Latest
-
O&M
Abrasion-Resistant Pipe Handles Ash Slurry
Steel piping systems are widely used at coal-fired power plants for a variety of purposes, including the conveying of coal ash slurry to nearby settling ponds, the transfer of limestone slurry to absorber spray towers for removal of SO2 and dilute hydrochloric acid from flue gases, and for transporting away the calcium sulfate by-product of the flue gas desulfurization process.
-
O&M
Air Casters Speed Equipment Moves
When it comes to moving megaton items like feedwater heaters or recirculating pumps, conventional moving tools such as wheel rollers, cranes, hoists, and come-alongs may be virtually useless. In some cases, moving large components is dangerous in a space-constrained location surrounded by delicate process control equipment. Feedwater heater and recirculating pump removal and replacement are […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
EPA’s Mercury Rule: Another Incarnation Coming
Much like the shape-shifting substance it regulates, the mercurial enforcement rule that governs mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants has changed unpredictably several times in recent years.
-
Nuclear
Collaborative Team Investigates Long-Term Nuclear Operations
The Atomic Energy Act originally established the length of a U.S. commercial nuclear reactor license as 40 years and made it renewable for another 20 years. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission has stated that it bases the length of these licenses (and the 50+ renewed licenses granted to date) not on any particular technical limitation but on whether the plant meets current safety requirements. Does this mean there could be reactor life after 60?
-
Nuclear
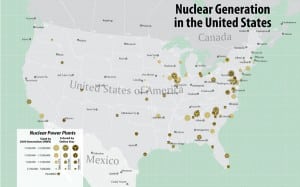
Map of Nuclear Generation in the United States
Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed. For full-sized maps, contact Platts.
-
Nuclear
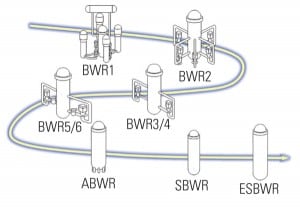
The Evolution of the ESBWR
The commercial nuclear industry is in the midst of developing multiple reactor technology options. Next in our series of articles exploring competing reactor technologies are GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) and Economic Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR). The design improvements incorporated into these reactors include passive safety systems, design and construction simplification, and component standardization to reduce construction and operating costs.
-
Gas
Smart Power Generation at UCSD
The University of California, San Diego has been accumulating awards for its savvy use of a constellation of power generation and energy-saving technologies. The campus already controls a fully functioning microgrid—including a cogeneration plant—and, as befits a research institution, is constantly looking for new ways to make its energy system smarter. This “living laboratory,” as campus leaders like to call it, demonstrates what it takes to build a smarter grid and why the effort is worth it.
-
Gas
Microturbine Technology Matures
Microturbine technology has evolved from early systems of 30 kW to 70 kW to today’s systems, which can have individual ratings of 200 kW to 250 kW. Packages up to 1 MW are now available that can be assembled into multipac units for projects of 5 MW to 10 MW. These modern units are packaged with integrated digital protection, synchronization, and controls; they produce high combined heat and power efficiencies; and they are capable of using multiple fuels.
-
Nuclear
Are Smaller Reactors Better?
Is a paradigm shift—an economic and engineering earthquake—in nuclear power plant design on the horizon? For most of the past 50 years, the mantra in planning new nuclear plants has been “bigger is better.” But a growing number of nuclear power engineers and designers are contemplating a world where small is beautiful.
-
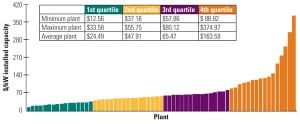
Nuclear
Benchmarking Nuclear Plant Capital Requirements
The EUCG Nuclear Committee’s primary goal is to optimize the costs and reliability performance of participating plants by publishing for its members a comprehensive database of performance metrics and best practices derived through surveys of its membership. Earlier reports examined staffing and performance data. In this exclusive EUCG report, we examine nuclear plant capital requirements.