Environmental
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.
-
O&M
Solid Fuels: Moving Material and Managing Emissions
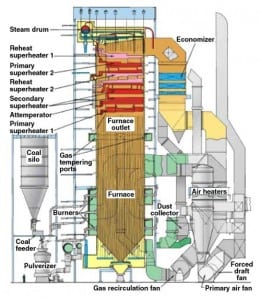
In today’s solid-fueled power plant, managing emissions and moving materials more defines the task than the traditional work of making megawatts. That’s the message that emerged from the coal and solid fuels track at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER.
-
Coal
Biomass Boiler Market Remains Unpredictable
Utilities struggling to meet renewable portfolio standards requirements have studied the conversion of existing coal-fired boilers to burn biomass. The results of those studies have been mixed, although test burns continue; the results of one such test are included. Overall, the market is tending toward smaller biomass projects, and the low price of natural gas is perhaps the biggest reason utility-scale projects are now few and far between.
-
Coal
Re-Industrializing America with Clean Coal Technologies
Balancing the rising energy needs of a globally expanding population (most of which lives in poverty) against the need to reduce increases in atmospheric emissions is a monumental problem. What role can clean coal technologies play?
-
O&M
Applying CFD to Optimize Furnaces Cofiring Biomass, and the Impact of Cofiring on SCR
The international policy framework regulating the emissions of greenhouse gases from industrial and utility boilers is in flux. Meanwhile, most boiler owners are evaluating potential strategies for when, not if, more stringent emissions reduction regulations are put in place. One of the most attractive compliance options is the cofiring of biomass in existing coal-fired boilers.
-
Coal
ERCOT Predicts No Coal Retirements from EPA Rules
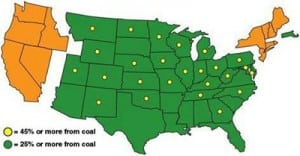
In surprising findings, given the state’s often-contentious relationship with the Environmental Protection Agency, a study released May 11 by the Texas grid operator concludes that a suite of looming EPA rules to reduce conventional and hazardous air pollution from power plants and to tighten power plant cooling water regulations likely would not force the retirement of any Texas coal plants.
-
Coal
Southern CEO Sees Federal "War on Coal"; Questions Dash to Gas
In a wide-ranging speech on U.S. electricity policy, Southern Co. Chairman, President, and Chief Executive Officer Thomas Fanning said that coal is "under attack" by the federal government, that natural gas may not be the panacea seen by some utilities facing environmental constraints on their coal plants, and that federal proposals to sharply reduce utility hazardous air pollution have unreasonable compliance deadlines that should be extended.
-
Coal
Proposed Clean Energy Agency Has Cost Issue
Even as Senate energy leaders gear up to re-introduce widely supported legislation to create the Clean Energy Deployment Administration, they have acknowledged that the bill faces a heightened problem this term: the need to find nearly $10 billion in offsets to pay for the new green energy financing authority at a time of overwhelming concern about the federal debt.
-
Coal
Large-Scale Tests Begin to Convert Flue Gas to Usable Water
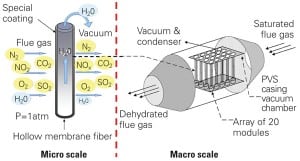
Subsidized by the Dutch government, a number of Dutch utilities, the European Membrane Institute at the University of Twente, and Dutch consulting firm KEMA have, for over a decade, been testing membrane technology that promises to directly convert water vapor from power and other industrial plants’ flue gases into drinking water. The technology could provide a new source of large volumes of potable water.
-
Environmental
Researchers Develop Supercritical CO2 Brayton Cycle Turbines
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories say a project that focuses on supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) Brayton cycle turbines is moving to the demonstration stage.