Coal
-
Coal
Virginia Moves to Repeal Incentives for Renewable Power
An agreement reached between the Virginia Attorney General’s office, Dominion Virginia Power, and Appalachian Power proposes to reduce financial incentives associated with the utilities’ generation of renewables and construction of new fossil fuel–fired power plants.
-
Coal
Federal Court Declines to Bind EPA to New Source MATS Deadline
A federal appeals court last week denied a motion from developers of new coal- and oil-fired power plants to force the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to finalize its reconsidered Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) for new sources by March and help them avoid a regulatory Catch-22 posed by a looming rule to curb greenhouse gas emissions in new plants.
-
Coal
EPA Rules, Economy, Natural Gas Prices Prompt Georgia Power to Retire 2 GW of Coal, Oil Power
Georgia Power on Monday said it was seeking state regulatory permission to decertify and retire 15 coal- and oil-fired generating units—a total capacity of 2,061 MW—citing several factors, including costs to comply with existing and future environmental regulations, economic conditions, and lower natural gas prices.
-
Coal
DOE, EPA Nab 25th Settlement for Emission Control under Clean Air Act New Source Review
A settlement reached with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Department of Justice to resolve alleged violations of the Clean Air Act will require Wisconsin Public Service (WPS) to invest about $300 million in pollution control technology, pay a civil penalty of $1.2 million, and spend $6 million on environmental mitigation projects.
-
Coal
Kentucky Utilities to Upgrade Ghent Plant as Part of EPA Settlement
In a settlement with the federal government, Kentucky Utilities has agreed to spend $57 million to install a sulfuric acid mist emission control system, replace a coal-fired boiler, and pay a civil penalty of $300,000 to resolve alleged Clean Air Act violations at its 2-GW coal-fired Ghent Station.
-
Coal
EPA Finalizes Standards for Industrial Boilers, Certain Incinerators
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Dec. 20 finalized changes to a specific set of adjustments to Clean Air Act that apply to a coal, oil, natural gas and biomass boilers and certain solid waste incinerators.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: The Coal Pile
About 1,199 new coal-fired facilities (as defined by the World Research Institute)—a total installed capacity of 1,401 GW—were being proposed globally as of July 2012, spread across 59 countries.
-
Coal
Safety a Main Theme at Asian Coal Users’ Meeting
Power plant operators, managers, and other professionals from across Southeast Asia met in Hong Kong in early November for the second annual Asian Sub-Bituminous Coal Users’ Group meeting, created to share information and best practices related to safety, handling, combustion, characteristics, and risk management of the fuel.
-
O&M
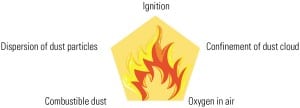
Controlling Fugitive Combustible Coal Dust
Regardless of how much prevention is employed to mitigate combustible dust in coal-fired power plants, fugitive coal dust is pervasive and can be dangerous. In coal-fired power plants, mechanical transfer points are leading sources for airborne fugitive dust. However, because coal dust travels quickly over large areas with minimal airflow, fugitive combustible dust settles in many areas.
-
O&M
Emerging Technologies Enable “No Regrets” Energy Strategy
Achieving a balance between affordable and sustainable electricity while improving reliability is a challenge unlike any the electricity sector has faced since its inception. Technology innovations in key areas such as energy efficiency, smart grid, renewable energy resources, hardened transmission systems, and long-term operation of the existing nuclear and fossil fleets are essential to shaping the future of electricity supplies.