POWER
-
News
Glycol Pumps for Gas Dehydration
Cat Pumps launched a new series of glycol pumps developed to supply triethylene glycol for natural gas dehydration systems. System reliability, especially of the pump, is essential to minimize production interruptions and costly equipment failures. The TEG triglycol pumps have been field-proven in the most rigorous dehydration systems, Cat Pumps says. The electric engine–driven TEG […]
-
Nuclear
THE BIG PICTURE: Underground Nuclear Waste Disposal
According to the International Atomic Energy Commission, deep disposal in stable geological formations is the only sustainable way to safely manage spent fuel and high-level waste (HLW) from nuclear power reactors. No permanent geological repository has yet been built, but some countries have found a location for a future repository. Others are researching the option…
-
O&M
Mitigating the Effects of Flexible Operation on Coal-Fired Power Plants
As coal-fired power plants increasingly operate in cycling modes, many plants are confronting the potential for higher levels of component damage and degraded performance of environmental control equipment. Generators and EPRI are working together to find ways to mitigate the effects of cycling operation and to manage the transition of formerly baseload plants to flexible operation.
-
Smart Grid
Milestones for Flywheel, Lithium Battery Grid-Scale Projects
Energy storage developments got a boost as Beacon Power Corp. in June announced that its first flywheel energy storage plant in Stephentown, N.Y., achieved its full 20-MW capacity, and AES Energy Storage said its Los Andes battery storage system in Chile had performed continuously for more than 18 months as a critical reserve unit for the nation’s northern grid.
-
Nuclear
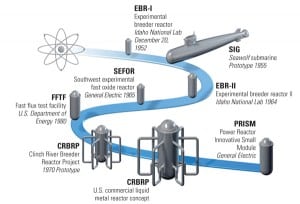
PRISM: A Promising Near-Term Reactor Option
PRISM is an advanced sodium-cooled reactor that simultaneously reduces proliferation concerns by consuming transuranics and weapons-grade plutonium and closes the nuclear fuel cycle. PRISM’s passive safety systems, successfully demonstrated in earlier liquid metal reactor programs, combined with modern design requirements, make PRISM invulnerable to most serious accidents that can affect light water reactors.
-
Gas
Alstom Launches Upgraded GT26
Just as GE Energy, Siemens, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) in May announced gas combustion technology developments—each seeking to push the 60% barrier with new gas turbine designs—Alstom has quietly been upgrading its KA26 combined cycle power plant. (See the July 2011 “Global Monitor” for more information on the GE, Siemens, and MHI turbines.) The firm says that the next generation of the 500-MW power plant, based on the advanced class GT26 gas turbine, features “achievable” efficiencies of over 61%, increased flexibility, and more than 350 MW, which can be delivered in less than 15 minutes to help integrate renewable energy sources (Figure 3).
-
Smart Grid
Accelerating the Pace of EV Deployment
A number of automotive manufacturers, electric utilities, electric power associations, and research groups are working to develop and evaluate technical approaches to integrating plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) into the U.S. electrical grid system. This is a key requirement of facilitating widespread, near-term adoption of PEVs by the American public.
-
Coal
Largest CCS Project in Operation
Companies continue to increase the size of carbon capture and sequestration test projects. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has launched operation of what it calls the world’s largest demonstration of carbon capture on a pulverized coal plant.
-
Marmaduke
Marmy’s One-Squirt Celebration
Steve Elonka began chronicling the exploits of Marmaduke Surfaceblow—a six-foot-four marine engineer with a steel brush mustache and a foghorn voice—in POWER in 1948, when Marmy raised the wooden mast of the SS Asia Sun with the help of two cobras and a case of Sandpaper Gin. Marmy’s simple solutions to seemingly intractable plant problems remain timeless. This Classic Marmaduke story, published more than 50 years ago, reminds us that an overhaul or startup may not go as planned, but it can still have a happy ending.
-
Hydro
Chile, Peru Put the Brakes on Mega-Hydro Projects
Weeks after Brazil’s environmental agency, IBAMA, granted final approval for construction of the mammoth 11.2-GW Belo Monte Dam in the Amazon region to proceed, an appeals court in Chile suspended plans for the 2.75-GW multi-dam HidroAysen project in the Patagonia region, and Peru’s government terminated a concession for the 1.5-GW Inambari in the Peruvian Amazon area after month-long mass protests (Figure 5).