Latest
-
News
Rust-Preventative Weldable Primer
Tempil introduced BLOXIDE°, a rust-preventive weldable primer that provides protection from rust formation on edges prepared for welding. It also acts as an oxygen/oxide scavenger in the weld pool. This results in a clean X-ray quality weld. Steel sections having their prepared edges coated with BLOXIDE° can be stored outside in open yards for extended […]
-
News
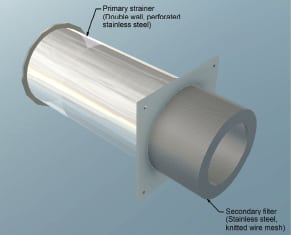
Patented Filter Medium for Core Cooling
Multi-disciplined engineering and consulting firm ENERCON received patents for a filter medium for strainers used in nuclear reactor emergency core cooling systems (ECCS). ENERCON’s Debris Bypass Eliminator was developed in response to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s Generic Safety Issue, GSI-191, “Assessment of Debris Accumulation on PWR Sump Performance.” During long-term recirculation for cooling of the […]
-
News
True Machine Train Alignment
Ascertaining the alignment of all machines in a multiple machine train has always been a cumbersome and time-consuming process. The new ROTALIGN ULTRA MultiCoupling feature allows the alignment of up to seven machines in a train to be measured simultaneously, with a single quarter rotation (or less) of the shafts. This saves time and resources […]
-
Commentary
Natural Gas: Secure Supply for Today and the Future
Ten years ago, I could not have written this column. The natural gas industry was different—limited domestic supply resulted in unstable prices. However, recent advancements in drilling technology have enabled the industry to discover, access, and produce abundant sources of natural gas in America. Because the industry has changed, the country’s energy future is now […]
-
News
NRC: SCE Must Address Unusual Tube Wear at San Onofre Before Restarting
Southern California Edison (SCE), operator of the San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station near San Clemente, Calif., must understand and address unusual wear on steam generator tubes before it can be allowed to restart the beleaguered two-reactor nuclear plant, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) said on Tuesday. California officials are meanwhile preparing contingency plans to prevent power outages this summer that could result from the plant’s indefinite shutdown.
-
News
NRC to Decide on SCANA COL on Friday
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) will decide on Friday whether to award a combined construction and operation license (COL) to SCANA Corp.’s proposed project for two 1,117-MW reactors at the site of the V.C. Summer Nuclear Station near Jenkinsville, S.C. If the SCANA Corp. project receives the NRC’s approval, it will be the second project in nearly 30 years to receive such approval.
-
News
AEP’s Planned Retirements Less Than Initially Anticipated
Official notifications to regional reliability organizations PJM Interconnection and Southwest Power Pool (SPP) made last week by American Electric Power (AEP) show that the company will retire about 4,600 MW of coal-fired capacity to comply with a series of Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) rules. The plan differs markedly from the 6,000 MW of anticipated retirements AEP announced in June 2011.
-
News
Bulgaria Scraps Russian-Led Belene Nuclear Project, Opts for Natural Gas Plant
Bulgaria on Wednesday definitively abandoned plans to build the Belene nuclear plant based on Russian technology, saying it would instead build a gas-fired power plant on the Danube River site. Bulgarian Prime Minister Boyko Borisov cited soaring costs as well as a failure to find Western partners for the projects after German company RWE withdrew from the project in 2009.
-
News
Regulators OK Gas-Fired Power Plants for Louisiana, Florida
Two natural gas–fired projects received key approvals from state regulators this week. The Florida Public Service Commission on Tuesday approved Florida Power & Light’s (FPL’s) proposed 1,277-MW gas unit for Broward County, Fla., and Louisiana’s Public Service Commission approved Entergy’s 550-MW gas project for Jefferson County, La.
-
News
DOE Boosts Small Reactor Design Development with $450M Funding Announcement
Pushing for an “all-out, all-of-the-above” energy strategy, the Obama administration last week announced new funding to advance the development of small modular reactors (SMRs) in the U.S.