Smart Grid
-
Legal & Regulatory
Speeding Forward with Integrating Plug-in EVs
Approximately 150,000 plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) are already on the road in the United States, according to various reports. These vehicles include relatively wallet-friendly PEV options like the
Tagged in: -
Smart Grid
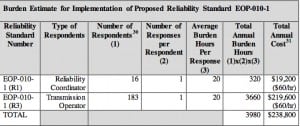
FERC Seeks Comments on Proposed Geomagnetic Disturbance Standard
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)—which notes that geomagnetic disturbances (GMD) can have potentially severe, widespread impact on the bulk electric power system—has issued a notice of proposed rulemaking (NOPR) to approve its first reliability standard concerning GMD operations. The NOPR issued on Jan. 16 concerning Reliability Standard EOP-010-1 is designed to mitigate the effects […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
A Rising Tide of Regulation and the “Kick-the-Can” Gambit
A tidal wave of pent-up federal regulations could surge across much of the electricity industry in 2014. In recent years, Congress has been unable to enact new laws in energy, which has led a frustrated
Tagged in: -
Commentary
How U.S. Power Generators Are Preparing for 2014
The business environment for generating companies worldwide continues to become increasingly complex, and not just as a result of regulations. Even in the U.S., the concerns and constraints faced by generators
Tagged in: -
Commentary
“Smart Grid” or “Strong Grid”? Words Matter
The Obama administration recently changed its nomenclature on a topic of much interest to readers of this publication and those in the power industry. The administration has said it prefers to talk about its policies advancing a “resilient grid” as opposed to its previous emphasis on developing a “smart grid.” The new policy thrust, for […]
-
Smart Grid
Impact of Electric Vehicle Charging on Grid May Be Far Less Than Feared
In recent years, the potential popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid-electric vehicles has had utility executives up nights worrying about spikes in demand at the end of every workday as EV owners all began charging their cars upon returning home. Now, a new study from Austin, Texas–based Pecan Street Research (PSR) suggests that […]
Tagged in: -
T&D
Potential Solutions for ERCOT’s Challenges
P at Wood III —former head of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and the Texas Public Utility Commission, and current consultant and non-executive chairman of Dynegy—addressed a packed house at the
-
Smart Grid
Vehicle-to-Grid Aggregated Project Sells Electricity to the Grid
A technology developed by the University of Delaware (UD) and NRG Energy that provides a two-way interface between electric vehicles and the power grid earlier this year became an official paid resource on PJM Interconnection’s regional grid (Figure 4). One of the first of its kind, the project proves the so-called “vehicle-to-grid” (V2G) concept can sell electricity from electric vehicles.
-
Smart Grid
EPB Chattanooga Uses Smart Grid to Future-Proof Its Business Model
A municipal utility in the South may not be where you’d expect to find an exemplary smart grid implementation, but that’s just fine with EPB Chattanooga. Its leaders are raking in the kudos—including POWER’s 2013 Smart Grid Award—and their community is attracting new businesses in response to a fiber-optic-based system that has helped raise the profile of their city and bolster the sustainability of their utility.
-
Smart Grid
Industry-Backed Bipartisan Cybersecurity Bill Passes Senate Committee
The Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation on Tuesday unanimously approved a bipartisan bill that bolsters efforts by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to craft a cybersecurity framework.