Nuclear
-
Nuclear
Initial Experiments Meet Requirements for Fusion Ignition
Scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s National Ignition Facility (NIF) in California speculate that a prototype nuclear fusion power plant could be operational within a decade, thanks to a test of the world’s largest laser array that confirmed a technique called inertial fusion ignition is feasible. Their first experiments have demonstrated a unique physics effect that bodes well for NIF’s success in generating a self-sustaining nuclear fusion reaction. Fusion energy is what powers the sun and stars.
-
Nuclear
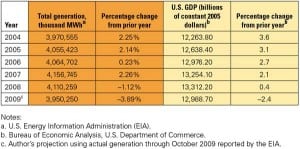
Benchmarking Nuclear Plant Staffing
The EUCG Nuclear Committee has collected benchmarking data of U.S. nuclear plant staffing for many years. A summary of this highly desirable data was gleaned from EUCG databases and is now, for the first time, made public through an exclusive agreement with POWER.
-
Nuclear
U.S. Spins Nuclear Wheels as Other Nations Roll Out New Plants
President Barack Obama’s January State of the Union speech called for incentives to make clean energy profitable — mainly through the construction of a new generation of nuclear power plants. That comment, an apparent effort to reach out to Republican members of Congress, drew furious applause. Within three weeks, the president’s backing of nuclear power had already made a significant impact on the U.S. nuclear sector.
-
Nuclear
China Nuclear Plant Construction Gets Boost—With Technology Transfer
China’s nuclear power plant building spree got a little more frenzied this January, as the country kicked off its 21st project at Ningde 3.
-
Nuclear
Concerns About Electromagnetic Interference in Nuclear Plants Related to Digital Upgrades
In order to operate aging nuclear power plant instrumentation and control systems for up to 60 more years or longer, there must be a smooth transition from existing analog technologies to advanced digital platforms. For this to occur, electromagnetic compatibility concerns related to both qualification testing and the electromagnetic environment must be addressed to ensure safe and reliable operation of these systems within the plant’s electromagnetic and radio frequency interference environment. By understanding the regulatory requirements and sharing implementation experience, digital system upgrades can be installed successfully.
-
Nuclear
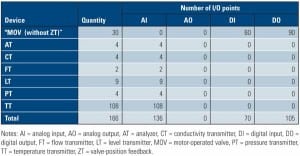
The Advanced Digital Fieldbus Option for Nuclear Plants
Digital fieldbus technologies, including Foundation fieldbus and Profibus, are increasingly being used with success in the nuclear and fossil fuel power industries. This article compares a conventional control system with a Foundation fieldbus – based digital control system used in a typical circulating water system in a nuclear power plant. As shown in this example, using digital fieldbus technologies can result in significant savings in terms of installation and hardware costs.
-
Nuclear
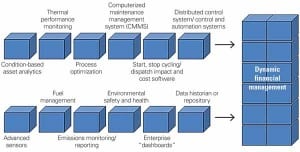
The Value of a Knowledge-Based Culture Grows in Lean Times
Given delays and cancellations of new generating capacity, pushing the existing power generation fleet is more important than ever. At ELECTRIC POWER 2009, multiple presentations explored the premise that an active knowledge management strategy — requiring a blend of digital and human elements unique to each power plant — will help you extract the most productivity from your assets.
-
Nuclear
Nontechnical Issues Affecting Digital Upgrades at Nuclear Power Plants
Existing nuclear power plants are increasingly facing the conversion to digital instrumentation and controls technology. Meanwhile, new nuclear designs have digital technology integrated throughout the plant. Digital controls will soon be inevitable, so how do we make the transition as smooth as possible? Without losing focus on the technical solutions, organizations have to pay attention to the nontechnical issues as well.
-
Coal
Digital Plant Controls Provide an Essential Edge
It’s a digital world, and even aging power plants are experiencing the benefits of digital controls technologies. The following cover stories provide insight into the latest options and inspiration for your own plant controls projects.
-
Coal
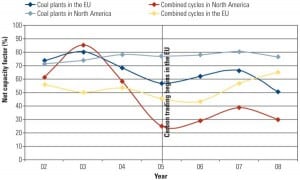
The Impact of Carbon Trading on Performance: What Europe’s Experience Can Teach North American Generators
The European carbon trading system experience suggests that North American generators should expect severely altered coal-fired power plant operating profiles if cap-and-trade legislation becomes law. In a groundbreaking study, Solomon Associates predicts the reduction in mean run time that North American generators should expect. The trends outlined in this study provide an overview of some of the broad challenges facing generators in moving to a carbon-constrained market environment.