Coal
-
O&M
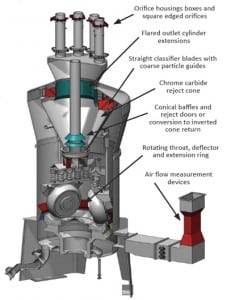
Pulverizers 101: Part I
Pulverizers prepare raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of three parts, we’ll examine the essentials of pulverizer capacity, what should be done after a coal pulverizer fire or other incident, and how to tune up pulverizer performance. In future articles we’ll discuss measuring pulverizer performance and performance optimization.
-
Coal
Is AEP Exaggerating Impact of Air Rules?
American Electric Power recently announced plans to retire over 6,000 MW of coal-fired generation in response to two looming Environmental Protection Agency air quality regulations. Is AEP exaggerating the impact of these regulations? Some members of Congress believe that to be the case. AEP disagrees.
-
Coal
House GOP Moves to Block EPA from Regulating Coal Ash as Toxic Waste
Continuing the House Republicans’ aggressive attack on Obama administration environmental proposals, a House subcommittee approved legislation in June to prevent the Environmental Protection Agency from regulating coal ash as a hazardous waste—one of two options the EPA is considering for tightening coal ash management regulations in response to a disastrous leak from a Tennessee Valley Authority ash impoundment in 2008.
-
Coal
Dominion to Convert Three Coal Plants to Biomass
Dominion Virginia Power has asked the Virginia Corporation Commission for approval to convert three aging and relatively small coal-fired plants to biomass, saying the move would provide substantial long-term savings to customers while cutting air emissions and creating hundreds of forest-related and trucking jobs in the state.
-
O&M
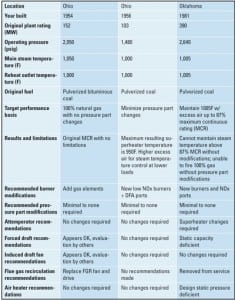
Natural Gas Conversions of Existing Coal-Fired Boilers
Why should utilities consider converting existing coal-fired plants to burn gas? We explore the rationale for fuel switching, some of the options available for the conversion of coal-fired units, technical considerations related to conversion, and some of the financial considerations that will impact the final decision.
-
Coal
Largest CCS Project in Operation
Companies continue to increase the size of carbon capture and sequestration test projects. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) has launched operation of what it calls the world’s largest demonstration of carbon capture on a pulverized coal plant.
-
Coal
Plant of the Year: KCP&L’s Iatan 2 Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
Kansas City Power & Light (KCP&L) began engaging stakeholders in 2003 to develop consensus on a regional energy plan designed to balance customers’ desire for low electricity costs with system reliability needs and environmental requirements. The culmination of that plan was the completion of Iatan 2, which entered service in August 2010. For executing an innovative energy plan that reduced overall fleet emissions, ensuring the region’s future electricity supply, and completing an approximately $2 billion project in time for the summer 2010 peak load by using innovative contracting and project controls, KCP&L’s Iatan 2 is awarded POWER’s 2011 Plant of the Year Award.
-
O&M
Make Your Plant Ready for Cycling Operations
Cycling your steam power plant is inevitable, so now is the time to learn how to minimize equipment damage and assess the true costs of cycling. Whether cycling is required by the grid operator because of renewable integration or other factors, you must be proactive about updating operating processes and upgrade equipment so the transition to cycling operation goes smoothly.
-
O&M
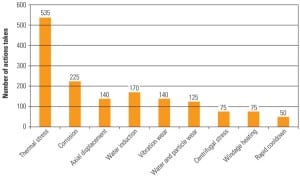
Mitigating the Effects of Flexible Operation on Coal-Fired Power Plants
As coal-fired power plants increasingly operate in cycling modes, many plants are confronting the potential for higher levels of component damage and degraded performance of environmental control equipment. Generators and EPRI are working together to find ways to mitigate the effects of cycling operation and to manage the transition of formerly baseload plants to flexible operation.
-
Coal
Using Fossil-Fueled Generation to Accelerate the Deployment of Renewables
It may seem counterintuitive, but the strategic coupling of simple- and combined- cycle technologies with renewable generation could establish the conditions necessary for adding more renewable megawatts to transmission grids around the world.