Water
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: Parched
Water scarcity as it relates to energy use is becoming a major concern.
-
Water
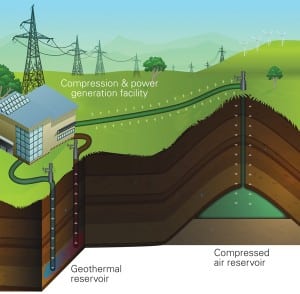
Energy Storage Developments and Demand Ramp Up
Despite technical and financial hurdles, annual global demand for grid-scale energy storage is expected to soar to 185.4 GWh by 2017, which means a possible 231% average year-on-year demand growth between 2012 and 2015, according to Lux Research.
-
Coal
Water Issues Challenge Power Generators
Drought and competing uses for water continue to challenge power plant operators worldwide. In response, innovative approaches for reducing water use are being explored from South Africa to China.
-
O&M
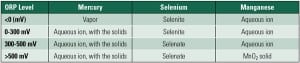
ORP as a Predictor of WFGD Chemistry and Wastewater Treatment
Recent studies have shown that system oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) is not only an important factor for predicting wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGD) absorber chemistry but also may be a predictor of process equipment corrosion and wastewater treatment requirements.
-
Coal
Your Guide to the White House Climate Action Plan
President Obama’s highly anticipated Climate Action Plan (CAP) released today outlines a wide variety of executive actions founded on three pillars: slashing U.S. carbon pollution through stringent rules for new and existing power plants while doubling renewables deployment and promoting fuel switching from coal to natural gas; preparing the U.S. for impacts of climate change; and leading international efforts to combat global climate change.
-
O&M
LADWP Harnesses LMS100 to Solve Once-Through Cooling Dilemma
Los Angeles sits alongside the world’s largest body of water, and naturally the city’s Department of Water & Power (LADWP) placed its generating stations along the shoreline to take advantage of that abundant resource for cooling. The LADWP built three coastal generating stations that provide the city with 2,162 MW, about 35% of the peak annual demand.
-
O&M
Microbial Control in Cooling Water Improves Plant Performance
Microbial inhibition, as part of a robust cooling water treatment program, presents a special challenge because of the variability in makeup water sources, plant processes, and discharge permits. Failure to maintain a proper microbial inhibition program will affect your bottom line as a result of heat rate degradation.
-
Water
A Moderating Tone from the EPA on 316(b)?
Final water intake structure rules from the EPA expected this June suggest the agency may be listening to industry and even moderating its tone. Stretch goals as part of the Section 316(b) rule are likely, but overall the rule may prove more reasonable than many expected.
-
Solar
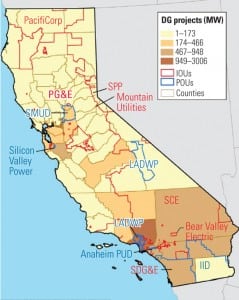
Distributed Generation: California’s Future
Once you synthesize all the elements of the Golden State’s clean energy strategy and extrapolate current trends, it’s easy to see that an impending break with the traditional power generation paradigm is coming, intended or not.
-
Water
Research Center Dedicated to Power Plant Water Use Opens
The Electric Power Research Institute and several partners—including the Southern Research Institute, Southern Co. subsidiary Georgia Power, and Southern Research—are testing a new technology that could reduce the amount of water needed for power plant cooling.