POWER
-
News
Correction
In “Siemens Releases ‘ShapingPower’ Option for Renewables Integration” (December 2011), the Figure 3 callouts for wind and solar were reversed. POWER regrets the error. A corrected version can be found in the online version of the article. â–
-
Solar
U.S.-China Solar Trade Dispute Gets Thornier
A trade row between the Chinese government and solar panel makers around the world intensified in December. As China’s Ministry of Commerce refuted allegations that the Chinese government uses illegal subsidies, discounts for raw materials, preferential loans, tax incentives, and currency manipulation to drive down prices and amplify exports of Chinese solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) affirmed the U.S. solar industry is “materially injured” by imports, at “less than fair value,” of Chinese crystalline silicon PV cells and modules.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Green Technology = Green Jobs?
In discussing implementation by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) of California’s new renewable energy law, CPUC Commissioner Timothy Alan Simon urged consideration of the economic, technical, and political consequences of the CPUC’s actions: “Renewable energy is a fuel source—it’s not a religion.” The promotion of renewable energy remains critical, but as Commissioner Simon admonishes, […]
-
Coal
Editors Select Top Five Stories of 2011
The POWER editorial staff’s picks for the most significant stories of 2011.
-
Coal
U.S. Confronts Pipeline Gaps While Europe Juggles Renewables and Debt
U.S. optimism has been restored by reports of abundant, reasonably priced natural gas to fuel most new generation; however, huge gaps in the fuel delivery system (thousands of miles of pipelines are needed) will soon challenge gas plant development. Meanwhile, the cloud of sovereign debt hangs over all major capital projects in Europe, where the UK moves ahead with new nuclear projects while many of its neighbors shut the door on nuclear and struggle to finance their commitment to renewables.
-
Coal
Gas Taxes: Carbon Taxes Around The World
A supplement to “The Big Picture: Gas Taxes” in our January 2012 issue.
-
Solar
Top Plant: Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center, Indiantown, Martin County, Florida
The 75-MW Martin Next Generation Solar Energy Center is the first hybrid solar facility in the world to combine a solar thermal array with a combined cycle natural gas power plant. Because the facility uses a steam turbine, transmission lines, and other infrastructure from an existing combined cycle unit, financial savings of approximately 20% were achieved compared to what a similar stand-alone solar plant would have cost.
-
News
Irrational Exuberance
Germany’s government has decided to shutter all 17 of its nuclear plants (23 reactors); eight plants are now closed for business, six more will be closed by 2021, and the final three will close by 2022. What is lacking is an honest discussion of the rising cost Germans will pay for electricity for what The Economist describes as “the greatest change of political course since unification.”
-
Hydro
Top Plant: Pelton Round Butte Hydroelectric Project’s Selective Water Withdrawal Project, Oregon
In December 2009, construction of an underwater tower and fish collection structure was successfully completed at the 465-MW Pelton Round Butte Hydroelectric Project. The first-of-its-kind fish bypass and intake structure returns temperatures in the lower Deschutes River to historic patterns and restores downstream passage of Chinook, steelhead, and sockeye salmon while maintaining existing generating capacity.
-
Waste to Energy
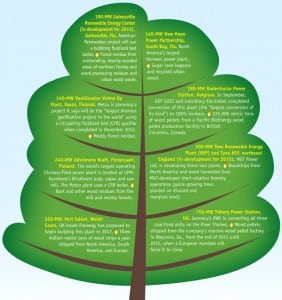
The Big Picture: Big Biomass
The world’s biomass power facilities, not counting those in the pulp and paper industry, average just 18 MWe to 20 MWe. In the U.S., passage of the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 ignited development of many existing biomass plants. Greenhouse gas rules and renewable policies around the world have kindled a new generation of much larger biomass facilities. New announcements routinely are for plants 50 MW or larger, presumably to leverage economies of scale.