Nuclear
-
Nuclear
Warm Water, Repairs, and a “Dropped” Control Rod Separately Prompt Reactor Shutdowns
As warmer-than-average waters in Connecticut’s Long Island Sound last week prompted Dominion to shut down one unit at its Millstone Nuclear Plant, an ammonia release caused an evacuation of part of Tennessee Valley Authority’s Watts Bar Unit 1, and Constellation Energy shut down of its Calvert Cliffs Unit 1 reactor after a control rod unexpectedly dropped into the reactor’s core. Then, on Tuesday, Xcel Energy shut down its Monticello Nuclear Generating Plant and Unit 1 of its Prairie Island Nuclear Generating Plant for repairs.
-
Nuclear
UPDATED: NRC Freezes Final License Decisions, Court Prolongs Yucca Mountain Saga
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) on Tuesday put a hold on all final licensing decisions—include those for 19 construction and operating licenses (COLs), 12 license renewals, and one operating license—until the federal body can hash out how it will deal with spent nuclear fuel. The order comes on the heels of an Aug. 3 federal court ruling that puts off a decision on whether to force the NRC to act on the Yucca Mountain permanent nuclear waste repository’s long-pending license application.
-
Nuclear
A Bumpy Road for Nukes
Washington, D.C., 6 August 2012 — It’s been a rough road for nuclear advocates in the U.S. of late, although nothing seems to dent the Pollyanna armor of the nuclear crowd, always appearing to believe a revival is just over the horizon and headed into view. Here are a few fraught developments for the nuclear […]
-
Nuclear
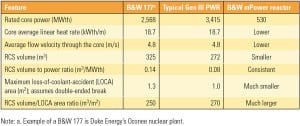
Small Is the New Big: The B&W Small Modular Reactor
Small reactors are big news, particularly the 180-MWe Generation III++ Babcock & Wilcox mPower small modular reactor (SMR). This SMR has all the features of its larger cousins, but the entire reactor and nuclear steam supply system are incorporated into one reactor vessel, all about the size of single full-size pressurized water reactor steam generator. Expect the first mPower—and probably the first SMR—to enter service before 2022.
-
Nuclear
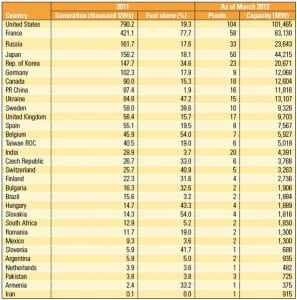
2011 Nuclear Industry Scorecard
The world nuclear industry experienced few substantial changes in performance metrics for 2011—beyond Japan, that is. In the aftermath of Fukushima, the once–world leading Japanese nuclear industry fell to the bottom of the rankings, perhaps for good.
-
Nuclear
Too Dumb to Meter, Part 3
As the book title Too Dumb to Meter: Follies, Fiascoes, Dead Ends, and Duds on the U.S. Road to Atomic Energy implies, nuclear power has traveled a rough road. In this POWER exclusive, we present the third chapter, “Micro-Mismanagement by Committee.” During the frenzy to manage atomic power after World War II, Congress created an executive branch agency that threatened to be too independent, too powerful, and too isolated from the rest of government. Compounding their errors, perhaps in recognition of what they had created, the solons also developed a way to insert their own power into the action. This proved to be a major mistake—blurring the lines between executive and legislative authority—causing no end of problems for the nation’s nascent atomic energy venture.
-
Nuclear
EIA: U.S. Nuclear Uprates Since 1977 Equal Construction of Six New Nuclear Plants
Since 1977, more than 6,500-MW of nuclear uprates and been approved and many implemented in the U.S.—equivalent to the construction of six new nuclear power plants, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) said in an update on Wednesday.
-
Nuclear
SCE: Most Tube Wear at San Onofre “Not Unusual”
Most steam generator tube wear or tube wall thinning at Southern California Edison’s (SCE’s) two-reactor San Onofre Generating Station (SONGS) was less than 20%—far below the 35% wall-thinning limit that would require the tubes to be plugged, data released last week by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission shows. Much of the wear was not "unusual," SCE said in a statement.
-
Nuclear
DOE Announces $13 M in Nuclear Innovation Awards
The Department of Energy (DOE) on Tuesday announced nearly $13 million in nuclear energy innovation awards. The awards include $10.9 million to 13 projects to solve common challenges, including improving reactor safety, performance and cost competitiveness and $1.6 million in three university-led education projects.
-
Nuclear
Court Increases Spent Nuclear Fuel Storage Award to Kansas Plant Owners
Owners of the Wolf Creek Nuclear Power Plant in Kansas are entitled to $12.6 million in damages stemming from the federal government’s partial breach of a contract for disposal of spent nuclear fuel, $2 million more than previously awarded, a federal court ruled last week.