Solar
-
Coal
Abundant Clean Energy Fuels Brazil’s Growth
Brazil’s power industry has long been dominated by its vast hydro resources, which historically have accounted for over 80% of the country’s generation capacity. With engineering marvels like the massive Itaipú dam and the proposed Belo Monte project, the country is a leader in the development and use of hydroelectricity on a grand scale. But as the 2001 energy crisis proved, dependence on a single source leaves the country vulnerable to severe shortages. Thanks to government programs designed to take advantage of the country’s favorable climate, Brazil is committed to diversifying its energy mix while continuing to maintain a renewable energy focus.
-
Coal
Editors Select Top Five Stories of 2011
The POWER editorial staff’s picks for the most significant stories of 2011.
-
Solar
The U.S. Military Gets Smart Grid
At home and abroad, U.S. military microgrid and smart grid projects are driven by energy security concerns. The pace of such projects, however, can be slow, and the potential for civilian grids to benefit from lessons learned and technologies developed for these important installations may be limited.
-
Coal
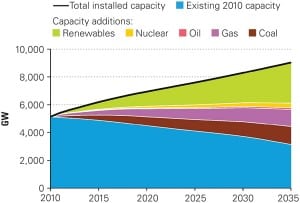
World Energy Outlook Forecasts Great Renewables Growth
Driven by policies to limit carbon emissions, as well as government subsidies, the share of worldwide nonhydro renewable power is set to grow from just 3% in 2009 to 15% in 2035, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its recently released World Energy Outlook 2011. Under the same scenario—which assumes that carbon pricing, explicit […]
-
Coal
U.S. Confronts Pipeline Gaps While Europe Juggles Renewables and Debt
U.S. optimism has been restored by reports of abundant, reasonably priced natural gas to fuel most new generation; however, huge gaps in the fuel delivery system (thousands of miles of pipelines are needed) will soon challenge gas plant development. Meanwhile, the cloud of sovereign debt hangs over all major capital projects in Europe, where the UK moves ahead with new nuclear projects while many of its neighbors shut the door on nuclear and struggle to finance their commitment to renewables.
-
Coal
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan Pushes Power Industry in New Directions
The Five-Year Plan is the expression of the centralized planning goals for China’s economy. The 12th Five-Year Plan, approved by the Chinese Government on March 14, 2011, established many social and economic goals, including significant expansion of the country’s power generation industry in many new directions.
-
Solar
U.S.-China Solar Trade Dispute Gets Thornier
A trade row between the Chinese government and solar panel makers around the world intensified in December. As China’s Ministry of Commerce refuted allegations that the Chinese government uses illegal subsidies, discounts for raw materials, preferential loans, tax incentives, and currency manipulation to drive down prices and amplify exports of Chinese solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) affirmed the U.S. solar industry is “materially injured” by imports, at “less than fair value,” of Chinese crystalline silicon PV cells and modules.
-
Solar
Top Plant: Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center, Indiantown, Martin County, Florida
The 75-MW Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center is the first hybrid solar facility in the world to combine a solar thermal array with a combined cycle natural gas power plant. Because the facility uses a steam turbine, transmission lines, and other infrastructure from an existing combined cycle unit, financial savings of approximately 20% were achieved compared to what a similar stand-alone solar plant would have cost.
-
Solar
Top Plant: Sarnia Solar Project, Sarnia, Ontario, Canada
The 80-MW Sarnia Solar Project is the world’s largest operational photovoltaic plant, with 1.3 million solar modules. The facility utilizes First Solar’s proven thin-film photovoltaic (PV) technology, which has the lowest environmental footprint and the fastest energy payback of current PV technologies.
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.