Features
-
Gas
Global Gas Glut: An Update
In our September article about the global profusion of natural gas, we based a portion of our discussion on the latest, vastly increased natural gas reserve estimates reported by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Since our article was published, the EIA has adjusted its estimates downward. We want you to be aware of those lower recoverable reserve estimates. We also want you to know that the conclusions reached in that article do not change with the new estimates of natural gas reserves.
-
O&M
Improving Condenser O&M Practices
Losses attributed to condenser tube leaks, fouling, and failures continue to climb, costing the power generation industry an estimated half-billion dollars annually in maintenance costs and loss of production. Investing in an effective condenser maintenance program will reduce those expenses in short order.
-
Coal
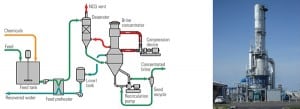
Fundamentals of Zero Liquid Discharge System Design
Power plants often produce wastewaters that contain salts, such as those from wet gas scrubbing, coal pile run-off, and leachate from gypsum stacks. Evaporation of those liquid wastes in a modern zero liquid discharge system produces clean water that is recycled into the plant plus a solid product suitable for landfill disposal. Here are the options to consider.
-
Coal
An SCR Can Provide Mercury Removal Co-Benefits
Complying with various state (and expected federal) requirements governing mercury removal from the stack gas of coal-fired power plants has usually been achieved by adding an expensive activated carbon injection system. Now there is another alternative: a catalyst that features higher mercury oxidization activity than conventional catalysts while maintaining the same SO2 to SO3 conversion activity—and all at a lower operating cost. Full-scale installations are under way at several Southern Company plants that burn a variety of coals.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
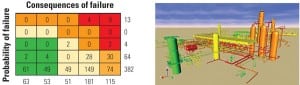
Managing Equipment Data Through Asset Virtualization
Asset “virtualization” extends and combines the technologies of 3-D visualization and virtual reality to a new, practical level for the life-cycle management of power industry equipment. All pertinent data for a component, subsystem, or plant is associated with, stored, and accessed through as-built 3-D digital models of the actual plant that are constructed using laser scanning techniques.
-
Coal
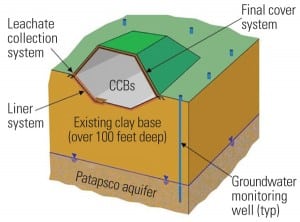
Constructing Maryland’s First Permitted Landfill for Coal Combustion By-products
Constellation Power Source Generation Inc., which owns and operates three coal-fired power plants in Maryland, has contracted with Charah Inc., an ash management company, to build a landfill to strict environmental requirements for the disposal of its plants’ coal combustion by-products that can’t be recycled for other uses.
-
Coal
U.S. Coal-Fired Power Development: Full Employment for the Lawyers
The EPA began rolling out its long-anticipated power plant regulations this year, causing some utilities to shutter some older coal-fired plants. Other utilities paused, perhaps hoping that a neighbor’s closure decisions would allow continued operation of some of their own older, smaller, less-efficient plants. As the nation sweated through a scorching summer, air conditioners hummed thanks to coal-fired power plants built 50 or more years ago. How many of them will be retired, and over what timeframe?
-
Coal
Top Plant: J.K. Spruce 2, Calaveras Power Station, San Antonio, Texas
CPS Energy, the largest municipally owned utility in the U.S. providing both natural gas and electric service, implemented an energy plan in 2003 that required energy conservation measures, use of available renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, and additional coal-fired generation. The $1 billion 750-MW Spruce 2 fits into that plan by being one of the cleanest coal-fired plants in the country.
-
Coal
Top Plant: John Twitty Energy Center Unit 2, Springfield, Missouri
Utilities of Springfield elected to add a 300-MW coal-fired plant to its fleet to meet rising demand for electricity. It was the first coal plant constructed by the utility since 1976. An extremely competitive construction market required the utility to adopt new contracting practices to meet a tight project schedule, an approach that proved very successful. The $555 million plant commissioned in January 2011 is expected to cover system growth at least through 2024.
-
Coal
Top Plant: Masinloc Power Plant, Zambales Province, Philippines
In April 2008, AES Philippines purchased the Masinloc coal-fired power plant in Zambales Province in the Luzon region. Originally constructed in 1998 as a two-unit, 600-MW plant, the facility uses coal from a variety of sources in the Pacific Rim. After AES finished overhauling much of its equipment, the expanded 660-MW (gross) plant’s availability increased from 48% to 74%, which enabled net electricity production to jump by 129% by 2010.