visit to Washington from Chinese government officials and a series of key agreements aimed at increasing “clean energy” cooperation between the two countries.
-
Gas
RAM Process Optimizes IGCC Design
New methods of reliability, availability, and maintainability (RAM) evaluation help facilitate more-accurate plant output and revenue predictions, identify strengths and weaknesses of possible plant configurations, and determine potential improvements and enhancements for integrated gasification combined cycle plants.
-
Nuclear
Small Nuclear Reactor Concept Goes Underwater
France in January announced its contribution to the wave of small and modular reactors (SMRs): a submarine-like nuclear plant that can be submerged in waters 60 meters (m) to 100 m deep and several kilometers offshore.