Coal
-
O&M
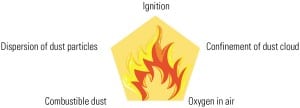
Controlling Fugitive Combustible Coal Dust
Regardless of how much prevention is employed to mitigate combustible dust in coal-fired power plants, fugitive coal dust is pervasive and can be dangerous. In coal-fired power plants, mechanical transfer points are leading sources for airborne fugitive dust. However, because coal dust travels quickly over large areas with minimal airflow, fugitive combustible dust settles in many areas.
-
O&M
Emerging Technologies Enable “No Regrets” Energy Strategy
Achieving a balance between affordable and sustainable electricity while improving reliability is a challenge unlike any the electricity sector has faced since its inception. Technology innovations in key areas such as energy efficiency, smart grid, renewable energy resources, hardened transmission systems, and long-term operation of the existing nuclear and fossil fleets are essential to shaping the future of electricity supplies.
-
Coal
Slow Growth Ahead—with Unexpected Flares of Activity
North American shale gas was supposed to realign the generation fleet here and abroad (thanks to anticipated exports) far into the future. Turns out, that’s not exactly how the near term is shaping up. Despite stagnant (and even putrid) economies and legislative bodies in the U.S. and EU, there promises to be sufficient market volatility to keep everyone alert.
-
Coal
Coal Battered Early, Later Rebounds
For the first time, U.S. generation from coal and natural gas was equal in 2012, although just momentarily. Gas dominated early in the year, but as gas prices rose in response to supply and demand forces, coal use rebounded. Expect more of the same give-and-take in 2013.
-
History
The Russian Power Revolution
Exports of natural resources have given Russia increased global political and economic clout. But domestically, the world’s fourth-largest generator of electricity has had to embark on the most ambitious reforms ever undertaken to modernize dilapidated Soviet-era power infrastructure and incentivize a massive capacity expansion to support a revived economy.
-
Coal
EPA Tightens Fine Particulate Matter NAAQS
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Friday issued a final rule that strengthens its National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) for fine particulate matter (PM2.5) to 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m3) but declared it would not finalize a proposal to update separate secondary PM2.5 standards. The final rule’s issuance was lauded by environmental and public health groups, though industry groups opposed it, citing concerns that nonattainment areas would suffer economic setbacks.
-
Coal
UPDATE: EPA’s First GHG Permitting Violation Reaps $34,000
Major oil and gas production company Vintage Production California and its subsidiary OXY USA last week agreed to pay $34,000 to resolve the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) first greenhouse gas (GHG) permitting violation case.
-
Coal
AEP to Retire 800-MW Big Sandy Coal Unit By 2015
Six months after withdrawing a $1 billion plan to retrofit its 49-year-old Big Sandy coal-fired plant near Louisa, Ky., from the Kentucky Public Service Commission (PSC), American Electric Power (AEP) operating unit Kentucky Power on Wednesday announced it would retire the plant’s 800-MW Unit 2 by 2015 and will decide on the future of its 278-MW Unit 1.
-
Coal
Reserve Margins in Texas Barely Healthy Again, ERCOT Says
Texas could again see tight power supplies in the summer of 2013 and beyond—with reserve margins dropping to 2.8% by 2022—even though the outlook has improved, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) warned in its latest long-term outlook released on Monday.
-
Coal
Report: Fuel for Power Generation to Lead Energy Growth Through 2040
Fuel for power generation will account for about 55% of demand-related energy growth through 2040, ExxonMobil forecasts in its freshly released annual energy forecast. Like several other forecasters, the Irving, Texas–based oil and gas company also predicts that natural gas will emerge as the leading source of electricity generation by 2040. Among key findings in […]